Executive Summary
In order to prepare our term paper on “On Site and Off Site Supervision of Schedule Banks by Bangladesh Bank”, we have included the functions, responsibilities, and practices of department of banking inspection and off site supervision of Bangladesh Bank.
We have shown the vital elements of banking operation which are included in banking inspection report prepared by an inspector appointed by the governor, Bangladesh bank for use in the supervision of the bank.
In addition, we have included the process and guidelines followed by the inspector in preparing the inspection report. We have explained the points included in the head office inspection report with the help of inspection manual followed by department of banking inspection of Bangladesh Bank.
The information contained in the inspection report is based upon the books and records of the bank, upon statements made to the inspectors by officers and employees, upon information obtained from the sources believed to reliable and presumed by the inspector to be correct.
The supervision of schedule banks is one of the significant functions performed by Bangladesh bank, so in our term paper, we have tried our best to include all the relevant data regarding this topic.
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
1.Origin of the Report
We are student of Bachelor of Business Administration of United International University. Our respectable course instructor Nazir Ahmed khan, school of business, UnitedInternationalUniversity, assigned this term paper, as the partial requirement of the course “Banking & Insurance” to gather knowledge to our work associated fields
2.Purpose of the Report
Our purpose is to know the functions, guidelines, and processes followed by department of on site and off site supervision of Bangladesh Bank to inspect the scheduled banks. Our main purpose was to identify their methods, policies and practices they use in inspecting the schedule banks.
3.Limitation
We, the members of the group, faced some problems when we tried to prepare our term paper properly. We faced some problems such as time management, organizing and developing group, and technical problem. Since we needed the information of the activities performed by the department of banking inspection and department of off site supervision, we searched information by going to the real life scenario. We went to respective address given by our teacher to collect information but they did not give us any data since banking inspection is very confidential matter. However, we have succeeded to complete our term paper with the sufficient data provided by our respectable course instructor. We have tried our best and we are feeling glad because we believe that we have overcome from all the difficulties and completed our term paper.
Chapter 2
Methodology
1.Information Need
Since our topic is related with the on site and Off site supervision of schedule banks by Bangladesh bank, we were seeking the related information. To obtain sufficient information we have specified our area of information. We have collected some information based on the functions and responsibilities of department of banking inspection and off site supervision and the methods and guidelines these departments follow for inspection.
2. Sources of Data
For our research, we collect and use the data from two sources:
- Primary Data
Primary data:
We have used relevant primary data from sources like: Inspection manual which is used by the bank supervision departments.
- Secondary Data
Secondary data:
We have used internet as secondary data to get the company profile of Bangladesh bank.
3. Conceptual Framework
We have not used any kind of complicated word in our report. Anybody can simply understand the whole things, just only need careful reading. Moreover, we have not tried to oversimplify to keep a standard and we have maintained judicial attitudes.
Chapter 3
Bangladesh Bank in Brief
Bangladesh Bank, the central bank of the country, was established as a body corporate vide the Bangladesh Bank Order, 1972 (P.O. No. 127 of 1972) with effect from 16th December, 1971. The general superintendence and direction of affairs and business of the Bank are entrusted to a nine member Board of Directors which consists of the Governor as chairman, a Deputy Governor, three senior government officials and four persons having experience and proven capacity in the fields of banking, trade, commerce, industry or agriculture – all nominated by the government.
The board, which is the highest policy making body, meets at least six times a year and at least once every quarter under the chairmanship of the Governor. The Governor, appointed by the government as the chief executive officer, directs and controls all the affairs of the Bank on behalf of the Board.
The broad objectives of Bangladesh Bank are:
- To regulate the issue of the currency and the keeping of reserves
- To manage the monetary and credit system of Bangladesh with a view to stabilizing domestic monetary value
- To preserve the par value of the Bangladesh Taka
- To promote and maintain a high level of production, employment and real income in Bangladesh; and to foster growth and development of the country’s productive resources for the national interest
Chapter 4
Machineries of Bangladesh Bank for Inspection
- Department of Banking Inspection (DBI)
- Financial Institution Department (FID)
- Money Laundering Prevention department (MLPD)
- Department of off site supervision (DSO)
Now descriptions;
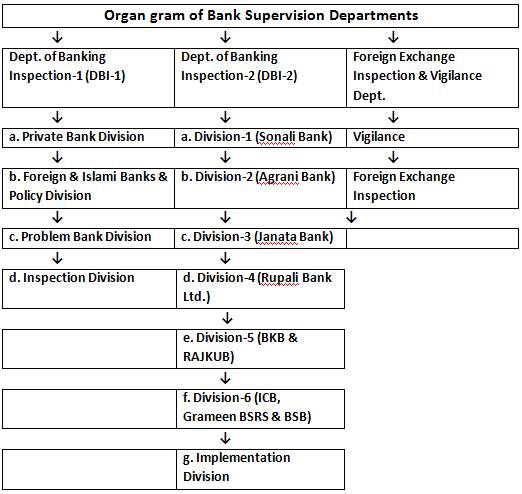
1. Department of Banking inspection (DBI)-1
Department of Banking Inspection-1 (DBI) conducts comprehensive inspection of the private commercial banks including Islami Banks and Foreign Commercial Banks according to a predefined annual inspection program. Branches of the a foreside banks which are authorized to carry on foreign exchange business, designated as Authorized Dealers also come under the purview on site inspection of DBI-1. On site inspection of banks including authorized dealers are carried out according to the annual inspection program chalked out by the department well ahead of the beginning of each calendar year. DBI-1 has also the responsibility to follow up inspection reports of the banks including authorized dealers and to enforce implementation of the recommendations contained therein and rectification of irregularities.
DBI-1 through on site inspection of the financial statements and books of accounts of private and foreign commercial banks undertakes to evaluate the financial position, operating soundness and quality of management of banks. In evaluating the overall performance of the banks DBI-1 also makes CAMEL rating of the head office of banks on the basis of the crucial dimensions capital adequacy, asset quality, management competence, earning capacity, and liquidity position. CAMEL rating of banks acts as an early warning system for the central bank to determine the level of supervisory concern and plan of action needed for banks not considered to be sound.
On site supervision of the authorized dealers of private and commercial banks is undertaken to ensure that foreign exchange business such as export and import, trade, in ward- out ward remittance and all other dealings in foreign exchange are done strictly in accordance with the foreign exchange regulation act and the guidance’s for foreign exchange transactions issued by Bangladesh Bank.
Department of Banking Inspection (DBI)-2
Department of Banking Inspection conducts comprehensive inspection of all the NCBs, Specialized Banks, and financial institutions like BSRS, BSB, Basic bank Ltd, Ansar VDP Unnayan bank, Grameen bank and ICB in accordance with the scheduled outlined in the Annual Inspection Program. Branches of a foreside banks authorized to deal in foreign exchange transactions come under the purview of DBI-2. Moreover, money changes are also under the purview of inspection of DBI-2.
An inspection team is required to evaluate the financial position, operational soundness, and management quality of bank branches including review of foreign exchange transactions. During head office inspection, CAMEL rating of the banks is also done highlighting the core indicators.
Some of the key areas of inspection are:
- Evaluating of assets with emphasis on classification & provisioning
- Assessing capital position to work out required capital
- Verification of artificial manipulation of figures relating to profit
- Review of liquidity position so that required amount of CRR & SLR is maintained
- Evaluation of loan operation, project financing, and other off balance sheet activities
- Analysis of large loans and concentration of credit
- Incidence of fraud, forgery, and action there of
- Evaluation of management quality as well as customer services at the branch level
- Compliance of various circulars issued by BB as well as respective banks.
2.Financial institution department (FID)
Financial institution department was created under financial institution act, 1993. Major functions are:
- Issuance of license for non banking financial institution
- Formulation of policies relating to functions of NBFIs
- Monitoring relevant compliance issues through on site and off site supervision
Presently FID supervises 28 NBFIs of which 1 is fully government owned, 2 are public sector join ventures, 10 are private sector joint ventures and the rest 15 are locally owned private sector financial institutions.
3.Money Laundering Prevention department (MLPD)
As per money laundering act (act 7 of 2002) the responsibility and power of Bangladesh Bank for prevention of money laundering activities are as follows:
In order to abate and prevent money laundering activities or crimes related there to Bangladesh Bank (Anti money laundering department) will;
- Investigate offence relating to money laundering
- Supervise and observe the activities of banks, financial institutions, and other organizations involved in financial activities.
- Call banks, financial institutions and other organizations involved in financial activities for submission of reports on any subject related to money laundering
- Review the report received under (3) above and take proper steps on the basis of those
- Arrange training for the offices and employees of banks, financial institutions and other organizations in financial activities.
- Department of off site supervision (DOS)
This department supervises and monitors the functions of the schedule banks in Bangladesh through off site surveillance. Through off site supervision the bank continuously analyses the overall position particularly financial condition of the scheduled banks on the basis of five crucial indicators of banking operation, capital adequacy, asset quality, management efficiency, earning power and liquidity position. Ratings are done on a scale of 1 to 5 in ascending order of performance deficiency. A bank is identified as problem bank if it has a CAMEL composite score of 4 or 5. Such problem banks are then brought under the fold of problem bank monitoring department for closer and more intensive supervision.
This department also performs the following functions:
- Asses the overall credit and liquidity position of the banking system
- Approves large loans extended by the scheduled banks.
- Monitors maintenance of reserve requirement by scheduled banks.
- Review approval procedures and techniques followed by the scheduled banks in approving loans amounting to taka. 10 million and above to ensure proper compliance of standard practices.
- Monitors capital adequacy of the scheduled banks, position of non performing assets and performance of top 20 defaulters.
- Maintains accounts of the liquidated banks and deals with the movable and immovable properties of the liquated banks as liquidator.
- Prepare and submits quarterly memorandum detailing financial conditions of the nationalized commercial banks to the board of directors of Bangladesh bank.
Chapter 5
Organ gram of Bank Supervision Departments:
Provisions for inspection lay down in certain statutes:
- Bangladesh Bank Order, 1972
- Bank Company Act, 1991
- Foreign Exchange Regulations Act, 1947
- Financial Institutions Act, 1993
- Financial Institutions Regulations, 1994
- Co-operative Society Ordinance, 1984
Provisions under which Bangladesh Bank conducts inspections:
Provisions | Institutions subject to inspections |
| (a)Under section 44(i) of the Bank Company Act-1991 |
|
| (b) Under Article 55 of the Bangladesh Bank Order, 1972 | Scheduled Banks, all branches of Scheduled Banks & other financial institutions |
| (c) Under section 19A of the Foreign Exchange RegulationsAct-1947 |
|
| (d) Under 82(i) (B) of the Co-operative societies Ordinance-1984 |
|
| (e) Under Article 3 of the Bank Company Act-1991 |
|
| (f) Under section 5 and 20 of the Financial Institutions Act-1993 and the Financial Institution Regulations-1994 |
|
Objectives of Inspection/Supervision :
SL. No. | Points |
a. | Asses the financial soundness bank and financial institutions |
b. | Dig out procedural defects/lapses/deficiencies and functional irregularities and to incorporate the same in the inspection reports |
c. | Bring out the various irregularities incorporated and recommendations made in the report to the notice of the top management of the organization concerned in order to put it on sound footing& |
d. | Develop sound banking practice in Bangladesh. |
Type of inspection:
- Comprehensive
- Special
- Summary
Policies / Procedures followed for Inspection:
Comprehensive: Branches covering normally 70%-75% of outstanding loans once in every year. Rest of the branches once in every three years.
Special: As and when any allegations received or published in national/local dailies.
Summary: To know/gather particular data/ information
Chapter 6
- Points subject to inclusion in branch inspection report:
- Introduction
- Compliance of last inspection report
- Cash verification & security arrangements
- Statement of assets & liabilities
- Deposits
- Profit & loss accounts
- Liquid assets
- Loans and advances
- Examination of F.E issues
- Other assets
- Frauds and forgeries
- Miscellaneous irregularities
- Inter branch transactions
- Customer services
- Internal audit & inspection
- Branch management
- Discussions
- Conclusions & recommendations
- Schedules / pages to be prepared & points to be included in the Head Office inspection report:
Inspectors Statement of assets and liabilities:
Banks which have branches in foreign countries must have a balance sheet and profit and loss statement on a fully consolidated on the date of inspection as prescribed by the banks of inspection. This date of the inspection will be used for the completion of all official returns. The primary purpose is to provide an accurate description on a uniform basis of each asset, liabilities & capital account segregation. Among the adjustments which will be necessary are the followings:
Cash and due from banks: Balances due from closed banks should be shown as “other Assets” rather than as “cash and due from banks” This adjustment maintains the “quick assets” liquidity which should necessarily characterize “cash and due from banks”
Loans and discounts: It includes cash credits, loans, over drafts and money at call on short notice. Bills discounts and purchase shown as a separate figure here. Fixed deposits receipts held by a bank which represent borrowings on the part of the issuing banks should be set under loans and discounts.
Deposits and other liabilities: Deposits of banks and government deposits should be shown separately on either as time or demand, depending on circumstances.
Capital account: A balance sheet is viewed as consisting of three parts: assets, liabilities and loss in the capital accounts. Generally reserve accounts excluding reserves for bad and doubtful assets are shown here. Depreciation of fixed assets which reflect the depreciated value from cost of an existing fixed assets and it should be subtracted from the asset gross book value and the asset shown net.
Not included in the statement of assets and liabilities:
These are off balance sheet items. All the contra accounts should be shown below the line and not included in the statement of assets and liabilities.
1. It’s an instrument in which a issuing bank undertakes to pay a party named in the instrument a sum of money on behalf of the banks customer. Issuing bank specifies documents as required by the terms of the letter of credit.
2. Undisbursed portions of irrevocable and unexpired loan commitments.
3. Commitments to purchase securities not yet delivered.
4. Foreign exchange contracts
5. Standby letter of credit and guarantees
Banks own Statement of Assets and Liabilities:
Adjustment and reconciliation worksheet by the inspector: Assets and liabilities will be shown on the reconciliation worksheet by the inspector
Inspection conclusions and recommendations: This provides an overview of the bank’s financial conditions which will indicate a bank’s principal points of weakness and their relative significance. All important orders should be primarily on an exception basis, describing areas of the bank’s operations and aspects of its financial condition that display weakness, deficiencies and recognizing positive actions taken by the management.
Inspectors should avoid personal references or reference to other banks. Inspectors should indicate action taken or promised by management. As a result of discussion during the inspection. The first part of the report addresses the components of the camel which should be explained and the appropriate key ratios in the description of each component. Then overall assessment of the bank’s condition should be made.
Content Check:
· Include a description of each component of the CAMEL?
· Include an assessment of the overall condition?
· List significant issues from the body of the report?
· Contain all significant recommendation?
· List all violations of law, in summary or by reference to report violations of the Law and Regulations?
· Include any open items from the previous inspection?
Violations of Law and Regulations: There are variety of banking laws and regulations. When violations are found, they should be presented in details. Significant violations should also be briefly described. “Inspection conclusions and recommendations”
Summary of assets subject to adverse classification:
Substandard Assets: Its inadequately protected by the current sound worth and paying capacity of the obligor if any. They are characterized by the distinct possibility that the institution will sustain some loss if the deficiencies are corrected. Doubtful assets: it has all the weaknesses inherent in one classified substandard with the added characteristic that the weaknesses collection or liquidation in full, on the basis of currently existing facts, conditions and values.
Loss assets: It considered uncollectible and of such little value that continuance as bankable assets are not warranted but rather it’s not practical or desirable to defer writing of this basically worthless asset even though practical recovery may be affected in the future. According to the BCD Circular no.34 of 1989 will be applied to all classified assets and BCD Circular no.20 of December, 1994. Other appropriate deductions are made from the asset to establish the base for the amount of the provision to be established. The individual inspection report of branch offices will include on report page 3 only a summary of the classification of assets of the branch. It’s the responsibility of the inspector to discuss his classifications with the branch management.
Detailed Statement of Assets Subject To Adverse Classification
Any loan that represents 1% of the total capital and reserves of the bank should be listed separately. Small loan can be shown in group totals. And the inspector in charge to decide what loans will be shown and what will be listed individually. Large branch loans representing 1% of the total capital and reserves of the bank should be shown separately.
Large Lines and Concentrations of Credit: This schedule is for the purpose of displaying all unduly large direct and indirect of credit to the same of the related interests, regardless of whether adversely classified in whole or in the part or of whether shown elsewhere in the inspection report. Loans of all types, overdrafts and all other forms of credit extensions are to be considered in determining a concentration.
Large Lines: Large line are objectionable if they violate a basic principle of sound banking, adequate risk diversification. The schedules sound includes only lines which are large in relation to the capital structure of the bank. The schedule is not intended to include small lines which are large in the sense that they are disproportionate to the borrower’s resources. All lines that represent 15% or more of the Capital and Reserve of the bank should be listed. Other large lines that represent a significant portion of the Capital and Reserves of the bank may be listed. This will be at the discretion of the inspector.
Concentrations of Credit: A line to an individual firm or obligor which is large in relation to the banker’s total capital structure is obviously a concentration, are extensions to two or more obligors, the repayment of which is based upon the same kind of collateral or the same type of production or business. In scheduling a concentration of credit which is composed of extensions to several different individuals or firms, the relationship between the advances should be made clear. The same is true of extensions to closely allied interests, the repayment of whose obligations is inter-dependent by reason of affiliated ownership or control. It is nearly impossible to list all types of concentrations which might exist. And an Inspector should use their informed judgment in deciding the extent of investigation necessary to disclose report of examination. The handling of concentrations in the report of examination is flexible and requires some degree of inspector judgment. A guideline for listing concentrations in the inspection report should be 25% or more of the bank’s capital structure.
Check – Up:
- Has a policy been adopted which specifically addresses concentrations of credits?
Have controls been instituted to monitor the following types of concentrations:
- Loans and other obligations of one borrower?
- Loans predicated on the collateral support afforded by a debt or equity issue of a corporation?
- Loans dependent upon one crop or herd?
- Loans dependent upon one industry group?
Extension of Credit to Directors, Shareholder and Their Interests and Executive Officers:
Indebtedness as used in this schedule includes all direct and indirect extensions of credit regardless of form. In general, a person may be said to be substantially interested in a concern, or if he is an active officer, or director of that concern, or if he has a substantial ownership interest. A substantial ownership interest need not be voting control, but it should not be interpreted as the ownership of only few shares.
Comments in this schedule with respect of management loans should be extremely brief. If a line is adversely classified or otherwise subject to comment, it will have been toughly discussed in other schedules of the report, to which reference may be made for supporting information. The total line and its classification are all that are necessary at this point. If a loan is not subject to adverse classification only the total line need be shown, since other details would be superfluous.
Duplications Within and Between Groups:
All duplications within and between groups should be eliminated in the recapitulation at the head of the schedule. If a line is direct in one instance and indirect in another the indirect should be eliminated. Notations should be made in the schedule of all lines duplicated in whole or in part so that a check can be made at any later date as to the accuracy of the eliminations.