Niobium oxychloride is the inorganic compound with the formula NbOCl3. It is usually a white to pale yellow solid. It is a white, crystalline, diamagnetic solid. It is often found as an impurity in samples of niobium pentachloride, a common reagent in niobium chemistry.
This compound is typically used in the preparation of other niobium compounds and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. It has applications in the field of materials science and chemistry due to its unique properties and reactivity.
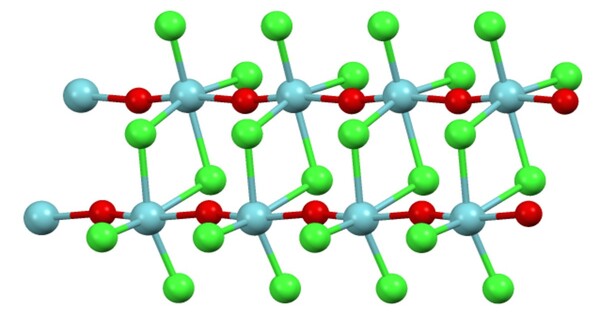
Structure
In the solid state the coordination sphere for niobium is a distorted octahedron. The Nb–O bonds and Nb–Cl bonds are unequal. This structure can be described as planar Nb2Cl6 core connected by O–Nb–O bridges. In this way, the compound is best described as a polymer, consisting of a double stranded chain.
In the gas phase above 320 °C the Raman spectrum is consistent with a pyramidal monomer containing a niobium–oxygen double bond.
Properties
Niobium oxychloride is soluble in water and reacts with it to form niobic acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a relatively reactive compound. It is typically a solid at room temperature. It can hydrolyze in the presence of moisture to form niobium dioxide and hydrochloric acid.
- Chemical formula: Cl3NbO
- Molar mass: 215.26 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white crystals
- Melting point: sublimes above 200 °C
Occurrences
- Natural Occurrence: Niobium oxychloride is not found naturally in significant quantities. It is primarily synthesized in the laboratory or industrial processes.
- Production: It is often produced from niobium-containing minerals or extracted from niobium ores. The compound is used in various chemical processes and in the preparation of niobium compounds.
Applications
Niobium oxychloride is used as a precursor in the preparation of other niobium compounds, such as niobium oxide and niobium metal. It plays a role in materials science, particularly in the development of high-performance ceramics and superconductors. It’s used in niche applications in industries that require niobium-based materials, such as in the aerospace and electronics sectors.