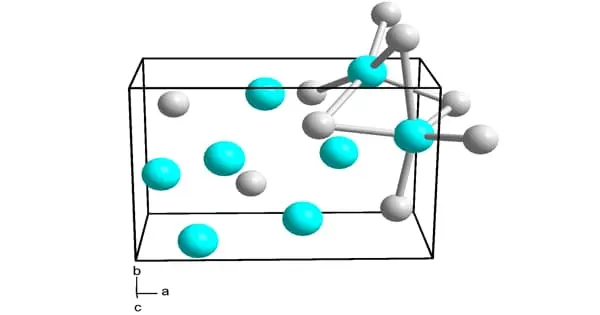
Nickel silicides are a class of intermetallic nickel-silicon compounds. Nickel silicides are important in microelectronics because they form at nickel-silicon junctions. Thin layers of nickel silicides may also be used to improve the surface resistance of nickel alloys.
Nickel silicide is emerging as the material of choice for contact applications in semiconductor device processing for 65 nm and beyond.
Compounds
Ni3Si, Ni31Si12, Ni2Si, Ni3Si2, NiSi, and NiSi2 are nickel silicides. The melting points of Ni31Si12, Ni2Si, and NiSi are congruent; the others form via peritectic transformation. Silicides can be created through fusion or solid-state reactions between the elements, diffusion at a junction of the two elements, and other methods such as ion beam mixing.
Properties
Nickel silicides are generally chemically and thermally stable. They have low electrical resistivity; with NiSi 10.5–18 μΩ·cm, Ni2Si 24–30 μΩ·cm, NiSi2 34–50 μΩ·cm; nickel-rich silicides have higher resistivity rising to 90–150 μΩ·cm in Ni31Si12.
- Molecular Weight: 145.47
- Appearance: solid
- Melting Point: N/A
- Boiling Point: N/A
- Density: 7.40 g/cm3
- Solubility in H2O: N/A
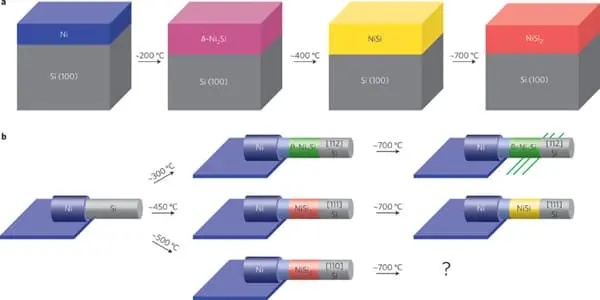
A silicide is a Si compound that contains an electropositive component. Silicides are commonly used in silicon-based microelectronics to reduce gate and local interconnect metallization resistivity. The well-known silicide candidates, CoSi2 and TiSi2, have some drawbacks. TiSi2 exhibits line width-dependent sheet resistance and has difficulty converting the C49 phase to the low resistive C54 phase. CoSi2 uses up more Si than TiSi2.
Nickel silicide is a promising material for silicide replacement because it has low resistivity, lower Si consumption, and a lower formation temperature. Ni silicide has recently emerged as an ideal electrical contact material for the source, drain, and gate in complementary metal oxide silicon devices, as well as exhibiting excellent scaling down behavior.
Uses
- Microelectronics
Nickel silicides are important in microelectronic devices because they are good conductors, with NiSi having a conductivity similar to elemental nickel. Nickel silicides and carbon are formed when nickel reacts with silicon carbide as a semiconductor at high temperatures.
- Other
Because of their corrosion, oxidation, and wear resistance, nickel silicides have the potential as coatings for nickel-based superalloys and stainless steel. The use of NiSi as a hydrogenation catalyst for unsaturated hydrocarbons has been investigated. Nickel silicide nanoparticles supported on silica have been proposed as a replacement catalyst for the widely used pyrophoric Raney nickel.