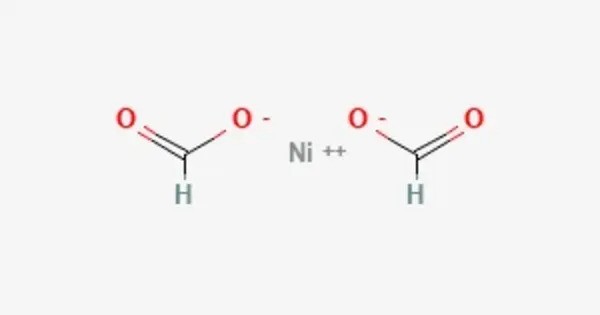
Nickel formate is the nickel salt of formic acid with the chemical formula Ni(HCOO)2. When heated, it can decompose to produce nickel oxide (NiO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) along with formic acid (HCOOH). It is often used in various industrial processes, including catalysis, and it can also be a precursor in the synthesis of other nickel compounds.
Synthesis and structure
Nickel formate can be obtained by reacting nickel(II) acetate or nickel(II) hydroxide with formic acid.
Ni(OH)2 + 2HCOOH → Ni(HCOO)2 + 2 H2O
Nickel formate can also be synthesized by the reaction of sodium formate with nickel (II) sulphate.
Properties
Nickel formate typically appears as a greenish or yellowish crystalline solid. It is soluble in water and can form an aqueous solution that is slightly acidic due to the presence of formate ions. It is relatively stable under standard conditions but can decompose under high temperatures, releasing formic acid and nickel oxide. It has a relatively high melting point, but specific values depend on its crystalline form.
- Chemical formula: C2H2NiO4
- Molar mass: 148.73
- Appearance: Green Solid
- Odor: odourless
- Density: 2.154 g/cm3
- Melting point: 130–140°C
- Boiling point: 180–200°C (decomposition)
- Solubility in water: Slightly soluble in cold water
- Solubility: insoluble in organic solvents, soluble in acids
Characteristics
As a dihydrate, nickel formate is a green, odorless, non-flammable solid that is sparingly soluble in water. The compound has a monoclinic crystal structure. The anhydride forms on careful heating at 130–140 °C. When heated in a vacuum to 300 °C, pure nickel is formed:
Ni(HCO2)2(H2O)2 → Ni + 2 CO2 + 2 H2O + H2
Such fine powders are useful as hydrogenation catalysts.
Occurrences
Nickel formate is not commonly found as a natural mineral, but it can be synthesized in laboratories or industrial processes. It is often produced in processes involving the reaction of nickel salts with formic acid or formates, and can also occur in certain electrochemical processes. In nature, nickel itself is more commonly found in minerals like nickel ores (e.g., pentlandite, garnierite), but nickel formate isn’t a naturally abundant compound in the environment.
Use
Nickel formate is used in the production of nickel and other nickel compounds such as nickel catalysts.
- Industrial Applications: It is used in the production of nickel catalysts, and it can be involved in reactions related to the production of other nickel compounds.
- Laboratory Use: It may be used in laboratory experiments as a precursor to nickel-containing compounds or for specific reactions where nickel ions are required.