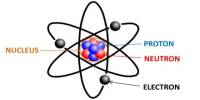
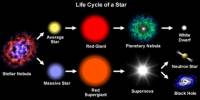
This lecture briefly describe on Newton’s Laws of Motion. First Law: Law of Inertia. An object at rest (v=0) remains at rest AND an object at constant velocity (v=c) remains at constant velocity UNLESS acted upon by an unbalanced force. Second Law: force definition. Acceleration is produced when a unbalanced force acts on a mass. The greater the mass of the object being accelerated the greater the amount of force needed to accelerate the object. Third law: action/reaction. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Newton’s Laws of Motion