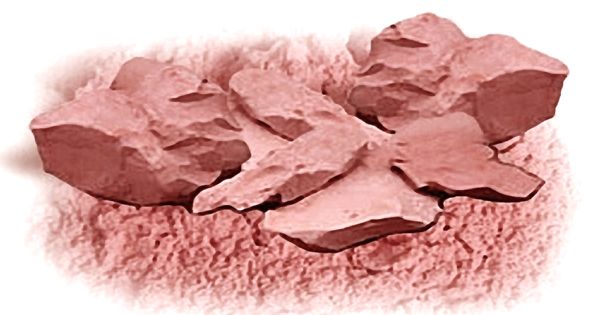
Montmorillonite is a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals that form when they precipitate from water solution as microscopic crystals, known as clay. It is a natural source of minerals. It has been reported to contain at least 67 different minerals, including calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, and manganese, as well as necessary trace elements. It is an important material available in nature.
It is named after Montmorillon in France. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite group, is a 2:1 clay, meaning that it has two tetrahedral sheets of silica sandwiching a central octahedral sheet of alumina.
General Information
- Category: Phyllosilicates (Smectite group)
- Formula: (repeating unit) (Na,Ca)33(Al,Mg)2(Si4O10)(OH)2 ·nH2O
- Crystal system Monoclinic
- Crystal class: Prismatic 2/m) (same H-M symbol)
- Color: White, pale pink, blue, yellow, red, green

Montmorillonite – a very soft phyllosilicate group of minerals
Properties
The important physical and chemical properties are summarized as a particle and layered structure, molecular structure and cation exchange effect, barrier property, and water sorption.
- Crystal habit: compact masses of lamellar or globular microcrystalline aggregates
- Cleavage: {001} perfect
- Fracture: Uneven
- Mohs scale hardness: 1–2
- Luster: Dull, earthy
- Diaphaneity: Translucent
- Specific gravity: 1.7-2
- Optical properties: Biaxial (-)
Occurrences
Montmorillonites are common in clays, shales, soils, Mesozoic and Cenozoic sediments, and nonmicaceous recent marine sediments. They usually occur in areas of poor drainage.
Uses
Montmorillonite is used in the oil drilling industry as a component of drilling mud, making the mud slurry viscous, which helps in keeping the drill bit cool and removing drilled solids. It is the primary component of volcanic ash known as betonite, which has been deposited into inland sea waters.
It is also used as a soil additive to hold soil water in drought-prone soils, used in the construction of earthen dams and levees, and to prevent the leakage of fluids. It is also used as a component of foundry sand and as a desiccant to remove moisture from air and gases
Montmorillonite clays have been extensively used in catalytic processes. It is used in some natural pet foods for a very specific purpose.