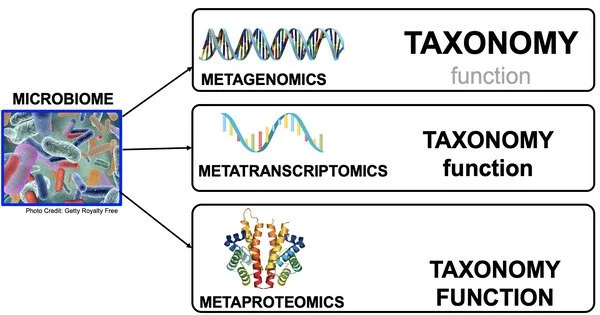
The metatranscriptome is a collection of approaches used to analyze gene expression in bacteria in natural environments. It is a discipline of molecular biology and genomics that focuses on the study of a microbial community’s or a specific environment’s total RNA content (the transcriptome). It gives information about the gene expression patterns and functional activities of a wide variety of microorganisms found in a given ecosystem, such as bacteria, archaea, and fungi.
While metagenomics studies the genomic content of a community and identifies which microbes are present, metatranscriptomics can be used to study the diversity of active genes within that community, quantify their expression levels, and monitor how these levels change under different conditions (e.g., physiological vs. pathological conditions in an organism).
Key aspects of metatranscriptomics include:
- Sample Collection: Metatranscriptomics typically begins with the collection of environmental samples, such as soil, water, or human gut contents, which contain a complex mixture of microorganisms.
- RNA Extraction: Total RNA is extracted from the collected samples. This RNA includes ribosomal RNA (rRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and other non-coding RNAs.
- Sequencing: Reverse transcription is used to convert the retrieved RNA into complementary DNA (cDNA). After that, the cDNA is sequenced using high-throughput techniques like next-generation sequencing (NGS).
- Data Analysis: The sequencing data is then processed and evaluated in order to identify and quantify the numerous transcripts found in the microbial population. This analysis can indicate which genes are actively expressed under specific conditions, offering light on the metabolic processes and functional roles of the community’s microorganisms.
The advantage of metatranscriptomics is that it can provide information about differences in the active functions of microbial communities that would otherwise appear to have similar make-up. It provides several important insights and applications, including:
- Understanding Microbial Communities: It helps researchers understand the diversity and functional roles of microorganisms within complex ecosystems, such as the human gut, soil, oceans, and more.
- Biotechnological Applications: It can aid in the discovery of novel enzymes and metabolic pathways for biotechnological applications, such as bioremediation, bioenergy production, and pharmaceuticals.
- Medical Research: In medical research, it can provide insights into the gut microbiome’s role in health and disease, as well as help identify potential biomarkers.
Metatranscriptomics is a useful method for investigating the functional potential of microbial communities, and it is frequently used in concert with other “omics” approaches like metagenomics (for examining genomic content) and metaproteomics (for studying proteins expressed). These methods, when combined, provide a full picture of microbial populations in their natural environments.