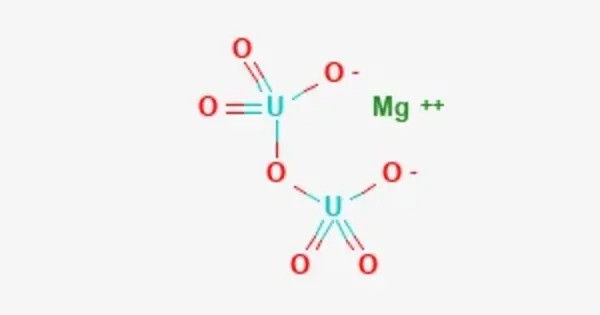
Magnesium diuranate (MgU2O7) is a compound of uranium. It is an inorganic compound, primarily known for its role in the nuclear industry. It is a complex uranium compound formed during uranium ore processing. It is known in the uranium refining industry as “MDU” and forms the major part of some yellowcake mixtures. Yellowcakes are an intermediate product in the uranium refining process.
To produce this form of yellowcake, crushed ore is mixed with hot water to a 58% solids slurry. The solids slurry is then processed through a series of tanks, where sulfuric acid, sodium chlorate, and steam are used to extract the uranium from the solids slurry. The average leaching efficiency for this process is 98.5%. The uranium-bearing solution is then decanted and directed to a solvent extraction (SX) process for further purification.
Properties
- Chemical formula: MgU2O7
- Molar mass: 612.36 g·mol−1
- Molecular Weight: ~626.37 g/mol
- Appearance: Yellow to greenish-yellow crystalline powder
- Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in acids
- Radioactivity: Radioactive (contains uranium in hexavalent form)
- Stability: Stable under dry conditions; reactive with acids
- Oxidation States: Uranium: +6 (as UO₂²⁺), Magnesium: +2
Structure
Magnesium diuranate is a double oxide containing uranium in the +6 oxidation state (U(VI)) and magnesium in the +2 oxidation state. It is one of several uranate compounds, characterized by the uranyl ion (UO₂²⁺).
Production
Magnesium diuranate is often produced during the refining of uranium ores. It is one form of “yellowcake”, a concentrated uranium compound obtained by leaching uranium ore with acid or alkaline solutions, followed by precipitation.
Production steps (simplified):
- Uranium ore is crushed and leached with an acid or alkaline solution.
- Uranium is precipitated using magnesium as a reagent.
- The precipitate is filtered, dried, and may be identified as magnesium diuranate.
Occurrence
Natural Occurrence:
- Does not occur naturally in significant amounts as a mineral.
- May occur as part of secondary uranium mineral deposits, but usually as a processing byproduct.
Industrial Production:
Produced during uranium ore milling and processing, especially via precipitation from uranyl solutions using magnesium compounds (e.g., Mg(OH)₂). It’s one form of yellowcake, though yellowcake can also be composed of other compounds like:
- Ammonium diuranate
- Sodium diuranate
- Uranium oxides (U₃O₈, UO₂)
Uses
- Nuclear fuel preparation: A precursor in the uranium refining process before conversion into uranium hexafluoride (UF₆) or uranium dioxide (UO₂) for use in nuclear reactors.
- Intermediate in uranium recovery: Especially in older or alternate extraction methods.
Safety and Handling
- Radioactive: Contains uranium, so it is radioactive and must be handled with care.
- Toxicity: Chemically toxic to kidneys; radiotoxicity is a concern with inhalation or ingestion.
- Storage: In sealed, labeled containers, in licensed facilities, following radiation safety protocols.