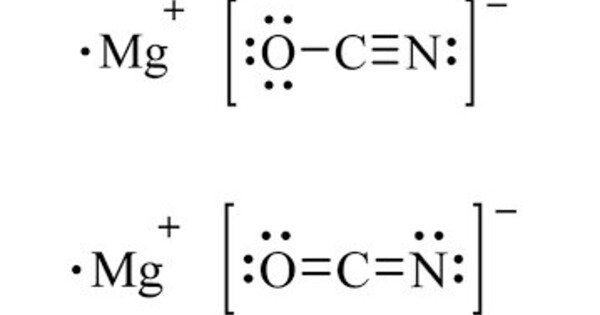Magnesium cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula Mg(CN)2. It’s a salt of magnesium and cyanide. It is a toxic white solid. Unlike calcium isocyanide, the cyanide ligands prefer to coordinate at carbon, with a 0.3‑kcal/mol isomerization barrier. When this salt is heated to 500 °C, it decomposes to magnesium nitride.
This compound is less commonly encountered compared to other cyanides, and its practical applications or significance are relatively limited compared to more well-known cyanide compounds like sodium cyanide or potassium cyanide. It is considered to be unstable in the presence of moisture or acids, as it can hydrolyze to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen cyanide gas.
Properties
- Chemical Formula: Mg(CN)2Mg(CN)2
- Appearance: Typically appears as a white, crystalline solid.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water.
Preparation
Magnesium cyanide can be prepared by reacting magnesium salts with cyanide salts, but handling it requires caution due to the toxic nature of cyanide compounds. In general, cyanides are highly toxic and can be dangerous if not managed properly. The first attempt to prepare magnesium cyanide was attempted in 1924. It was attempted by reacting a solution of hydrogen cyanide in water with magnesium metal:
HCN + Mg → Mg(CN)2 + H2
However, no magnesium cyanide was observed, only magnesium hydroxide formed. To avoid this problem, instead of using water as the reaction medium, pure ammonia was used at -30 °C. This formed magnesium cyanide ammoniate, which in turn was heated to 180 °C to produce magnesium cyanide. Other methods are possible, such as the decomposition of magnesium ferricyanide in an electric carbon tube, which produces iron carbide as a byproduct.
Uses
- Industrial Applications: Magnesium cyanide is used in some industrial processes, including the production of cyanide compounds and in electroplating.
- Chemical Synthesis: It can be used as a reagent in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
- Laboratory Research: It may be used in chemical research and experiments due to its reactivity and role as a source of cyanide.