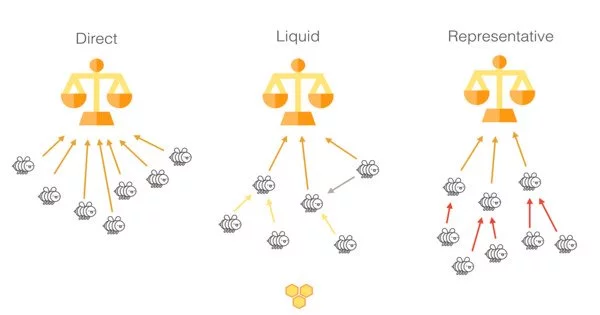
Liquid democracy is a type of delegated democracy in which the electorate participates in collective decision-making through direct participation and dynamic representation. This democratic system incorporates aspects of both direct and representative democracy.
In a liquid democracy system, each person has the option of voting directly on specific issues or transferring their voting power to someone else, known as a proxy or delegate. This transfer of voting power can be temporary, issue-based, or permanent. Individuals may reassign their voting power at any time, and proxy assignments are not limited to one person.
The concept of liquid democracy seeks to address some of the limitations of traditional representative democracy, such as infrequent elections and limited opportunities for participation between elections. It aims to improve decision-making flexibility and responsiveness by allowing individuals to have a more direct impact on policies and issues.
Voters in a liquid democracy have the right to vote directly on all policy issues, as in direct democracy; they also have the option, as in representative democracy, to delegate their votes to someone who will vote on their behalf. Any individual may be delegated votes (referred to as “proxies”), and these proxies may in turn delegate their vote as well as any votes delegated to them by others, resulting in “metadelegation.”
One of the benefits of liquid democracy is that it allows people to participate in decision-making to whatever extent they want. They can vote directly on issues that are important to them, or they can delegate their voting power to knowledgeable representatives who can make informed decisions on their behalf. This adaptability enables people to participate at various levels based on their interests and expertise.
Liquid democracy also has the potential to make decision-making more efficient and informed. Delegated votes can be cascaded, which means that representatives can delegate additional voting power to people they trust or domain experts in specific areas. Individuals with expertise or knowledge on the subject can make decisions in this manner.
However, implementing liquid democracy can be difficult. People need to feel confident that their proxies will vote in their best interests, so determining the credibility and trustworthiness of representatives becomes critical. Furthermore, ensuring secure and transparent systems for vote delegation and tallying is critical to maintaining the process’s integrity.
Overall, liquid democracy is a developing concept that seeks a balance between direct and representative democracy. By allowing for more flexible voting and delegation mechanisms, it aims to empower individuals, increase participation, and improve decision-making processes.