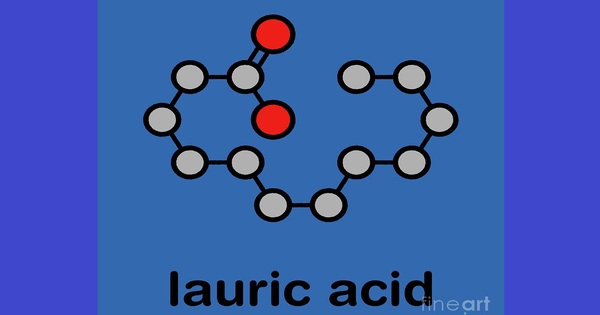
Lauric acid, systematically dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus having many properties of medium-chain fatty acids. It consists of a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylic acid functional group. Its systematic name is dodecanoic acid. It is a bright white, powdery solid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap. The salts and esters of lauric acid are known as laurates.
It is a white, waxy solid at room temperature and melts at around 43°C (109°F). It is soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and ether but has limited solubility in water. As a medium-chain fatty acid, it is metabolized differently than long-chain fatty acids, often providing quick energy.
Properties
- Chemical formula: C12H24O2
- Molar mass: 200.322 g·mol−1
- Appearance: White powder
- Odor: Slight odor of bay oil
- Density: 1.007 g/cm3 (24 °C), 0.8679 g/cm3 (50 °C)
- Melting point: 43.8 °C (110.8 °F; 316.9 K)
- Boiling point: 297.9 °C (568.2 °F; 571.0 K), 282.5 °C (540.5 °F; 555.6 K) at 512 mmHg
- Solubility in water: 37 mg/L (0 °C), 83 mg/L (100 °C)[5]
- Solubility: Soluble in alcohols, diethyl ether, phenyls, haloalkanes, acetates
Occurrence
Lauric acid, as a component of triglycerides, comprises about half of the fatty-acid content in coconut milk, coconut oil, laurel oil, and palm kernel oil (not to be confused with palm oil), Otherwise, it is relatively uncommon. It is also found in human breast milk (6.2% of total fat), cow’s milk (2.9%), and goat’s milk (3.1%).
Lauric acid is most abundantly found in coconut oil, comprising about 47-53% of its total fatty acid content. It is also present in palm kernel oil, though in lower amounts compared to coconut oil.
Industrial Applications
- Food Industry: Used as a food additive and in the production of flavoring agents.
- Cosmetics: Commonly included in personal care products for its moisturizing properties.
- Detergents and Surfactants: Employed in the manufacture of soaps and detergents due to its emulsifying properties.