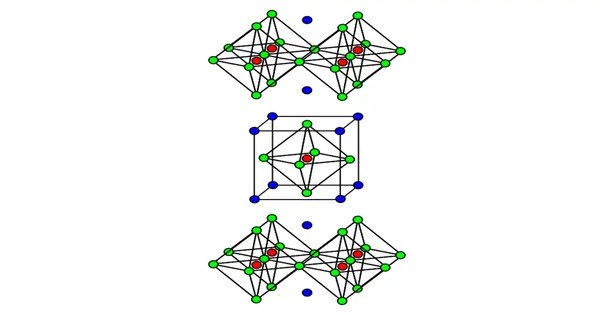
Lanthanum cuprate usually refers to the inorganic compound with the formula CuLa2O4. The name implies that the compound consists of a cuprate ([CuOn]2n-) salt of lanthanum (La3+). It refers primarily to lanthanum copper oxide (La₂CuO₄), a compound of lanthanum, copper, and oxygen. In fact it is a highly covalent solid. It is prepared by high temperature reaction of lanthanum oxide and copper(II) oxide follow by annealing under oxygen. It is best known for being the parent compound of the first high-temperature superconductor discovered: La₂₋ₓBaₓCuO₄.
The material adopts a tetragonal structure related to potassium tetrafluoronickelate (K2NiF4), which is orthorhombic. Replacement of some lanthanum by barium gives the quaternary phase CuLa1.85Ba0.15O4, called lanthanum barium copper oxide. That doped material displays superconductivity at −243 °C (30.1 K), which at the time of its discovery was a high temperature. This discovery initiated research on cuprate superconductors and was the basis of a Nobel Prize in Physics to Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller.
Properties
- Chemical formula: CuLa2O4
- Molar mass: 405.353 g·mol−1
- Appearance: solid
- Density: 7.05 g/cm3
- Crystal Structure: Orthorhombic (at room temperature); can become tetragonal at higher temps.
- Appearance: Black or dark brown solid.
- Magnetic Behavior: Antiferromagnetic below ~325 K.
- Electronic Behavior: Insulating (Mott insulator) in its pure form.
- Thermal Stability: Stable at high temperatures.
- Superconductivity: Not superconducting in pure form, but becomes superconducting when doped (e.g., with Ba or Sr).
- Density: ~6.44 g/cm³
Occurrence and Synthesis
Lanthanum cuprate does not occur naturally; it is a synthetic compound produced in laboratories.
Synthesis Methods:
Solid-state reaction: Common method where La₂O₃ and CuO are mixed and heated at high temperatures (~1000°C).
Sol-gel or co-precipitation: Used for making more uniform or nanoscale materials.
Thin film deposition techniques: Used in electronics and materials research (e.g., PLD, sputtering).
Superconductivity and Importance
Lanthanum cuprate is historically significant because:
La₂₋ₓBaₓCuO₄, a doped version of La₂CuO₄, was the first high-Tc superconductor discovered by Bednorz and Müller in 1986.
This discovery led to the development of the cuprate superconductors family, including YBCO, BSCCO, and others.
In pure form:
La₂CuO₄ is an antiferromagnetic insulator.
Hole doping (substituting La³⁺ with Sr²⁺ or Ba²⁺) introduces charge carriers, enabling superconductivity at temperatures up to ~35 K.
Applications
While La₂CuO₄ itself is not widely used directly, its doped variants are vital in:
- Superconductor research.
- Quantum materials studies.
- Thin-film technology.