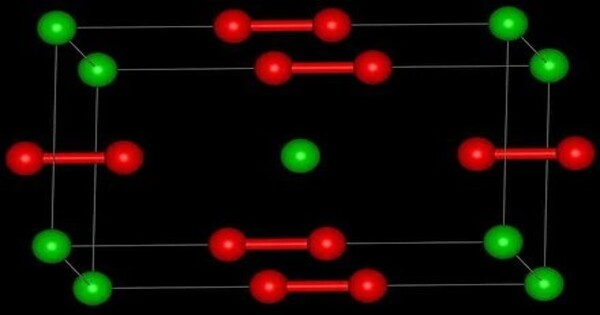
Lanthanum carbide (LaC2) is a chemical compound. It is notable for its high melting point and hardness, making it useful in various high-temperature applications. It is being studied in relation to the manufacture of certain types of superconductors and nanotubes. It is significant in various high-tech and industrial applications, particularly where thermal and electrical stability is required.
Preparation
LaC2 can be prepared by reacting lanthanum oxide, La2O3, with carbon in an electric furnace, or by melting pellets of the elements in an arc furnace.
Reactivity
Lanthanum carbide reacts with water and acids, producing lanthanum hydroxide and hydrocarbons. It can react with water to form lanthanum hydroxide and methane gas. It is also known to react with acids.
Properties
Lanthanum carbide is a grayish-black solid that exhibits good electrical conductivity and thermal stability. It has a high melting point, typically around 2100 °C (3812 °F).
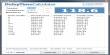
- Chemical formula: LaC2
- Molar mass: 162.927 g/mol
- Appearance: tetrahedral crystals
- Density: 5.29 g/cm3, solid
- Melting point: 2,360 °C (4,280 °F; 2,630 K)
- Electrical Conductivity: It exhibits semiconducting properties, making it useful in certain electronic applications.
- Thermal Conductivity: It has good thermal conductivity, which can be advantageous in high-temperature applications.
Synthesis
It can be synthesized through methods such as the direct reaction of lanthanum metal with carbon at high temperatures or through chemical vapor deposition.
Applications
- Refractory Materials: Due to its high melting point, it’s used in applications that require materials to withstand extreme temperatures.
- Metal Production: It can be used as a carbon source in the production of other metals and alloys.
- Nuclear Applications: Lanthanum carbide has potential uses in nuclear reactors due to its properties.