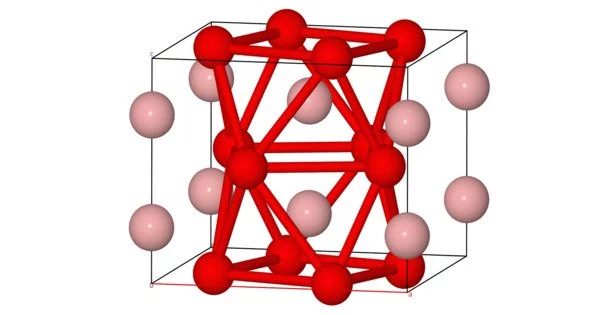
Iron boride is an inorganic chemical with the formula FexBy. FeB and Fe2B are the two most common iron borides. Magnetism, electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and high hardness are all features of some iron borides. Some iron borides have been used to strengthen iron coatings.
Iron borides have ceramic features such as hardness as well as metal properties such as thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. Boride coatings on iron are superior in terms of mechanical, frictional, and anti-corrosive properties. Iron monoboride (FeB) is a grey powder that is water insoluble. FeB is tougher than Fe2B, yet it is fragile and quickly shattered when struck. The crystal structures and characteristics of these substances differ.
- FeB (Iron Monoboride): FeB is a binary compound of iron and boron. It typically forms with a hexagonal crystal structure and is often produced by reacting iron with boron at high temperatures. It exhibits interesting mechanical and magnetic properties, making it useful in certain applications.
- Fe2B (Iron Diboride): Fe2B is another iron boride compound. It has a tetragonal crystal structure and is commonly found in certain steels and hardfacing materials. Fe2B is known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it valuable for wear-resistant coatings and cutting tools.
Properties
- Chemical formula: FeB
- Molar mass : 66.656
- Appearance : grey powder
- Density: ~7 g/cm3
- Melting point : 1,658 °C (3,016 °F; 1,931 K)
- Solubility in water: insoluble
Some iron borides have fascinating magnetic characteristics and have potential applications in magnetics and electronics. Certain iron borides have showed promise as catalysts in chemical reactions, contributing to developments in catalysis research.
Applications
Boriding, also known as boronizing, is frequently used to improve abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and oxidation resistance. It is utilized in the oil and gas refinery, chemical extraction, automotive, agricultural, stamping, textile extrusion, and injection molding sectors.
It can be used in hard-facing applications, where it is coated to the surface of a metal component to improve its wear resistance and hardness. This is useful in industries such as mining, building, and metallurgy, where equipment is subjected to abrasive wear.
Iron-based coatings have recently acquired popularity due to their mechanical, frictional, and corrosion-resistant qualities. In comparison to the ceramic or cermet materials that people have previously utilized, iron-based materials are comparatively inexpensive, less strategic, and can be produced economically using various thermal processes with ease of fabrication and machining.