Industrial ecology is a field of study that focuses on the sustainability of industrial systems and their interaction with the environment. It seeks to understand and optimize the flow of materials, energy, and information within and between industrial and ecological systems. The global industrial economy can be modeled as a network of industrial processes that extract resources from the Earth and transform them into products and services that can be bought and sold to meet humanity’s needs.
Industrial ecology draws on principles from ecology, engineering, economics, and other disciplines to promote the efficient and responsible use of resources, reduce waste and pollution, and minimize the environmental impact of industrial processes.
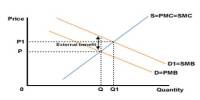
The goal of industrial ecology is to quantify material flows and document the industrial processes that allow modern society to function. Industrial ecologists are frequently concerned with the environmental effects of industrial activities, the use of the planet’s natural resources, and waste disposal issues. Industrial ecology is a young but expanding multidisciplinary research field that combines engineering, economics, sociology, toxicology, and natural sciences.
Examples of industrial ecology approaches include the use of life cycle assessments to evaluate the environmental impact of products throughout their entire lifecycle, the development of closed-loop systems that recycle and reuse materials, and the integration of renewable energy sources into industrial processes.
The ultimate goal of industrial ecology is to create a more sustainable and resilient industrial system that operates in harmony with the natural environment and supports long-term human well-being. The field of industrial ecology involves a wide range of disciplines, including engineering, economics, environmental science, and policy. It requires an understanding of the entire life cycle of a product, from the extraction of raw materials to its disposal or recycling.
The definition of industrial ecology is a “systems-based, multidisciplinary discourse that seeks to understand emergent behavior of complex integrated human/natural systems.” The field approaches sustainability issues from multiple perspectives, typically involving aspects of sociology, the environment, the economy, and technology. The name is derived from the idea that natural system analogies should be used to aid in understanding how to design sustainable industrial systems.
Industrial ecology has practical applications in many industries, including manufacturing, energy production, transportation, and agriculture. By adopting the principles of industrial ecology, businesses can reduce their environmental impact and improve their sustainability, while also realizing cost savings through more efficient use of resources.