Gastric Glands
Definition
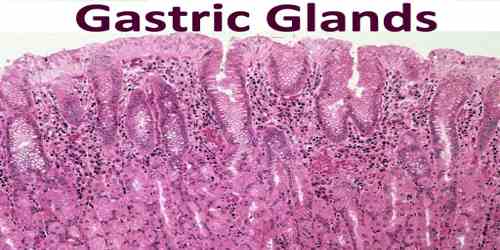
Gastric gland is the basic secretory unit of the stomach and contains a variety of component cells located in characteristic locations. It is also called fundus gland, gastric follicle. It is any of the branched tubular glands in the mucosa of the fundus and body of the stomach, containing parietal cells that secrete hydrochloric acid and zymogenic cells that produce pepsin. The various cells of the glands secrete mucus, pepsinogen, hydrochloric acid, intrinsic factor, gastrin, histamine and bicarbonate.
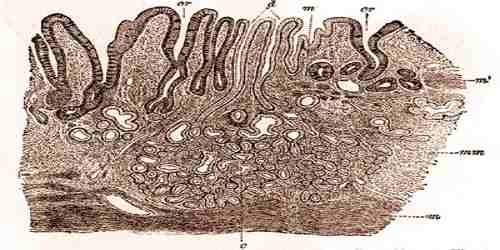
The gland begins at the gastric pit, the opening to the lumen of the stomach. The pit itself contains mostly mucous-secreting cells, visible because of their pale-staining mucous droplets. The isthmus and neck of the gland lead down to the lowest portion, its base. Parietal cells, which secrete HCl and intrinsic factor, are located primarily in the isthmus and neck regions and appear highly eosinophilic, while the chief cells responsible for pepsinogen secretion are located closer to the base of the gland and appear granulated and basophilic.
Fundic gland polyposis is a medical syndrome where the fundus and the body of the stomach develop many polyps.
Pernicious anemia is caused when damaged parietal cells fail to produce the intrinsic factor necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. This can be one of the causes of vitamin B12 deficiency.
Types and Functions of Gastric Gland
There are three types of gastric glands, distinguished from one another by location and type of secretion. The cardiac gastric glands are located at the very beginning of the stomach; the intermediate, or true, gastric glands in the central stomach areas; and the pyloric glands in the terminal stomach portion. Both the cardiac and pyloric glands secrete mucus, which coats the stomach and protects it from self-digestion by helping to dilute acids and enzymes.
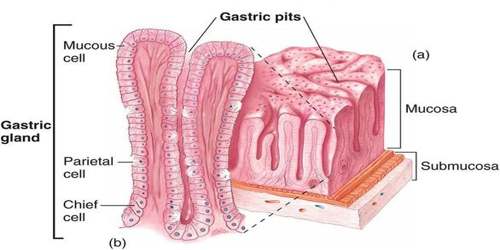
The intermediate gastric glands produce the bulk of the digestive substances secreted by the stomach. These glands contain three primary cell types: parietal, zymogenic and mucous neck cells. The zymogenic or chief cells produce the enzymes pepsin and rennin. Pepsin digests proteins and rennin curdles milk.
The parietal cells located throughout the gland are responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is essential to activation of other enzymes in the body. Mucous neck sells are vital to mucus secretion.
The G cells are mostly found in pyloric glands in the antrum of the pylorus; some are found in the duodenum and other tissues. The G cells secrete gastrin. The gastric pits of these glands are much deeper than the others and here the gastrin is secreted into the bloodstream not the lumen.
Reference: