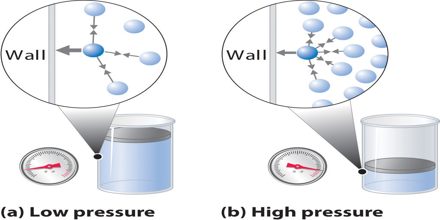
Prime objective of this lecture is to present on Gas Pressure and Volume. Gas Pressure is determined by the flow of mass from a high pressure region to a low pressure region. For example, suppose we have a theoretical gas confined in a jar with a piston at the top. The initial state of the gas has a volume equal to 4.0 cubic meters and the pressure is 1.0 kilopascal. With the temperature and number of moles held constant, weights are slowly added to the top of the piston to increase the pressure. When the pressure is 1.33 kilopascals the volume decreases to 3.0 cubic meters. The product of pressure and volume remains a constant (4 x 1.0 = 3 x 1.33333 ).
Gas Pressure and Volume