Introduction
Financial institutions are investment intermediaries linking the savers users of fund. These intermediaries are interposed between the ultimate borrowers and lenders permitting them efficient transfer of funds. Individuals having surplus funds can lend them for reasonable return to entrepreneurs who needs funds to take the advantage of economically and financially viable investment opportunities.
The key to successful banking lays in the ability of balance many activities simultaneously. The bank must maintain a healthy growth rate, while at the same time it must take action to minimize the risk s it faces. The bank must also maintain enough cash on hand to meet obligations. All of these are related to sound performance of the bank. Trust Bank Ltd. Has a responsibility to ensure efficient and effective banking operation in a sound manner. The study will look at the amount of liquidity that TBL has available to meet any reasonable demands that might have to met, how it manages asset/liability. Foreign exchange operation, what is the position in terms of profitability and how the bank manages its capital so that it has sufficient funds to remain solvent. This study is an attempt to the in-depth analysis of the foreign exchange performance of the Trust Bank Ltd
Origin of the Report
Now a day, education is not just limited to books and classroom. From education the theoretical knowledge is obtained from course of study, which is only the half way of the subject matter. Practical knowledge gas no alternative. The perfect coordination between theory and practice is of paramount importance in the context of the modern business world in order to resolve the dichotomy between these two areas. Therefore an opportunity is offered by University of Liberal Arts Bangladesh, for the potential business graduates to get three month practical experience, which is known as “Internship program”. To complete of the internship program ,the author of the study was placed in a bank namely, “Trust Bank Ltd “,Sena Kalyan Branch for the period of three months starting from September 19,2010 to December 18,2010.Internship program brings a student closer to the real life situation and thereby helps to launch a career with some prior experience.
Objectives of the Study
Prime objective
The primary objective of the study is to observe and evaluate foreign exchange activities performance of the Trust Bank Ltd.
Specific objective
- To focus on service portfolio
- To know export procedure
- To know import procedure
- To analyze the foreign remittance process of Trust Bank Ltd
- To analyze the foreign remittance performance of Trust Bank Ltd
- To understand the future prospects of remittance utilization of Trust Bank Ltd
Methodology
Research design
The study requires a systematic procedure from selection of the topic to final report preparation. In this study, exploratory research was undertaken to gain insight and understanding of the foreign exchange operation of TBL.To perform the study data sources were identified and collected, they were classified,analyzed,interpreted and presented in a systematic manner and key points are found out. This overall process of methodology is given in below that has been followed in the study.
In this section, we have used the following methods of social science research:
- Library work method
- Interview method
- Observation method &
- Desk study method.
Data analysis and reporting
To analyze the gathered data of foreign exchange department, I used different types of chart, table and graph.
Scope of the study
My decision and analysis are done based on the practices applied at Trust Bank Ltd.The study was wide spread and has greater scope to focus on different aspect of foreign exchange on banking sector but my study probably will not reflect the practices in the overall banking sector. Moreover it does not include the foreign exchange practices done by non banking financial organization. It focuses on-
- An overview of modern banking activities of TBL
- Foreign exchange operation
- Financial performance of TBL
- Import and export performance
- Service offered by the bank
FOREIGN EXCHANGE OPERATIONS OF TBL
Foreign Exchange:
It is well known fact that money is a medium of exchange for all transaction that takes place inside the country as well as outside the country. Foreign trade financing is an integral part of banking business. With the globalization of economics international trade has become quite competitive. Timely payment for exports; quicker delivery of goods is therefore a pre-requisite for the success of international trade operation. Growing complexity of international trade underline the need of evolving a system that balances between the expectation of the seller and the buyer.
According to foreign exchange regulation Act, “Foreign Exchange” means foreign currency and it includes any instrument drawn, accepted, made or issued under clause (13), Article 16 of the Bangladesh Bank Order, 1972, all deposits, credits, balances payable in any foreign currency.
Bangladesh Bank does not deal directly with the members of public. The transactions are done by authorized dealers in accordance with the guidelines given by the Bangladesh Bank. Bangladesh Bank authorizes few branches of commercial banks to deal with the foreign exchange. These branches are known as ‘Authorized Dealer’. They act as an agent of the central bank and work under the exchange control regulation. Bangladesh Bank issues Authorized Dealer License by observing the bank’s performance and also by observing the customers associated with the bank for conducting foreign dealings. TBL, Principal Branch works as an ‘Authorized Dealer’ for the financing of foreign trade and dealing with foreign currency. This branch’s foreign exchange department is mainly divided into three wings in accordance with two major activities, which are as under:
Foreign Exchange Accounts:
Foreign exchange transactions involve movement of funds from one place to another, one bank to another and one account to another. Based on the requirement each bank has to open and maintain foreign currency accounts in different places of the world for settlement of their international transactions. These accounts are called Foreign Exchange Accounts.
Foreign currency accounts are frequently termed as ‘Nostro’, ‘Vostro’, and ‘Loro’. These are all Italian words.
- Nostro Accounts: Nostro account means “our account with you”.
- Vostro Accounts: Vostro account means “Your account with us”.
- Loro Accounts: Loro account means “their account with you”.
Import Section:
Import of merchandise involves two things: bringing of goods physically into the country and remittance of foreign exchange towards the cost of merchandise and services. In case of import, the importers are asked by their exporters to open a Letter of Credit. Because that their payment against goods is ensured. Documentary Credit has emerged as a vital system of trade payment. It is a key player of foreign trade.
Letter of Credit (L/C):
Letter of Credit is a payment guarantee to the seller by the buyer’s bank. It is a Credit Contract whereby the buyer’s bank on behalf of the buyer is committed to pay an agreed amount of money to the seller under some agreed conditions. If the conditions of the credit do not require for presentation of specified documents, it is called “Clean Credit”. On the other hand, if the presentation of specified documents is obligatory, the credit is called a “Documentary Credit”. Documentary Credit is an assurance of payment by the bank. It is an arrangement under which the bank at the request of the buyer or on its own undertakes to make the payment to the seller provided specified documents are submitted. In foreign trade, seller uses the Documentary Credit widely because payment acceptance or negotiation of the credit made by the bank upon presentation of specified documents (e.g. Bill of Lading, Invoice, Inspection Certificate). Buyer and seller enter into contracts for buying and selling of goods/services and the buyer instructs his bank to issue Letter of Credit in favor of the seller. Here the bank assumes fiduciary function between the buyer and seller.
Letter of Credit Authorization Form (LCAF):
The Letter Of Credit Authorization Form is the form prescribed for the authorization of opening letter of credit or payment against import and used in lieu of import license. The authorized dealers are empowered to issue LCA forms to the importers to allow import in Bangladesh. If foreign exchange, it is intended to be bought from Bangladesh Bank against a LCAF, it has to be registered with Bangladesh Bank’s Registration Unit located in the concerned area office of the CCI&E. the LCA forms available with the authorized dealers are issued in a set of five copies each.
- First copy is exchange control copy, which is used for opening of L/C and effecting remittance.
- Second copy is the custom purpose copy, which is used for clearance of imported goods from custom authority.
- Triplicate and Quadruplicate copy of LCAF are sent to concerned area of CCI&E office by authorized dealer/Registration Unit of Bangladesh Bank.
- Registration Unit keeps quadruplicate copy as office copy.
- When a client approaches for issuance of letter of credit, Import section of Trust Bank Ltd. Checks the following:
- Whether the item for import of which the documentary letter of credit need to be opened is permissible i.e. not include in the restrictive list as per Import policy Order in force.
- Whether there is any legal/technical defects/restrictions in opening the letter of credit under the various sources as intended by the customer.
- Whether the bank is holding satisfactory credit report on the beneficiary to satisfy the guidelines for foreign exchange transactions.
Importer Application for L/C Limit:
The importer must have sufficient credit line for opening an L/C. In case the client does not have approved credit line for opening an L/C the Manager of the branch takes necessary arrangement to submit a proposal to the Credit Committee/Executive
Committee of the Board an keeps pending of opening the L/C till its approval. On receipt of the approval the Manager issues a sanction letter to the client providing copies of the same to Credit Division. To have an import credit line, an importer submits an application to the Foreign Exchange Department of TBL, Principal Branch furnishing the following:
- Full particulars of bank account.
- Nature of the business.
- Required amount of limit.
- Payment terms and conditions.
- Goods to be imported.
- Offered security.
- Repayment schedule.
A credit officer scrutinizes this application and prepares the proposal accordingly and forwards it to the Head Office Credit Committee. The Committee, if satisfied sanctions the credit line and returns back to the branch. Thus the importer is entitled to the credit.
Bill of Exchange:
Bill of Exchange is an unconditional order written (signed) by the drawer, to another person (the drawee) which directs to pay a certain sum at sight or at fixed or further determinable date to the order of the party which is to receive payment. Officials checks the following:
- That the bill of Exchange has been properly drown and signed by the beneficiary as mentioned in the L/C terms.
- That the draft amount drawn does not exceed the amount available under the credit.
- That the amount is identical with that mentioned in the invoice.
- That the bill exchange is in order and endorsed properly.
Commercial Invoice:
Commercial Invoice issued by exporter is the bookkeeping instruments for the import. The invoice is the list of articles containing their particulars and prices. Here the following points are checked.
- That the merchandise is properly invoiced by the beneficiary.
- That the merchandise is invoiced to the importer on account of whom the L/C was opened.
- That the description of the merchandise as shown in the invoice correspond to that required in the L/C.
- That the unit price of the merchandise in the invoice tallies with that of the unit price stipulated in the L/C and indent.
- That the invoice has been correctly and properly drawn and signed by the beneficiary as per terms of L/C.
- That the relevant LCA form number, IRC number of the importer along with the Registration number of the indenter with Bangladesh Bank, are correctly incorporated in the invoice.
Bill of Lading:
A bill of lading is a document generally issued by a carrier to a shipper, usually stipulated in a credit when exporter dispatches the goods. It is an evidence of a contract of carriage, and is a document of title to goods. It also constitutes a document that is or may be, needed to support an insurance claim. The key check points are as follow:
- That the bill of lading is clean “Shipped on Board” B/L showing fright prepaid and properly endorsed.
- That the bill of lading covers the merchandise described in the invoice.
- That the port of shipment, port of destination, date of shipment, the name of the consignee etc. shown in B/L are in agreement with those mentioned in the L/C.
- That the bill of lading is properly signed by authorized signatory of the Shipping Company or by their authorized agents.
- That the bill of lading is not stale and has been produced in full set as per terms of L/C.
Certificate of Origin:
In case of certificate of origin the officials check that the certificate of origin of the merchandise is in conformity with that stipulated in the L/C.
Packing list
For shipment of Jute Goods, hides skin, packing list or specification is essential. It is prepared for each package showing each bale-wise weight, measurement and total weight both gross and net.
For shipment of jute goods packing list must show details of each package for full quantity, if 800 bales are shipped packing list must show bale-wise details from bale No.1 to 800. For shipment of hides and skin specification must show selection and average.
It must show full description of goods, and full marks as stated in transport documents.
It is titled as packing list.
Banks are not responsible for checking mathematical calculations of extensions or additions on the packing list.
The document appears to relate to the invoiced goods/packages.
Weight Certificate/List
- If the credit stipulates a weight certificate, it is so titled and signed and dated.
- If the credit stipulated a weight list, it should be so titled but need not be signed and dated unless stipulated by the credit.
- It states the weight(s) of the goods being invoiced.
The weights on the certificate/list correspond with the weight on the transport document and/or invoice. Banks are not responsible for checking mathematical calculations, extensions or additions on the weight certificate/list.
Inspection Certificate
It is properly titled, signed and dated
It complies with the inspection requirements contained in the credit, if any; Statements referring to the condition of the merchandise will be disregarded unless otherwise stipulated in the credit.
The document appears to relate to the invoiced goods.
If the credit requires a “Clean report of Findings” ensure that the document presented is so titled, and signed and dated.
Unless otherwise stipulated in the credit, statements that only a sample or samples of merchandise has been inspected are acceptable.
Marine Insurance Policy or Insurance Certificate
- Exporters name and address have been correctly stated.
- Policy or certificate is issued in the name of the bank or endorsed in favor of the negotiating bank and properly stamped.
- Insurance certificate, broker’s cover note etc. cannot serve the purpose of Insurance Policy as substitute if the LC requires policy.
Name of port of loading and discharge, name of carrying vessels, voyage number as indicated in B/L, marks and description of goods and quantity thereof must be consistent with other documents including B/L. There should not be any qualifying clause adversely affecting the interest of the bank.
Amount of Insurance Policy must be at least equal to C&F value or the amount stipulated in LC but generally goods are issued 10% higher than invoiced value.
Amount of Insurance Policy must be in the same currency as in invoice and LC & the claim must be payable at the destination of merchandise. . It is issued for the amount required by the credit, if an amount is not indicated, then the minimum insurance amount will be 110% of the CIF value, or 110% of CIP value. If the CIF or CIP value cannot be determined, banks will accept as minimum 110% of the amount of which payment, acceptance, or negotiation is requested, or 110% of the gross amount of the invoice, whichever is larger.
Policy covers all risks as specified I n the LC. If B/L indicates transshipment, policy must cover transshipment risk.
Policy must be issued by the Insurance Company in negotiable form and must be signed by its authorize agents or by an under writer. Cover note issued by broker will be rejected.
Policy is to be dated on or before the date of shipment as per B/L and the cover of the risk should commence not later than the date of shipment.
Policy to contain name and address of the agent to who claim should be made.
The policy must be taken out by the beneficiary of the LC as assured. Third party policy is not acceptable.
Port of shipment and port of destination as given in the policy must be identical with those shown in B/L.
The policy must be current and not a stale one.
All originals are presented, if issued in more than one original. “Original” and “duplicate original” are presented, if the credit requires the insurance policy or certificate in duplicate. All originals are issued and signed by the insurance company or its agent or by the underwriter or his agent.
If the credit requires the cover of insurance to be irrespective of percentage, the insurance document does not contain a clause stating that cover is subject to franchise or an excess deductible.
The document relates to the invoiced goods and transport details.
All insurance riders are affixed to the insurance document and are cross-referenced and stamped or signed to form a part of the document.
Other Documents:
Other documents called for in the credit to be checked whether drawn and issued in accordance with the terms of the credit.
Lodgment of Import Document:
On scrutiny, if it is found that the documents drawn in conformity with the terms of the credit, Trust Bank Principal branch lodges the documents in Payment Against Documents (PAD) register/database giving a bill reference serially in numerical order.
The Bank that opens the letter of credit is bound to honor its commitment to pay for import bills when these are presented for payment, if drawn strictly in terms of letter of credit. The opening bank will lodge the shipping documents to their book and will respond to the debit advice originated by the foreign correspondent to the debit of “Payment Against Documents A/C” or “Bills of Exchange A/C” and present the bill to the importer for payment.
Shipping Guarantee:
In the absence original documents, goods may be cleared by non-negotiable copies of documents against shipping guarantee issued by L/C opening bank. The importer requests the bank to issue shipping guarantee/indemnity for clearance of consignment against non-negotiable copies of documents received directly from the exporter as per clause incorporated in the L/C. before issuance of shipping guarantee, bank recover full value of import documents and collect an undertaking from the importer that they will accept original documents in spite of any discrepancy and bear rate fluctuation of foreign currency at the time of lodgment.
Export Section:
According to Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 1947, nobody can export by post and otherwise any goods either directly or indirectly to any place outside Bangladesh, unless a declaration is furnished by the exporter to the collector of customs or to such other person as the Bangladesh Bank may specify in this behalf that foreign exchange representing the full export value of the goods have been or will be disposed of in a manner and within a period specified by Bangladesh Bank. Payment for goods exported from Bangladesh should be received through an Authorized Dealer in freely convertible foreign currency or in Bangladeshi Taka from a Non-Resident Account. The Export section deals with two types of Letter of credit that are as follows:
- Export Letter of Credit
- Back-to- Letter of Credit
Export financing can do pre-shipment credit and post–shipment credit. In case of pre-shipment financing 90% is financed by the bank, 75% is by Back-to-Back L/C and 15% by cash credit
Export Letter of credit:
The other type of L/C facility offered by Trust Bank, Principal branch is Export L/C . Bangladesh exports a large quantity of goods and services to foreign households. Readymade textile garments (both knitting and wove) jute, jute-made products, frozen shrimps, tea are the main goods that the Bangladeshi exporters export to foreign countries. Garments sector is the largest sector that exports the lion share of the country’s export. Bangladesh exports most of its readymade garments products to USA and European Community (EC) Countries. Bangladesh exports about 40% of its readymade garments products to USA. Most of the exporters who export through Trust Bank Ltd. are ready made garment exporters. They open L/C in this branch to export their goods, which they open against the import L/C opened by their foreign importers. The following services provided by Trust Bank Ltd. Principal Branch against export L/C:
Advising of Export L/C:
- The advising bank getting the import L/C sent by the issuing bank located abroad will advise the L\C to the beneficiary without any engagement or responsibility on their part. It will see the following only:
- Authenticity of L/C (Test agreed in case Telex L/C and signature verified in case (Air Mail L/C)
- Merchandise specified in the L/C is permissible and clauses incorporated in the L/C are not against country’s regulations.
Add Confirmation of Export L/C:
Bank may add addition confirmation to export L/C where there is specific instructions from the L/C issuing bank to do so. Additional confirmation of L/C gives the seller a double assurance of payment. Bank’s require of adding confirmation:
- Issuing Bank should be a reputed bank.
- Credit line /Arrangement with the L/C issuing bank.
- L/C clause is to be acceptable to confirming bank
- Approval from the competent authority for adding confirmation of exports L/C.
- Confirmation charges are to be recovered as per rules.
Negotiation of export Bill:
Negotiation means that negotiating banker pays to the drawer the value of the bill on the assurance given by the opening banker. When documents are presented for negotiation under letter of credit, the same is thoroughly examined from the point of view of correctness and completeness in all respect of terms of credit. The exporter submits the documents to bank as per requirement of bank.
Formalities for Export Letter of Credit:
The export trade of the country is regulated by the Import and Export Control Act, 1950.There are number of formalities that an exporter has to fulfill before and after shipment of goods. These formalities or procedures are enumerated as follows:
Export Registration Certificate (ERC)
The exports from Bangladesh are subject to export trade control exercised by the Ministry of Commerce through Chief Controller of Import & Exports (CCI&E). No exporter is allowed to export any commodity permissible for export from Bangladesh unless he is registered with CCI&E and holds valid ERC. The ERC is required to be renewed every year. The ERC number is to be incorporated on EXP (Export) Forms and other documents related with export.
The EXP Form:
After having the registration, the exporter applies to Trust Bank Ltd. Principal Branch with the Trade License, ERC and the Certificate from the concerned Government Organization to get EXP Form. If the branch is satisfied, an EXP Form is issued to the exporter. An EXP Form usually contains the following:
- Name and address of the Authorized Dealer.
- Particulars of the commodity to be exported with description and code number.
- Name and address of the exporter.
- Name and address of the importer.
- Country of origin.
- Port of shipment.
- Port of destination.
- Quality.
- L/C value in foreign currency.
- Terms of sale.
- Bill of lading /Railway Receipt/ Airway Bill /Truck Receipt number and date.
- Shipment date.
- CCI&E’s registration number and date.
Securing the Order:
Upon registration, the exporter may proceed to secure the export order. Contracting the buyer directly through correspondence can do this.
Signing of the Contract:
- While making a contract, the following points are to be mentioned:
- Description of Goods
- Quantity of the commodity
- Price of the commodity
- Shipment
- Insurance and Marks
- Inspection
Procuring the Material:
After making the deal and having the L/C opened in his favor, the next step for the exporter is set about task of procuring the merchandise.
Registration of Sale:
This is needed when the proposed items to be exported are raw jute and jute made goods.
Shipment of Goods:
The following documents are normally involved at the stage of shipment:
- EXP Form
- Registration Certificate
- Contract
- Copy of L/C
- Freight Certificate from the bank in case of payment of freight if the port of lading is involved.
- Truck Receipt, Railway Receipt;
- Shipping Instruction;
- Insurance policy.
The following points should be checked.
- The terms of L/C are in conformity with those of the contract.
- The L/C is an irrevocable one, preferably confirmed by the Advising Bank.
- The L/C allows sufficient time for shipment and reasonable time for registration.
- If the exporter wants the L/C to be transferable, advisable, he should ensure those stipulation are mentioned in the L/C
At last the exporter submits all these documents along with a letter of Indemnity to Trust Bank Ltd. Principal Branch for negotiation. An officer scrutinizes all the documents. If the documents are clean one the bank might decide to purchases the documents within the limit sanctioned to the exporter, after verifying the confirmed order covering each export. This is known as Foreign Documentary Bill Purchase (FDBP)
Risk Involved in Negotiation:
If the bank failed to identify any discrepancy in documents prepared by the Exporter, on that time if the amounts are paid to the exporter then the Bank face a great loss. In this situation the Negotiating Bank try to contact with the party and if they agree to deliver the required documents, the Bank gets rid of the huge loss.
Back-to-Back Letter of Credit:
Back-to-Back L/C is a secondary L/C opened by the seller’s bank based on the original/master L/C to purchase the raw materials and accessories for manufacturing of the export products required by the seller.
Under the ‘Back-to-Back’ concept, the seller as the beneficiary of the master L/C offer it as a security to the advising bank for the issuance of the second L/C. The beneficiary of the Back–to-Back L/C may be located inside or outside the original beneficiary’s country. In case of Back-to-Back L/C, the bank takes no cash security (margin). Bank lines the Master L/C and the drawn bill is a Time bill.
Readymade garment industries and specialized Textile units have been allowed the facility of importing fabrics and other material / accessories needed for manufacturing garments / specialized textile, free of duty under bonded warehouse system against back-to-back L/C arrangement, without involving cash foreign exchange from Bangladesh Bank. The Bangladesh Bank has therefore allowed the authorized dealer to open Back-to-Back L/C for import of raw materials by the readymade garment industries / Specialized textile unit to carry out their export orders against export L/C.
In our country, export oriented Garment Industry, operating under bonded warehouse system are availing Back-to-Back facilities. In Trust Bank, Principal Branch most of the Back–to-Back L/C opened on Garment Industry Account.. Therefore the discussion is based on account of garment Industry in Bangladesh.
Payment of Back-to-Back L/C:
Payments of import bills against Back-to-Back L/Cs are made from relative export proceeds of export oriented Garment Industry operating under bonded warehouse system. Therefore at the time of negotiation of export bills on account of garment factory bank retains a portion covering to Back-to Back liability to a separate foreign currency account from the export proceeds. The amount is kept in Foreign Bills Payment Awaiting Remittance (FBPAR) A/C. After realization of export proceed, payment against import bills are made from FBPAR A/C. L/C wise and party wise A/Cs are maintained in FBPAR ledger.
On 30/60/90/120/180 days of maturity period, deferred payment is made. Payment is given after realizing export proceeds from the L/C Issuing Bank. For garment sector, the duration can be maximum 180 days. In case of export failure or non-realization /short realization of export proceeds forced loan i.e. OAP has to be created in order to settle the Back-to-Back L/C payment.
Vouchers and accounting treatments are the same normal L/C opening except margin. In this case, the bank takes no margin. After lodgment, maturity date of the import bill is intimated to foreign bank as per L/C terms. The documents are delivered to the order of opener duty endorsed for clearance of goods from custom authority. Goods are cleaned through approved clearing and forwarding agent of the bank.
Foreign Remittances:
Foreign remittance means money remitted in foreign currency. Foreign Remittance represents remittances in foreign currency that are received in and made out abroad. From March 1994 Bangladesh Taka becomes convertible for current account transactions and thus most of the foreign remittances are allowed by authorized dealers as empowered by Bangladesh Bank. There are two types of Foreign Remittance:
- Foreign Outward Remittance
- Foreign Inward Remittance
Modes of Remittances
- Issuance of Foreign Demand Draft (FDD)
- Issuance of Foreign Telegraphic Transfer(FTT)
- Mail Transfer (MT)
- Issuance of Travelers Cheques (TC)
- Endorsement of USD in Passport.
F.T.T. (Foreign Telegraphic Transfer)
T.T. is an order for payment of money sent by telex or Cable. Funds are paid to the beneficiary in the foreign centre usually on the same day. No loss of interest or expenses on stamp duty etc. is involved.
M.T. (Mail Transfer)
M.T. is an instrument issued by a remitting Bank to the paying Bank advising in writing to make payment of certain amount to specific beneficiary. This involves loss of interest to the purchaser and hence banks can afford to make M.T. rate cheaper than T.T. rate.
F.D.D. (Foreign Demand Draft)
A foreign demand draft is a negotiable instrument issued by a Bank drawn on other Bank with the instruction to pay of certain amount to the beneficiary of demand.
T.C. (Travelers’ Cheque)
People usually use TC’s to meet their expenses for overseas travels. It reduces the risk of carrying currency notes. These are drawn in freely convertible currency such as US dollar and pound sterling for fixed denominations, which can be encased into local currency at the foreign centre, at the ruling rate of exchange. The purchaser puts his signature at the space provided for the purpose while purchasing the same and again signs at the prescribed space in the presence of the paying banker at the time of encashment. If both the signature tallies, payment is made.
Foreign Outward Remittances:
Outward Remittances means sale of foreign currencies which constitutes remittances from Bangladesh by TT, MT, FDD, TC etc. to a foreign country or local currency credited to non-resident Taka account of foreign banks or convertible Taka account and also endorsement (issue) of Foreign currency including TC on foreign travel purpose.
Approval of Bangladesh Bank.
Most outward remittances are approved by the Authorized Dealers on behalf of the Bangladesh Bank following declaration of Taka as convertible for current account payments from March 1994. No remittance can be transferred outside Bangladesh without prior permission of Bangladesh Bank. Following documents are required for approval.:
Modes of outward Remittances
- Issuance of Foreign Demand Draft (FDD)
- Issuance of Foreign Telegraphic Transfer (FTT)
- Mail Transfer (MT)
- Issuance of travelers cheques (TC)
- Endorsement of USD in Passport
Purpose of Outward Remittances:
The Foreign Remittance department of Trust Bank Limited Principal Branch is equipped with a number of foreign remittance facilities. Following are the types of foreign remittance facilities offered by Trust Bank Limited.
a. Remittances of Profit of Foreign firms / Companies
Foreign Firms /Companies /Banks/Institutions operating in Bangladesh are allowed to remit their net profit on payment of taxes after fully complying with the requirements. The application or remittances of profit is to be made on T/M Form supported by some main documents like, Audited Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss A/C certified copies of Final Income Tax Assessment Orders and Forms etc.
On approval of T/M Form by Bangladesh Bank, the Taka amount approved for remittance is converted into Foreign Currency at the OD /TT selling rate as of the date of remittance and the following entries to be passed:
- Client’s A/C ……………………………………………………..…………..Debit
- Trust Bank Limited General A/C, Head Office ………Credit
- Income A/C Commission ……………………………………………..Credit
In the IBCA to Head Office full particulars of the remittance showing the amount in foreign currency as well as local currency, name of NOSTRO A/C etc. should be given.
b. Remittances of Dividends
Remittances of dividends payable to Nonresident shareholders of the companies operating in Bangladesh are allowed by Authorized Dealer Branches without prior approval of Bangladesh Bank on receipt of the application in the prescribed form in triplicate duly signed by the company and certified by the auditors and supported by some documents like, Certificate of Incorporation, Final Income Tax Assessment Order etc.
Entries to be passed :
- Clients A/C ………………………………………….Debit
- Trust Bank Limited General A/C……………Credit
- Income A/C Commission …………………….Credit
Foreign Inward Remittances:
Authorized Dealers purchase foreign currencies including TT, MT, FDD, TC etc. also raise debits to non-resident Taka accounts of the respective bank branches. Two forms as prescribed by Bangladesh Bank are used for purchase of foreign currencies such as;
EXP Form: Remittance receives against exports of goods from Bangladesh are done by EXP.
Form C: Inward remittance of USD 2,000.00 and above should be reported on form “C”. The purpose of remittance should be clearly written in form ‘C’ and declaration on this form is not required against remittances sent by Bangladesh nationals working abroad.
Types of Account: There are three kinds of F.C account, which are below:
- Private F.C Accounts.
- Resident Foreign Currency Deposit (RFCD) Account
- Non- resident Foreign Currency Deposit (NFCD) Account.
a) Private Foreign Currency Accounts:
Private F C Accounts may be opened in the of –
- Bangladesh nationals residing abroad.
- Foreign nationals residing abroad or in Bangladesh and also foreign firms registered abroad and operating in Bangladesh or abroad.
- Foreign missions and their expatriate employees.
i) FC Account opened by Bangladesh nationals residing in abroad:
- Opened without initial deposit.
- Remains operative ever if operation not made for a particular time.
- Both the account holder and the nominee can operate the account.
- FC account holder can remit fund from abroad.
- First transaction normally takes place when remittance deposited.
- FC account holder can also deposit currency notes, travelers cheques, drafts brought into Bangladesh.
- Entire remittance from abroad is free from income tax.
- The account holder can freely remit fund from this account in foreign currency of anywhere in the world.
All payments in Bangladesh should be in local currency.
Documents Required:
- Account opening form duly filled in and signed.
- Photographs of the account holder.
- Photocopy of Passport of the account holder (first 7 pages) and VISA (valid).
- Photograph of the employment contract executed with the foreign employer.
- Photograph of the nominee duly attested by the account holder.
- Letter of Authority (for nominee).
- Specimen Signature card which is used both for the account ho9kder and the nominee.
- Any other pertinent information/documents if required.
Any person intending to open FC account from abroad may send all the aforesaid papers duly attested by Authorized officers of nearest Bangladesh Mission to the authorized dealer in Bangladesh.
ii) Foreign Nationals residing in Bangladesh:
- Foreign currency can be deposited into this account in the following forms:
- Electronic transfer from abroad.
- Internal transfer from another FC account.
- Transfers from another currency account maintained with another Ads.
Documents Required:
- Account opening form duly filled in and signed along with signature cards.
- Photographs of the account holder.
- Photocopies of the Passport of the account holder.
- Six months valid Visa for Bangladesh Bank.
b) Resident Foreign Currency Deposit (RFCD) Account:
Persons ordinarily resident in Bangladesh may open and maintain Resident Foreign Currency Deposits (RFCD) Accounts with the foreign exchange brought in at the time of their return from travel abroad. These accounts may be opened by any amount of foreign exchange brought in with declaration to customs authorities in the form of FMJ and up to US$ 5000/- on equivalent foreign currency. RFCD accounts may be maintained as long as the account holder desires.
It is not a receipt against export of goods or services from Bangladesh.
It is not a commission due from abroad arising from business deal in Bangladesh.
Interest in foreign exchange shall be payable on balances on such accounts if the deposits are for a term of not less than one month and the balance is not less than US$ 1000/- or Pound Sterling 500/- or its equivalent .
The rate of interest shall be one quarter present less than the rate at which interest is paid on balances of banks in their foreign currency clearing accounts maintained with Bangladesh Bank.
c) Non-Resident Foreign Currency Deposit (NFCD) Accounts:
All non-resident Bangladesh nationals and persons of Bangladesh origin including those have dual nationality and ordinarily residing abroad may open/maintain interest bearing time deposit accounts named “Non-Resident Foreign Currency Deposit (NFCD) Account with the Ads.
NFCD Accounts may also be opened by Bangladesh nationals serving with embassies/High Commissions of Bangladesh in foreign countries and the officers/staffs of the government/semi-govt./autonomous/nationalized banks and employees of body corporate posted abroad on deputed with international and regional agencies like IMF, WB, IDB, ADB etc. during their assignments abroad may open such accounts.
Accounts may also be opened with funds transferred from existing foreign currency accounts maintained by the wage earners with the Ads in Bangladesh. The accounts are in the nature of term deposits maturing after one month, three months, six months and one year.
NFCD may open by initially with minimum amount of US$.1000/- or UKP.500/- or equivalent.
These accounts may be maintained as long as the account holder’s desire. Eligible persons are also allowed to open such accounts within six months of their return to Bangladesh.
The Ads will pay interest on deposits into the accounts at Euro currency deposit rates. The interest on deposits into this account is exempt from the tax payable under income tax act.
The account holder can freely repatriate the balance and the interest accrued thereon in foreign exchange to the country of his residence or any where he chooses and may at his option.
Separate monthly statements summarizing currency-wise transactions in the NFCD accounts of all AD branches of a Bank should be submitted from the Head Offices of the Banks to the FEPD at the Head Office of Bangladesh Bank by 15th day of each month following that to which it relates.
Function of the Bank:
Product and Services:
Trust Bank Limited has been established with the objective of providing efficient and innovative banking services to the people of all sections of the society. Towards this end TBL offers full range of normal banking service that include deposit banking, loans and advances, export import, inward worker remittances etc.
Deposit Schemes Includes:
- Trust Smart Saver Scheme (TSS)
- Trust Double Scheme (TMDS)
- Trust Money Making Scheme (TMMS)
- Trust Edu-care Scheme (TES)
- Monthly Benefit Deposit Scheme (MBDS)
- Lakho Pati Saving Scheme (LSS)
- Interest First Fixed Deposit Scheme (IFFDS)
Retail Loan Products Includes (General):
- Car Loan
- Doctors Loan
- Education Loan
- Travel Loan
- Hospitalization Loan
- Any Purpose Loan
- Apon Nibash Loan
- CNG Conversion Loan
- Marriage Loan
- Advance Against Salary Loan
Retail Loan Products Includes (Defense)
- HBL (Regd. Mortgage & Commutation Benefits)
- OD (Against Salary)
- RRDH (Micro Credit)
- Above General Loans
International Trade Related Services:
- Private Foreign Currency Account
- Non-Resident And Resident Foreign Currency Deposit Account
- Travelers’ Endorsement (Case And Travelers Cheque)
- Remittance Of Foreign Currency
- Import And Export Transaction
- Foreign Exchange Dealings
- Purchase Of Foreign Currency Drafts
- Cheques And Travelers Cheques
- Wage Earner’s Development Bond.
Other Services Of TBL Includes:
- Trust Locker Service
- Trust Tele Banking
The bank is committed to ensure customized, qualitative and hassle free services in its banking operations along with the focus to broaden the clientele base.
Card Services (Debit, Credit & ATM):
Trust Bank holds the principle member License from VISA International to issue & acquire the world’s most widely used Credit Card. It also offering Debit Cards and ATM Cards. For account holders, TBL offering ATM Cards without any costs.
Services:
(1) TBL is operating Online Banking, which ensures reliable any branch banking for customer through Real Time Data Processes sing system.
(2) SWIFT facility ensures effective communication between our bank & other local/ foreign banks. Especially for the Foreign Exchange Departments.
Import Procedure:
To import through TBL, a customer requires-
- Bank account
- Import Registration Certificate
- Tax Paying Identification Number
- Pro-forma Invoice Indent
- Membership Certificate
- LC Application form duly attested
- One set of IMP Form
- Insurance Cover note with money receipt
- Others
To import, a person should be competent to be an importer. According to Import and Export Control Act, 1950, the Office Of Chief Controller Of Import and Export provides the registration (IRC) to the importer. After obtaining the IRC, the person has to secure a letter of credit authorization (LCA) from Bangladesh Bank. And then a person becomes a qualified importer. He is the person who requests or instructs the opening bank to open an L/C. He is also called opener or applicant of the credit.
Importer’s Application for L/C Limit/Margin:
To have an import L/C limit, an importer submits an application to the Department of credit furnishing the following information, –
- full particulars of bank account
- nature of business
- required amount of limit
- payment terms and conditions
- goods to be imported
- offered security
- repayment schedule
A credit Officer scrutinizes this application and accordingly prepares a proposal (CLP) and forwards it to the Head Office Credit Committee (HOCC). The Committee, if satisfied, sanctions the limit and returns back to the branch. Thus the importer is entitled for the limit to open Letter of Credit
The L/C Application:
TBL provides a printed form for opening of L/C to the importer. A special adhesive stamp is affixed on the form. While opening the L/C, the stamp is cancelled. Usually the importer expresses his desire to open the L/C quoting the amount of margin in percentage. The importer gives the following information,-
- Full name and address of the importer.
- Date and place of expiry of the credit
- The mode of the transmission of document (mail/courier/telex)
- Whether the confirmation of the credit is requested by the beneficiary or not
- Whether partial shipment of goods is allowed or not
- The type of loading (loading on board)
- Brief description of the goods to be imported.
- Availability of the credit by sight payment acceptance /negotiation/deferred payment.
- The time bar within which the document should be presented.
The above information is given along with the following documents, –
- Pro-forma Invoice stating description of the goods including quantity, unit price etc.
- The insurance cover note, issuing company and the insurance number.
- Four set of IMP Form
Transmission of L/C:
The transmission of L/C is done through tested telex or fax to advise the L/C to the beneficiary.
Advising a Letter of Credit:
The advising or notifying bank is the bank through which the L/C is advised to the exporter. It is a bank situated in the exporting country and it may be a branch of the opening bank. It becomes customary to advise a credit to the beneficiary through an advising bank. Advising depicts the proof of authenticity of the credit to the seller. The opening bank has corresponding relationship or arrangement throughout the world by which the L/C is advised. Actually the advising bank does not take any liability if otherwise not requested.
Adding Confirmation:
Adding confirmation is done by the confirming bank. Confirming bank is a bank which adds its confirmation to the credit and it is done at the request of the issuing bank. The confirming bank may or may not be the advising bank. The advising usually does not confirm it if there is not a prior arrangement with the issuing bank. By being involved as a confirming agent the advising bank undertakes to negotiate beneficiary’s bill without recourse to him.
a) Issue L/C and request to add confirmation
b) Review the L/C terms
c) Provide reimbursement
d) Drafts to be drawn on L/C opening bank
e) Availability of credit facilities
f) Line allocation from the business & ownership units in the importer’s country
g) Confirm & advise L/C
Credit Report:
If the amount of L/C exceeds a certain limit, TBL takes the credit report of the beneficiary to ensure the worthiness of the seller of supplying the stipulated goods.
Amendment of Letter Of Credit:
Parties involved in a L/C, particularly the seller and the buyer cannot always satisfy the terms and conditions fully as expected due to some obvious and genuine reason .In such a situation, the credit should be amended. TBL transmits the amendment by tested telex to the advising bank .In case of revocable credit; it can be amended or cancelled by the issuing bank at any moment and without prior notice to the beneficiary. But in case of irrevocable letter of credit, it can neither be amended nor cancelled without the agreement of the issuing bank, the confirming bank (if any) and the beneficiary. If the L/C is amended, service charge and telex charge is debited from the party account accordingly.
Presentation of the Documents:
The seller being satisfied with the terms and the conditions of the credit proceeds to dispatch the required goods to the buyer and after that, has to present the documents evidencing dispatching of goods to the negotiating bank on or before the stipulated expiry date of the credit. After receiving all the documents, the negotiating bank then checks the documents against the credit. If the documents are found in order, the bank will pay, accept or negotiate to TBL. TBL check the documents. The usual documents are,-
- Invoice
- Bill of lading
- Certificate of origin
- Packing list
- weight list
- Shipping advice
- Non negotiable copy of bill of lading
- Bill of exchange
- Pre-shipment inspection report
- Shipment certificate
Payment Procedure of the Import Documents:
This is the most sensitive task of the Import Department. The Officials have to be very much careful while making payment. This task constitutes the following,-
- Date of payment: Usually payment is made within seven days after the documents have been received. If the payment is become deferred, the negotiating bank may claim interest for making delay.
- Preparing sale memo: A sale memo is made at B.C rate to the customer. As the T.T & O.D rate is paid to the ID, the difference between this two rates is exchange trading. Finally, an Inter Branch Exchange Trading Credit Advice is sent to ID.
- Requisition for the foreign currency: For arranging necessary fund for payment, a requisition is sent to the International Department.
- Transmission of SWIFT: A SWIFT message is transmitted to the correspondent bank ensuring that payment is being made.
Compare the documentary credit process with the other international trade payment systems.
In international trade there may come across a number of modes of payment that are being used for receiving trade proceeds. These are as follows:
- Cash in Advance: In this method of payment, the buyer places the funds at the disposal of seller prior to shipment of goods in accordance with the sales / purchase contract, which is certainly to be concluded between exporter and importer before the trade transaction.
- Open Account: This is an arrangement between the buyer and seller whereby the goods are manufactured and delivered before payment is required. Open account provides for payment at some stated specific future date and without requiring the buyer to issue any negotiable instrument evidencing his legal commitment.
- Documentary Collection: This is an arrangement whereby the goods are shipped and the relevant bill of exchange / draft is drawn by the seller on the buyer and documents are sent to the seller’s bank with clear instructions for collection through one of its correspondent bank located in the buyers domicile.
- Documentary Credit : The documentary credit is an undertaking issued by a bank on behalf of the buyer to pay the beneficiary the value of the draft and / or documents provided that the terms and conditions of the credit are complied with.
From the above-mentioned descriptions about the four modes of payment in international trade, we can state the superiority of Documentary Credit.
The prime thing is the ‘risk’ affiliated with the parties. At the time of all international trade both the exporter and importer try to go for a safer position during the payment takes place. Except the ‘Documentary Credit’, not all other modes can provide equal benefits to both the parties. In ‘Cash in Advance’, process risk goes to the importer while the importer makes the payment before arrival of the goods and on the other hand in ‘Open Account’, system the exporter occupying the riskier placer by manufacturing the goods before the payment has made. When we talk about the ‘Documentary Collection’, system where there is no undertakings about the settlement by any third party (Except exporter and importer).
All of the lacking that we have discovered from discussion can be only be fulfilled by the fourth modes of payment, that is ‘Documentary Credit’. Here all the parties are equally risk averse and the undertaking of a third party has properly backed international settlement.
Export operation of TBL
All exports from Bangladesh are subject to export trade control exercised by the Ministry of Commerce through Chief Controller of Imports and Exports (CCI&E) under the provisions of “Import & Exports (Control) Act 1950” read with provisions of Importers, Exporters and Indenters (Registrations) Order, 1981.
The ensuing Export Process Guidelines have been presented in six (6) sections covering under mentioned areas:
(I) Receiving export LC & advising to beneficiary
(II) Procurement of raw material by opening BTB LCs or Export-Reprocessing LC.
(III) Pre-shipment finance
(IV) Export document scrutiny, processing and negotiation
(V) Post shipment finance
(VI) Proceed realization
Receiving export LC and advising to beneficiary Scrutiny of export/master LC:
On receipt of the Airmail LC or Cable/Telex/SWIFT LC (short or full), the branch should proceed in the following manner to scrutinize the LC after filling the checklist
- See whether the issuing bank is our correspondent bank.
- Verify the signatures appearing on the airmail LC with the specimen signature of the authorized officials of the issuing bank recorded with us.
- If the signature of the authorized official on the airmail LC differs, bring the same to the notice of the issuing bank immediately by mail/telex/SWIFT for proper authentication.
- See that the goods specified in the LC are permissible for export.
- Examine the terms and conditions of LC very carefully ensuring its conformity with the existing Guidelines for Foreign Exchange Transactions (GFET) or Trade Regulations. If any term or condition in the LC is not in accordance with these regulations, advise the issuing bank by telex (at beneficiary’s or opener’s cost) to get the terms and conditions amended. The beneficiary should also be kept posted with the developments in the matter.
- If the test number of the cable/telex LC does not agree or if the cable/telex in not a tested one, take up the matter at once with the issuing bank through telex for proper authentication and wait for the mail confirmation or tested telex confirmation. The charges incurred in this regard should be recovered from the beneficiary immediately. Only after receipt of mail confirmation or tested telex confirmation, LC should be advised to the beneficiary. Branches may however give preliminary notice to the beneficiary only for his information without any responsibility on our part.
- In absence of any such indication in the cable/telex LC advice, the branch may treat the cable/telex as the operative credit instrument and advise the beneficiary accordingly.
viii.Test number and signature to be verified in all cases.
- Where signatures cannot be verified or there is doubt as to the genuineness of the LC, a telex or any other kind of message should be sent to the Issuing Bank.
- In any event, no LC must remain unadvised for more than 4 days without the bank from who received, is contacted and informed.
Procurement of raw material by opening Back to Back LCs or Export-Reprocessing LC:
Back to Back L/C:
The word Back to Back is derived from the situation where one credit backs another. It may so happen that the beneficiary/seller of an LC is unable to supply the goods directly as specified in the Export LC. Consequently, beneficiary may need to purchase the same and make payment by opening a second Letter of Credit favoring the ultimate supplier. The second Credit in this case is called Back to Back Credit. The master LC (original LC) stands as underlying support or ultimate security.
Back to Back Credit is opened in conformity to the terms and conditions as stipulated in Master LC except the price of the goods, shipment period and validity of LC. In Back-to- Back Credit the price negotiated with ultimate supplier is quoted. The shipment period and validity of Back to Back Credit are given shorter than validity of Master LC. This helps the seller of the first credit to substitute his drafts, commercial invoices and other required documents for ultimate supplier’s documents. These are the classical characteristic of a Back-to-Back LC. From the above, it is clear that BB LC will be similarly worded as the Master LC except in the following points:
- Value of the BB LC may be curtailed
- Shipment and presentation period may be earlier than the date stipulated in the Master LC in order to substitute own Invoice and Bill of Exchange.
BB LC as concept but used as export re-processing LC:
In our country, however, as practiced widely, a Back to Back Letter of Credit means an export reprocessing LC. Such BB LCs is opened mostly for importing or procuring locally the raw materials needed to reprocess and manufacture the exportable merchandise. Value of BB Import letter of Credit is restricted up to a maximum amount of FOB value of the Master export LC. Branches may open BB LCs against export LCs received by export oriented industrial units (client of CBL) operating under the bonded warehouse system. This will be subject to observance of domestic value addition requirement stated in terms of permissible limit of CFR value of imported inputs as percentage of FOB export value of output, prescribed by the Ministry of Commerce from time to time.
The applicant of the BB LC is the beneficiary of the export LC (Master LC), who offers it as backup document to the bank for issuance of BB LC. As the applicant for the BB LC, the exporter is responsible for covering the bank for payment made against BB LC on due date regardless of whether or not he himself is paid under the Master LC at that point of time. Normally the import payment is made from the export proceeds but if export proceeds are not received in time, the applicant is allowed to purchase foreign currency to meet import liability on due date. Such purchase of FC is met form exporter’s own resources or by creation of a Demand Loan Account.
Pre Shipment Finance:
Pre shipment Finance refers to an exporting transaction where bank facilitates export processing by extending funded lending facility or making commitments to discharge exporter’s obligation. If the facility is funded CBL terms it as PCC or ECC. The extensively practiced non-fund commitment is called Back to Back LC or BB LC.
In this section, we shall discuss the funded lending aspect of Pre Shipment Finance:
Packing Cash Credit: Pre-shipment finance allowed under the name of “Packing Cash Credit”, is essentially a short term advance granted by the bank to an exporter to enable him to procure, process, manufacture, pack and ship the goods to the buyers abroad in conformity with the terms of Export Letter of Credit.
Export document processing and negotiation:
1. Presentation of Documents to Bank:
The exporters by exporting of goods to the importing countries submit the related export documents to the authorized dealing branch for repatriation/realization of export proceeds.
As per Guidelines for Foreign Exchange Transactions (GFET), all exports must be made through EXP forms which must be submitted with other export documents by the exporter within 14 days from the date of shipment of goods.
Besides EXP the other common documents usually constitutes a full set of export documents are:
- Bill of exchange or draft
- Commercial invoice
- Transport documents such as bill of lading/airway bill/truck receipt /railway receipt etc.
- Packing list
- Inspection certificate
- Country of origin
- Export license
viii. Bill of Exit
viii.Freight Certificate (if on CRF basis)
Post shipment finance:
Post shipment Finance refers to a transaction where bank extends finance to the exporter to cover him for the period between placement of export documents at bank counter and collection of export proceeds. Such finances are allowed to accommodate the exporter during this transition.
Precede realization:
After getting advice from Head Office to the effect that the procede is credited to Nostro A/C, the fund is realized from H.O. A/C and all the outstanding liabilities including PC, BB LC, FDBP etc. are adjusted. If the maturity date of the BB LC is on a later period the amount is kept in Foreign Bill Proceeds Awaiting for Remittance (FBPAR) A/C. Contingency Fund should also be built up and party may keep some of the proceeds to Retention Quota A/C. Then the rest amount is credited to exporters A/C and the file is closed.
The remittance and the performance of TBL as a company and under the industry
Analysis of foreign exchange performance
Despite of the political unrest and labor turmoil, export amount stood at 607.88 cores at the end of FY08, registration a respectable growth of 51% over that FY07.most of the major export items posted positive growth rates. This happen because our economy experience export earnings from woven –RMG sector increased significantly by 10.9% export of knitwear –RMG posted at 21.5% growth. Export of tea recorded an impressive growth of 114.6% over the export of FY07.however, major decline export was recorded by fertilizer,27%And up to June 2009 Trust Bank recorded 361.70 core TK of export transaction.
|
Import payment during FY 2008 stood, 1666.10 core tk registering a growth of 19% compared FY07.This happen because in year 2007-2008 our economy experience the following except capital machinery. Payments for all import items increased substantially during FY08.Capital machinery import decreased by 13.7%. Food items, consumer and intermediate good and capital goods and other contributed to the rise of imports.
During the year 2008 the bank signed money transfer agreement with overseas exchange companies. As a result , remittance was tk 578.25 core tk as against tk 261.2 core in 2007 registering an increase of 121%.and up-to 2009 June remittance amount was 507.20 core tk which is near equal to 2008.So it is expected that this year Trust Bank will certainly increase up their remittance earning by 55-65% at least.
Growth analysis
| Year | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 |
| Income | 5800000 | 6600000 | 25900000 | 41200000 | 59328000 |
| Growth rate | 0% | 12% | 74% | 37% | 44% |
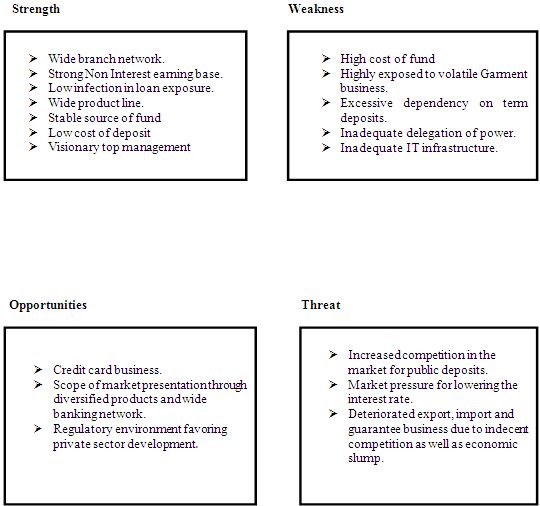
Swot analysis:
In this section we have tried to point out the strength, weakness, opportunity & threat of TBL:
Findings:
Findings of the report refer to the identification of problems and the drawbacks of the Import Documentary Credit Process of Trust Bank Limited those have been encountered during the research process. As it has been mentioned to the Report Proposal that Observation Method will followed. And according to that my job was to go through the whole process during my internship program. According to my research method findings of the report are as follows,
1) Drawbacks at the initial stage:
- At the time opening Sight L/C a problem rises regarding collecting the commissions and charges. Our clients have some accounts with the bank (TBL) and when a client open their letter of credit with us after opening the L/C bank charges it’s commissions and other charges like amendment charge, document handling charges, etc. which generally deducted from those accounts. Usually it is a simple and general process. But when they do not have enough balance on the accounts and for their (clients) time constraint they open their L/C without recharge their account balance. Then bankers have to open a TOD or Temporary over Draft against the L/C in order to fulfill the bank’s need that means in order to collect the charges and commissions. This is an authorized step but the problem arises when time of meet up over draft. It is one kind of loan and the bank get interest for this but the amount of money was not that huge and the client’s unwillingness to clear this amount increases our Account Receivables and reduces the cash collection. The amount for a single client is not that a matter of concern but we have to maintain TOD with most of the clients against their several number of L/Cs. So, at the end of a period we accumulated TOD amounts make a quite big amount.
For these reason branches have to face clarification to the higher authority like head office, audit, etc. that why these TODs have not collected yet.
On the other hand for better customer satisfaction bankers can’t create pressure to the clients for this. There are big clients like Bengal Group, Home Textiles, etc open there letter of credit with Trust Bank Ltd of their importation purposes and they are having a long relationship with the bank. They are importing huge amount of products and raw material for production and exportation.
Another problem regarding L/C opening that all most all clients do not fill up the IMP and L/C application form completely and properly. Lacking of most of the information is a serious problem. Described below,
- Bankers have to fill up all the unfilled information by wasting their own time during their office hour. That leads to a less productive output, because doing these things beside or sometime hampering their own works. Some time it makes some other clients wait for a long time, which is not good for a bank reputation.
- Secondly, in order to fill up these information bank officers, who are related with these jobs have to look for more or less all the documents. For example, to find out BA Number we need to go through IRC Form, for quantity and unit we have to go through Commercial Invoice and like these some other things are there.
- Some time there different shorts of products found in the invoice where there are different type of product with different measurement quantity. Suppose, one product’s measurement unit is Metric Ton where as another one is in Set in an invoice against single Letter of Credit. So, it becomes really confusing, that which one we should consider. Because, in the IMP there is only one type of measurement unit is allowed
2) Lack of Proper documentations:
- In our country all the regulations and rules are not followed properly by the Importers. According to the Bangladesh Bank rules all letter of credit applicant companies have submit their Value Added Tax Certificate and TIN Certificate or Tax Identification Number. These certificates are needed as a pre-requisite for L/C opening. When the bank authority gets these certificates and other staffs, they can easily identify the present condition of our client company. But most of the cases these elements are not available to the clients. And to carry on the banking business the bank has to proceed forward. TIN and VAT Certificates are the tools using which any bank and others financial institute can see the true picture of any organization. And that is really important for them because by knowing the backgrounds of the organizations, it will be easy to make rational and accurate decisions.
- Another vital thing is “Credit Report”. Some of the clients are not willing to show their accurate credit report. For new clients it is really tough to make an exact or riskless decisions without proper credit report. Any problem regarding inaccurate credit report of any client can crate savvier problem. Credit report can be said as the credit historical preview of a company. Based on this report many important decisions are made. Before opening any import documentary credit, the bank (TBL) will take the decision about whether making any relationship with the desired organization or not. If the answer is yes then, what will be limit of providing facilities, like credit facility, margin facility, etc.
3) Some Drawbacks during Dealing with Foreign Correspondences:
Trust Bank Limited has just celebrated its 8th year of establishment. Good news for the bankers but still it’s nothing that much time period to earn the highest limit of goodwill. So, it does not have any strong position to the foreign correspondences. And in today’s competitive banking market has created such a critical scenario where rarely people (importers) want to switch off from their existing correspondences (banks).
Another thing is that being a new and local bank most of the foreign correspondences do not know that much about Trust Bank or not at all. So, Trust Bank Ltd has to call for a help for “Confirming Bank” for issuing the undertaking the whole process and settlement. And for that reason TBL has to counter an expense named “Confirming Charge”. For these reasons multinational banks are having better advantage then the local banks.
4) Problems that arise at the time of reporting to the Central Bank (Bangladesh Bank):
There are some problems arise during and after the reporting of export-import, which we can mention as some drawback of our less or non-updated reporting system, sated by Bangladesh
There are some problems arise during and after the reporting of export-import, which we can mention as some drawback of our less or non-updated reporting system, sated by Bangladesh Bank.
- Firstly, the old EXP (export) and IMP (import) forms are still not change and for that reason, some irrelevant areas have not still removed.
- All the banking tasks have been fully computerized (99%) especially for the private banks. All their day-to-day tasks to yearly closing everything become fully computerized. Only the primary entries then the baking software’s for example Flora Banking Software, Carnell, etc made the rest of the reports (like voucher, balance sheet) Whereas, our Central Bank yet not that fully dependent on computerized automated system. It is still following the old manual system for most of the purposes.
- Most of the time hand written EXP and IMP forms refused by Bangladesh Bank due to unclear handwriting or due to in sufficient information. In addition, this is quite impossible in computerized system.
6) Identifying the problems arises at the time of audit of foreign exchange department (Both Internal and External):
It is a regular matter for all private banks. At the time of auditing the foreign exchange department of TBL the department executives have to gone through some unavoidable scenarios. Some of those have been discussed bellow,
- For some time the clients update the import registrar by themselves. But updating the registers is the task of the executives and the officers of the banks. This is an informal but regular and normal matter. This is one of the important concerns of audit.
- Most of the time the auditors do not maintains any predetermined timing. Like, some time they charge one department (Foreign Exchange) while they were auditing another department (Credit).
- Some time they charge the department officers and related persons for allowing the clients hampering or disturbing their duties.
- There is another problem that we have gone through at the time of our IPO that the auditors were carrying on their auditing during the IPO time. Where all the executives and officers were busy with their both IPO related work and regular banking works.
7) Basis of some managerial decisions about providing some flexibility to some specific client:
As we know it is a service business and like the other banking business we have to satisfy
our clients. For this reason, we need to allow some selective clients to enjoy some flexibility.
These are completely managerial basis dissensions and magnitude of the ranges of flexibility depends on the relationship with our client. Flexibility indicates providing some advantages to the client beyond the regulation.
A Synoptic View
Trust Bank Limited offers Full range of banking service s that include deposit banking, loan & advances,export,import and financing national and international remittance facilities etc. Foreign exchange department has three sections. They are export, import and remittance. The number of L/C opening for export is decreasing and the number of L/C opening for importing is increasing. The income from foreign exchange operation is more than previous year. A country can’t continue for long time to have a deficit on foreign current account but a favorable balance of payment on current account may conceal a heavy adverse balance of payments with one individual country or group of countries.
As developing country, Bangladesh is striving to reduce its trade gap. Government is taking necessary steps to enhance its export sector through the help of market mechanism as well as different financial and institutional incentives to the exporters. At the same time it is taking necessary steps to attract foreign investments and creating efficient human resources to fight the edge of competition. In the time of liberalization of our economic sector ,our current account has already been made convertible along with floating exchange rate. With the help of continuous increase in wage earners remittance and inclusion of nontraditional items in export list, Bangladesh emerging towards a more stable economy.
Recommendations
Recommendations for the problems those have been encountered during the research (observation) process described below,
Recommendations on Drawbacks at the Initial Stage:
For these part I will recommended, that to carry on the present situation, because the higher authority should understand that in here TOD matters can be an advantage for TBL like it is one kind of flexibility to the client from the bank. It increases the number of transaction as well as increases the revenue. Same thing is applicable in IMP and Application form fulfillment matter..
Recommendations on Absence of Proper documentations:
There is a straight but simple thing to do. That is to create force by the central bank to the client that means the to the business organizations who have business related with importation. That they will be strictly treated by law if there is any mismanagement of proper documentations. Bangladesh Bank can create this pressure through their auditors. Bangladesh bank should make compulsory rules for presenting latest credit report, TIN and VAT Certificates.
Recommendations on the Drawbacks during Dealing with Foreign Correspondences:
This is matter of time period and the objectives of the bank authority. That whether they will broaden their business out of the border and expand globally or not. Vision of the bank can be changed time to time. Trust Bank need to do more both worldwide and local exposure. As it has been one step ahead by issuing their primary share (IPO).
But for these section I will recommend,
- To offer more flexibility on settlement in Import Documentary Credit Operation to the clients, like lower margin, less amendment and other charges, etc.
- To go for more potential and outcome oriented advertisement, like send the officers to different organizations both in banking sector and non banking sectors.
Recommendation for regular update data
As it was mentioned that the Central Bank that means Bangladesh Bank still maintaining old manual reporting system for Import Documents. Bangladesh Bank should convert this process into computerized system in order to make this process faster and more accurate. To do that our Central Bank can setup an upgraded Main Frame Server Network whit will be connected with an intranet or extranet networking system or both. It will be connected with all the commercial banks so that the commercial banks can make input of the import reporting online and then authorized by the managers then update through batch processing system after each period (monthly).
Some other recommendation are-
a) Advertisement-The management should impart more emphasis on the advertisement of the bank in different electronic and printing media. the basic goal of the advertisement should be firstly to make people know and understand that the bank is universal one and permits anyone’s access.
b) Decision making-Since decision making is the fundamental of all business operations, the management should be bold and quick in making decision considering the internal efficiency and external market competitiveness.
c) Extension mechanism-The spread out mechanism of the bank should be faster and progressive as well. Being established in1999, the bank established only 42 branches in ten years. the mode of extension is much slower than other contemporary and equivalent banks.
d) Personnel management-The management should care of the personnel more. At the recruitment stage ,it should go for the best candidates and after selection the personnel should be allowed with proper opportunity to be expert on particular task bestowed on them.
e) Product diversification-more products of varied interests should be introduced for the diversified client group.
f) Direct social involvement-To enhance the image of the bank and to assume social responsibility, the bank should engage itself to various social program like scholarship to poor but meritorious students, empowerment of the children in abject poverty, campaign against dowry and other social evil etc.
Conclusion
At conclusion it can be said that, this is a complete report on “Import Documentary Credit Operation” which contains almost all the theoretical and practical information on the basis of three months observation. It is a positive side that at present the complete procedure of foreign exchange of all commercial banks is being monitored under a strict authority than it used to be. And our central bank Bangladesh Bank is now setting up their new updated automated and mainframes computerize system, which make the banking operations as well as the reporting of Import Documentary Credit Operation faster than it used to be. According to the internal and external observation from various aspects, a positive mentality about Trust Bank Limited has been developed based on which the future prospect of the company as commercial bank is strongly expected.