Foreign Exchange
Foreign Exchange Department is international department of any Bank. It deals globally. It facilitates international trade through its various modes of services. It bridges between importers and exporters. If the branch is authorized dealer in foreign exchange market, it can remit foreign exchange from local country to foreign country. This department is called foreign currency department.
Some national and international laws regulate functions of this department. Among these, Foreign Exchange Act. 1997 is for dealing in foreign exchange business, and Import and Export Control Act, 1950 is for Documentary Credits (UCPDC) 1993 revision & International Chamber of Commerce Publication no-500 is also an important law for settlement of terms and conditions between exporter and importer in international trade. Government’s Import & Export policy is another important factor for import and export operation for banks.
In banking arena the term foreign exchange originated from the exchange. Exchange has several meanings. One term commonly used in banking is the “clearing house exchange”. Banks in a community, who have formed a clearing House Association exchange the items in their possession but draw on other banks in the community and with these other banks at the daily meeting of the clearing Housing Association. Settlement to all items exchanged is simplified because the exchanged is settled on a “net basis” wherein the “losing banks” pay the “winning banks” the net difference in the exchange of items.
The term is also used to denote a service charge, or exchange fee, made by banks for cashing checks, usually items drawn on distant point “Exchange” in financial circles also describes meeting place where stocks, bonds and commodities are bought and sold or traded in. Example: stock exchange curb exchange, grain exchange and cotton exchange.
Foreign Exchange refers to trading that involves foreign currencies. The principal foreign exchange markets are in New York City where many banks have private wires to all foreign countries. By this communication service, these banks are able to buy and sell for immediate or even future delivery funds of foreign countries, these funds to be used to pay for imports or exports in the currency describe by the seller of the goods.
Import:
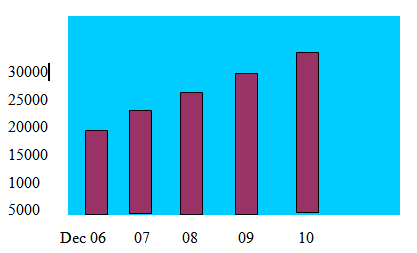
The import business including local L/Cs of the bank increased to tk 32096 million in the year under review from tk 21363 million of the previous years. Increase in the in the import business is 50% compare to the previous year.
Export
The volume of export business including local bills rose to Tk 28211 million from Tk 18219 million in 2009 showing a growth of 55%. Ready Made Garments, frozen food and leather add this growth in 2010.
Function of Foreign Exchange Department
- L/C Opening.
- L/C Amendment.
- Foreign Bill Purchase.
- Local Bill Purchase.
- Foreign Remittance.
- FC (Foreign Currency).
- A/C Maintaining.
- Foreign Currency Remitting.
- TC (Traveler Check).
Foreign Exchange Mechanism
- L/C Opening.
- Issue the L/C by issuing bank and send to advising bank.
- Advised and confirm the L/C by advising and Confirmation bank.
- Submit the Documents to negotiating bank by export.
- The negotiating bank makes payment.
- The Negotiating bank forward/sends documents to issuing bank.
- Issuing bank makes payment to negotiating bank.
- An issuing bank instructs to pay or reimburse the paying bank makes payment or
reimburse the negotiating bank.
- Issuing bank sends documents to the importer. 10. The importer makes payment.
Documents of International Trade
Documents are important in international trade because they control the international movement of goods; in some cases, they are legal title of the goods. It is important that the correct documents should be in the right place at the right time and in order to speed delivery of the goods and subsequent payment that they should correctly completed. A seemingly minor discrepancy in the documentation will almost certainly lead to a delay in receiving payment.
In the rest of this chapter we shall learn the information to be found on the basic documents of international trade and list the documents that are required when a contract is established between two parties.
Invoices
- An invoice is prepared by the seller of the goods and contains the following details:
- Name and address of the seller.
- Name and address of the buyer.
- Date of the invoice.
- A description of the goods together with the price.
- Details of the way in which the goods are in create cases or drums-and shipping marks on the packages.
- The terms of sale (CIF, C & F, FOB and so forth); the charges for insurance and
- freight, if applicable, may also be detailed on the invoices;
- If applicable, details of import licenses and exchange permits required by the importing country.
- The total amount payable.
An invoice is the list of items along with the prices of products produced by a certain organization. If such an invoice is sent from an exporter towards an importer for the purpose of trade, then it is called proforma Invoice. Now, if a trade agreement is signed between the exporter and the importer on the basis of the proforma invoice, upon their unanimous consent, from that moment the invoice is termed as commercial invoice.
The details of the invoice should tie up with the contract of sale; if a documentary letter of credit has been opened, the invoice should conform exactly to its terms. Several copies of invoice are normally required for the use of the buyer, customs and the import authorities abroad. Some countries may require a certified invoice or certificate of origin to confirm that the goods come from a particular country; Britain certain chambers of Commerce authorized by the Department of trade to make declarations of origin.
Method of Payment in International Trade
The terms of payment and the method by which settlement is to be effected are agreed between the exporter and his customer in their contract. The terms and method of payment required by exporter will depend very much on the previous experience, if and, that he has in the particular market, on his knowledge of the overseas customer and on the tatter’s financial standing.
The main methods of securing payment starting with the safest are:
- Payment in Advance.
- Payment under a Documentary letter of Credit.
- Documents against payment or acceptance of the exporter’s bill of exchange and open Account.
(a)Payment in of Advance
This is undoubtedly the safest way to receive payment for exports but buyer is seldom prepared to pay for goods in advance of shipment, other than for small consignments. The buyer through his bank by means of a bank draft or generally makes any such payment by mail or telegraphic transfer in favor of the exporter.
(b)Documentary Letter of Credit
After payment in advance this represents the safest and faster way of obtaining payments for exports as the exporters can personally retain control of the documents of title to the goods until the moment of payments or acceptance of a bill of exchange the parties to a credit are:
- The applicant (usually the buyer), who arranges to open a credit in accordance with the terms of the contract he made with the beneficiary (usually the seller).
- The beneficiary in whose favor the credit is issued.
- The issuing bank which commits itself in accordance with the applicant’s instructions.
- The advising bank, which is located in the country of the beneficiary and is usually the issuing bank’s correspondent.
Letter of credit is an instrument or document issued by a bank or another bank or banks, foreign or domestic, or upon its
lf. The letter of credit gives the buyer (probably unknown to the seller) the prestige and financial backing of the bank who issues the letter of credit on his behalf. The acceptance by the bank of draft drawn under the letter of credit satisfies the seller and his bank in the handing of the transaction. The buyer and the accepting bank also have an arrangement as to payment for the drafts as they are presented. Documentary letter of credit refers to the letter of credit along with the papers relevant to it. Mathematically we can say:
DLC=LC+RNP
Where, DLC = Documentary Letter of Credit.
LC= Letter of Credit
RNP= Relevant Necessary Papers.
Where the terms of the contract call for payment under a credit, The buyer (or applicant) applies to his bank (the issuing bank) to open a credit in favor of the exporter (the beneficiary).
a bank in his own country (the advising bank). Under the terms of credit, the issuing bank undertakes that the seller will be paid for his goods provided he complies with certain stated conditions. This will for certain documents, such as invoices, bill of lading and insurance documents (depending on the precise responsibility of the exporter covering the quantity and quality of goods agreed in the contract between the exporter and the overseas buyer).
Before issuing a credit the bank must make certain of its customer’s creditworthiness; if this is satisfactory, the credit is then advised to the exporter through
Provided that the documents presented to the advising bank agree exactly with the requirements of the credit, the exporter receives the payment due to him in exchange for the documents. The advising bank sends to the issuing bank airmail, upon receipt, they are handed to the buyer, who then awaits the Arrival of the arrival of the carrying vessel.
When the ship docks, the buyer presents the bill of lading to the representatives of the shipping company and, in discharge of the shipping company’s responsibilities under the contract of the carriage, receives the goods. Payment for the goods by the buyer to the issuing bank is a matter of agreement between them and of no concern for the exporter. The settlement between the banks for the amount paid by the issuing bank is carried out through their agency accounts. The issuing bank’s account in the records of the advising bank is debited, and the account of the advising bank in the records of the issuing bank is credited.
Besides the Advising of credit to the exporter, who knows that he will receive payment provided he complies with its terms, there are benefits to the buyer. He knows that payment will be made by the advising bank when the exact documents specified have been received as these are the documents of title, then once they are in hands of the advising bank, it will only be a matter of time before they are sent to him. Allowing him to collect the goods.
There is however a risk to the issuing bank because the credit only deals in documents and not in goods, so that provided the exporter complies with the terms and conditions of the credit he will be paid even through the creates supposedly containing the goods have been packed with sawdust and old newspapers. A status inquiry by the bank on the exporter is therefore essential.
Characteristics of the Importer Who Wants to Open a L/C
- Must have an A/C in the branch.
- Member of the Chamber of Commerce.
- Must be a TIN Tax Identity Number) holder.
Import Mechanism
To import, a person should be competent to be an importer. According to Importer and Exporter Control Act, 1950 the office of Chief Controller of Importer and Exporter provides the registration (IRC) to the importer. After obtaining this, the person has to secure a letter of credit authorization (LCA) from Bangladesh Bank. Then a person becomes a qualified importer. He is the person who requests or instructs the opening bank to open an L/C. He is also called opener or applicant of the credit.
Importers Application for L/C Limit/ Margin
To have an import L/C Limit, an importer submits an application to the Department of The City Bank Limited furnishing the following information:
- Full particulars of bank account.
- Nature of Business.
- Required amount of limit.
- Payment terms and conditions.
- Goods to be imported.
- Offered security.
- Repayment schedule.
A credit officer scrutinizes this application and according prepares a proposal (CLP). The Committee v if satisfied, sanctions the limit and returns back to the branch. Thus the importer is entitled for the limit.
The L/C Application
The City Bank Limited provides a printed from for opening of L/C to the importer. This from knows as Letter of Credit Application form. A special adhesive stamp is affixed on the form. While opening, the stamp is cancelled. Usually the importer expresses his desire to open the L/C quoting the amount of margin in percentage. The importer gives the following information:
- Full name and address of Importer.
- Full name and address of Beneficiary.
- Draft amount.
- Availability of the credit by sight payment
- Acceptance/negotiation/deferred payment.
- Time bar within which the documents should be presented.
- Sales type (CIF/FOB/C&F)
- Brief Specification of commodities, price, quantity, indents no etc.
- Country of origin.
- Bangladesh Bank Registration no.
- Import License/ LCF no.
- IRC no.
- Account no.
- Documents required.
- Insurance cover note/ policy no. Date, amount.
- Name and address of Insurance Company.
- Whether the partial shipment is allowed or not.
- Whether the Trans-shipment is allowed or not.
- Last date of shipment.
- Last date of negotiation.
- Other terms and conditions if any.
- Whether the confirmation of the credit is requires by the beneficiary.
The Above Information is given Along With the Following Documents
- Bill of exchange.
- Proforma Invoice stating Description of the goods including quantity, unit prices.
- Bill of lading/ truck receipt/ airway bill.
- Commercial Invoice.
- Packing list.
- Insurance cover note, issuing company and the insurance number.
- Five set of IMP Form.
- Certificate of Origin.
- Credit
The Letter of Credit Authorization Form
- Name and address of Importer.
- IRC no. And year of renewal.
- Amount of L/C applied for (both in figure and in word).
- Description of item(s) to be imported.
- ITC Numbers.
- H.C code.
- Stamp and signature of the Importer with seal.
Types of L/C
(a) At sight L/C.
(b) Deferred L/C.
(c) Back to Back L/C
(a)At sight L/C
At Sight L/C, an exporter (Original exporter of Mother L/C) can get payment immediately against the exporter’s presentation of the documents.
(b)Deferred L/C
For deferred L/C, an exporter (Original exporter of Mother L/C) can get payment after 60 or 90 or 120 or 180 days after negotiation.
(c)Back-to-Back L/C
In case of Back-to-Back Letter of Credit a new L/C (an Import L/C) is opened on the basis of an original export L/C or Mother L/C. Under the Back-to-Back concept, the seller is the beneficiary and the beneficiary/ Exporter of an original export L/C or Mother L/C is the importer/ buyer. The beneficiary of the Back-to-Back L/C may be located inside or outside of the original beneficiary’s country. Normally, an applicant or the importer (beneficiary of original Export L/C or Mother L/C) will be able to open a Back to Back L/C maximum 75% value of original export L/C or Mother L/C.
As security, original Export L/C or Mother L/C or Master L/C will be under lien on bank. For Back to Back L/C, an Importer (Exporter or Beneficiary of the original Mother L/C or Master L/C) will have to import the goods or products within the validity of the original mother L/C. otherwise, importer and exporter will communicate for amendment.
Scrutinizing of L/C Application
The City Bank official scrutinizes the application in the following
- The terms and conditions of the L/C must be complied with UCPDC 500.
- Exchange Control and Import Trade Regulation.
- Eligibility of the goods to be imported.
- The L/C must not be opened in favor of importer.
- Radioactive report or certificate in cases of old machinery.
- Survey report or certificate in case of old machinery.
- Carrying vessel is not Israel.
- Certificate declaring that the item is in operation not more than 5 year in case of car.
Precautions Taken by Officer Before Issuing L/C
After submission of documentary letter of credit application form, the concerned officer scrutinizes the terms and conditions that mentioned in application. He must check the following things:
- Whether the terms and conditions of L/C application are consistent with Exchange Control and Import Trade regulation UCPDC-55.
- L/C must not be opened in favor of the importer or his agent.
- The importer agreeing all conditions mentioned in the application must sign L/C.
- Indenting registration number.
- Whether IMP form dully filled and signed.
- Validity of IRC.
- Insurance cover note with date of shipment.
- The HS code of the goods.
- The balance of the goods.
- The balance of the accounts of the importer.
- The goods are not form Israel and vessel to the used are not of Israel.
In The City Bank Ltd. Documents Required for Submission for Opening of Back-to-Back L/C
- Master L/C.
- Valid Import registration certificate (IRC) & Export Registration certificate (ERC).
- L/C application and Agreement for confirmed Irrevocable without recourse to
drawer’s letter of credit.
- LCA form duly filled in signed.
- Performs invoice.
- Insurance cover note with money receipt.
- IMP form duly signed.
In addition to the above following papers/documents are also required for Export oriented garments industries while requesting for opening of Back to Back L/C:
- Textile permission
- Valid Bonded warehouse license.
- Quota allocation letter issued by Export promotion Bureau (EPB) in favor of the
applicant in case of quota items.
(a)Amendment of Letter of Credit
Parties involved in a L/C, particularly the seller and the buyer cannot always satisfy the terms and conditions in full as expected due to some obvious and genuine reasons. In such a situation, the credit should be amended. The City Bank Limited transmits the amendment by tested telex to the advising bank. In case of revocable credit, it can be amended or cancelled by the irrevocable letter of credit, it can neither be amended nor cancelled without the agreement the issuing bank, the confirming bank (if any) and the beneficiary. If the L/C is amended, service charge and telex charge is debited from the party account accordingly.
(b)Presentation of Documents
The seller satisfied with the terms and conditions of the credit proceeds to dispatching of goods to the negotiating bank on or before the stipulated expiry date of the credit. After receiving all the documents, the negotiating bank then checks the documents against the credit.
If the documents are found in order, the bank will pay, accept or negotiates to The City Bank Limited. The City Bank Limited checks the documents. The usual documents are-
- Invoice.
- Bill of leading.
- Certificate of Origin.
- Packing list.
- Shipping advice.
- Non-negotiable copy of bill of lading.
- Bill of exchange.
- Pre-shipment inspection report.
- Shipment certificate.
(c)Examination of Documents
The City Bank Officials checks whether these comments have any discrepancy or not. Here, Discrepancy means the dissimilarity of any of the documents with the terms and conditions of L/C.
(d)Dispatching the Import L/C
After opening of import L/C, The City Bank Limited Kawran Bazar Branch dispatches the L/C. Kawran Bazar Branch sends an original copy of the L/C for negotiating and a copy to the advising bank for advising. It also sends in imbursement.
(f)Receiving Document
If the beneficiary is being satisfied with the term and conditions of the L/C then dispatching the goods to the buyer. After that dispatch the documents evidencing dispatching of goods to the negotiating bank on or before the stipulated expiry date of L/C.
(g)The Documents Includes
- Commercial Invoice.
- Bill of lading.
- Bill of Exchanging.
- Shipping Certificate.
- Pre-shipment Inspection Certificate.
- Certificate of origin.
- Packing list.
- Weight list.
- Insurance Cover Note.
- Radio Activity Report (applicable for import of foods only.)
After receiving all the documents, the negotiating Bank then checks the documents against the credit. If the documents are found in order, the bank will send to The City Bank Limited.
(h)Lodgment & Retirement Section
Lodgment means retirement of funds. If the documents receiving from the negotiating Bank (The City Bank) Kawran Bazar Branch also scrutinize the documents. The offer carefully examines the following points.
(i)Invoice
The invoice should contain quality, quantity, unit price, and total value.
The number of copies should exactly meet the requirement of the credit.
The shipper must sign all the copies.
(ii)Bill of Lading
It must be duly signed and endorsed.
It must state payment of freight. If the invoice price is on C&F basis the bill of lading must be marked “Freight of Pay” is marked on B/L.
(iii)Certificate of Origin
It should provide evidence of the goods as specified in the bank. It is by the Chamber of Commerce of beneficiary’s country.
(iv)Bill of Exchange
Is the Bill of Exchange drawn in the language of the credit?
Is the bill of exchange properly prepared accordingly to the credit conditions (on a sight or time basis) and drawn on the specified bank?
Is properly dated and signed?
Is the amount in figure corresponded exactly with the amount in word?
Does it contain all the prescribed notations and clauses?
Any other documents such as Weight and Measurement Certificates, Insurance Certificates, packing list etc. as stipulated in the credit must be examined before negotiation.
After scrutiny of these documents, if there is any discrepancy in the document, the officer sill promptly advise the importer and the negotiating bank and asks them to rectify these discrepancies. But if there is no discrepancy, then he will prepare some voucher to adjust the payment.
(v)Payment Against Document
This is the most sensitive task of the Import department. The officials have to be very much careful while making payment. This task constitutes the following things:
(vi)Date of payment
Usually payment is made within seven days after the documents have been received. If the payment is become deferred, the negotiation bank may claim interest for making delay.
(vii)Preparing Sale Demo
A sale memo is made at B.C rate to the customer. As the T.T & O.D rate is paid to the ID, the difference between these two rates is exchange trading. Finally, an Inter Branch Exchange Trading Credit Advice is sent to ID.
(viii)Loan Against Merchandise
Loan against import merchandise through the bank may be allowed retaining Margin prescribed on their Landed Cost, depending on the categories and credit restrictions imposed by the Bangladesh Bank/ head office from time to time. Branches shall also obtain letter of undertaking and indemnity from the clients. Before getting goods cleared through LIM account. Clearance of the goods should be taken through Approved Clearing Agent of the Bank.
Remittance Department
Foreign Remittance Business
In the year 2009 City Bank Limited has established new inward foreign remittance relationship with 8 exchange house located in U.K, UAE, Oman and Qatar which helped the Bangladeshi expatriates to remit their foreign currency through proper banking channel. The bank handled foreign remittance business amounting Tk 9780 million directly through 14-exchange house in the year 2009. Total amount of foreign remittance received through exchange houses and banks was Tk 12473 million. The amount in the same period of the last year was Tk 7158 million. The growth of the foreign remittance business in 2010 was 104% compare to the previous year.
The City Bank Limited is one of the fastest growing banks among all the private commercial banks in Bangladesh. This bank constantly looks for ways & means to improve productivity by rendering to its customers in order to remain competitive in the market.
The City Bank Limited plays a significant role in various fields in the economy such as industry, trade & commerce, transportation, deposit mobilization etc. It is playing a crucial role in human resource development and in creating new employment opportunities. It is also undertaking various welfare activities for the betterment of the society, in this context the bank has established The City Bank Foundation.
The reliability of the customers on The City Bank Limited is increasing promptly day by day. The overall performance of The City Bank Limited solid revenue growth together with strict discipline on expenses. The bank constantly reviews its systems, policies, process and prices of its products and services with the changing marketing reality.
References
1. Annual Report of The City Bank Ltd.
2. Web side of The City Bank
www.thecitybankltd.bd
3. Different document of The City Bank
Limited, Kawran Bazar Branch
4. Search engine: Google, Wikipedia
5. Strategic Management, Charles W. L. Hill and Gareth R. Jones, 7th Edition
6. Principle of Marketing, Philip Kotler and Gary Armstrong, 11th Edition