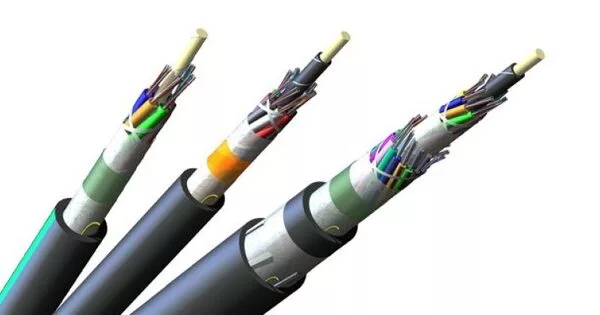
A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is a cable assembly that is similar to an electrical cable but contains one or more optical fibers that carry light. Individual optical fiber elements are typically coated with plastic layers and housed in a protective tube appropriate for the environment in which the cable is used. For optical communication, various types of cable are used in various applications, such as long-distance telecommunication or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
A fiber-optic cable’s core is made of a highly transparent material, typically glass, and is surrounded by a cladding layer with a lower refractive index. This design allows light to be internally reflected within the core, ensuring that signals travel with minimal data loss along the fiber.
Design
Because of the difference in refractive indexes, optical fiber is made up of a core and a cladding layer that are designed for total internal reflection. In practical fibers, the cladding is typically coated with an acrylate polymer or polyimide layer. This coating protects the fiber but has no effect on its optical waveguide properties. Individual coated fibers (or fibers formed into ribbons or bundles) are then extruded with a tough resin buffer layer or core tube(s) to form the cable core.
Depending on the application, several layers of protective sheathing are added to form the cable. Light-absorbing (“dark”) glass is sometimes placed between rigid fiber assemblies to prevent light from leaking out of one fiber from entering another. This reduces crosstalk between the fibers, or reduces flare in fiber bundle imaging applications.
Here are some key characteristics and benefits of fiber-optic cables:
- High Bandwidth: Fiber-optic cables have a very high bandwidth, which means they can transmit a large amount of data at the same time. As a result, they are well-suited for high-speed internet, video streaming, and other data-intensive applications.
- Long Transmission Distance: Optical fibers can transport signals over long distances with little loss or degradation. They can transmit data for several kilometers without needing to regenerate the signal.
- Speed and Low Latency: Fiber-optic cables have extremely high data transfer rates, allowing for real-time communication. They have low latency, which makes them suitable for applications requiring instant responsiveness, such as online gaming or financial transactions.
- Immunity to Interference: Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber-optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, radio frequency interference, and crosstalk. This results in more reliable and stable data transmission, even in environments with high levels of electrical noise.
- Security: Fiber-optic cables offer enhanced security for data transmission. They do not emit electromagnetic signals, making it difficult for hackers to tap into the cable and intercept the transmitted data.
Application
Fiber-optic cables are widely used in telecommunications networks, internet infrastructure, data centers, and other industries that require fast and dependable data transmission. They have transformed communication by enabling the rapid and efficient transfer of massive amounts of data around the world.
For indoor applications, the jacketed fiber is generally enclosed in a lightweight plastic cover, along with a bundle of flexible fibrous polymer strength members like aramid (e.g. Twaron or Kevlar), to form a simple cable. Each end of the cable can be terminated with a specialized optical fiber connector, making it simple to connect and disconnect from transmitting and receiving equipment.