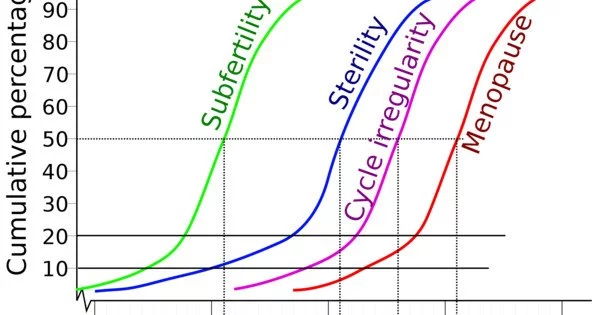
Female fertility generally declines with age, particularly after the age of 35. As women get older, the number and quality of their eggs decrease, which can make it harder for them to get pregnant. Female fertility is affected by age and is a major factor in female fertility. From the late teens to the early thirties, a woman’s fertility is generally of high quality, though it gradually declines over time. Fertility begins to decline more rapidly around the age of 35. While many sources suggest a more dramatic drop at around 35, this is unclear due to a lack of studies since the nineteenth century.
A 2004 study of European women found only a 4% difference in fertility between the 27-34 and 35-39 age groups. A woman starting to try to conceive at the age of 45 will have no live birth in 50-80% of cases. Menopause, or the cessation of menstrual periods, usually occurs between the ages of 40 and 50 and marks the end of fertility, though age-related infertility can occur before then. A woman’s “biological clock” refers to the relationship between age and female fertility.
In general, women are most fertile in their twenties and early thirties. After age 35, fertility begins to decline more rapidly. By age 40, a woman’s chances of getting pregnant in any given month are less than 5 percent. However, it’s important to note that fertility varies from woman to woman and is influenced by many factors, including overall health, genetics, and lifestyle choices. Some women may still be able to conceive naturally at an older age, while others may experience infertility earlier in life.
If you are concerned about your fertility or are having trouble getting pregnant, it’s a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help assess your fertility and provide guidance on next steps, including fertility treatments if necessary.
In addition to age, other factors can also affect female fertility, including medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and thyroid disorders, as well as lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and being overweight or underweight. If you are trying to conceive and are concerned about your fertility, it is important to talk to your doctor, who can help you understand your fertility and provide guidance on how to optimize your chances of getting pregnant.