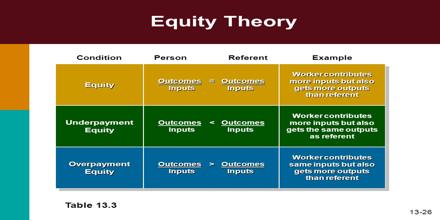
In 1963, John Stacey Adams introduced the idea that fairness and equity are key components of a motivated individual. Equity theory is based in the idea that individuals are motivated by fairness, and if they identify inequities in the input or output ratios of themselves and their referent group, they will seek to adjust their input to reach their perceived equity. Adams suggested that the higher an individual’s perception of equity, the more motivated they will be and vice versa: if someone perceives an unfair environment, they will be de-motivated.
Equity Theory