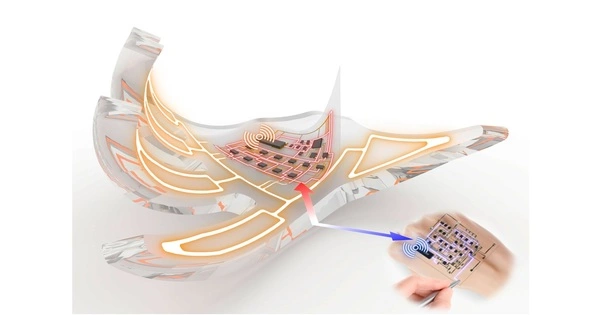
Electronic skin is a term that refers to flexible, stretchy, and self-healing electronics that can replicate the functions of human or animal skin. A flexible and thin electronic material that mimics the qualities and functions of human skin is referred to as e-skin or smart skin. It is meant to sense and respond to external stimuli like as pressure, temperature, and humidity in the same way that human skin does. The vast class of materials frequently comprises sensing abilities designed to mimic the ability of human skin to respond to environmental stimuli such as changes in temperature and pressure.
Electronic skin is a significant advancement in wearable technology and human-machine interaction. Electronic skin research advances are focused on developing materials that are elastic, strong, and flexible. Flexible electronics and tactile sensing research have advanced significantly; nonetheless, electronic skin design tries to bring together breakthroughs in several areas of materials research without sacrificing specific benefits from each field.
Recent advancements in the field of electronic skin have concentrated on incorporating green material ideals and environmental awareness into the design process. Because one of the major obstacles in the creation of new electronic skins is the ability of the material to tolerate mechanical strain while maintaining sensing or electrical qualities, recyclability, and self-healing properties are very important in the future design of new electronic skins.
Here are some key aspects of electronic skin:
- Sensing Capabilities: It is outfitted with a variety of sensors, including pressure, temperature, and humidity sensors, as well as sensors for detecting chemical or biological contaminants. It can sense and respond to environmental events thanks to these sensors.
- Flexibility: E-skin is often comprised of stretchy and flexible materials that allow it to conform to irregular shapes and move with the wearer’s body. This adaptability is critical in applications like as prosthetics, robotics, and wearable gadgets.
- Real-time Data: It sensors can offer real-time data, making it useful for healthcare, robotics, and environmental monitoring applications. It can, for example, monitor a patient’s vital signs or provide feedback on the actions of a robot.
- Biocompatibility: In some cases, it is designed to be biocompatible, meaning it can be integrated with biological tissue without causing harm or discomfort. This feature is particularly important for medical applications like prosthetics and artificial skin.
Applications: Electronic skin has a wide range of potential applications, including but not limited to:
- Prosthetics: Electronic skin can improve the sense of touch and control in prosthetic limbs.
- Robotics: It can enhance the dexterity and sensitivity of robotic hands and other robotic systems.
- Healthcare: E-skin can be used for remote health monitoring, wound care, and drug delivery.
- Human-Machine Interfaces: It can enable more natural and intuitive interactions with machines and devices.
- Environmental Monitoring: E-skin can be used to monitor environmental conditions, such as pollution levels or structural integrity in infrastructure.
Researchers and engineers are working to improve the performance, durability, and versatility of electronic skin in order to broaden its variety of applications. This technology has the potential to transform numerous fields by allowing for more smooth and delicate interactions between humans and robots, as well as improving our ability to monitor and understand our surroundings.