E-commerce Footprint
E-Commerce:
By definition, ecommerce or electronic commerce, is the buying and selling of products or services via the Internet. This is type of business model, or segment of a larger business model, that enables a firm or individual to conduct business over an electronic network, typically the internet. Electronic commerce operates in all four of the major market segments: business to business, business to consumer, consumer to consumer and consumer to business.
It can be thought of as a more advanced form of mail-order purchasing through a catalog. Almost any product or service can be offered via ecommerce, from books and music to financial services. Nowadays the thought of living without ecommerce seems unfathomable, complicated and an inconvenience to many.
History:
Ecommerce was introduced 40 years ago and, to this day, continues to grow with new technologies, innovations, and thousands of businesses entering the online market each year.
In 1960 to 1982 EDI replaced traditional mailing and faxing of documents with a digital transfer of data from one computer to another.
Trading partners could transfer orders, invoices and other business transactions using a data format that met the ANSI ASC X12, the predominant set of standards in North America.
Once an order is sent, it is then examined by a VAN and finally directed to the recipient’s order processing system. EDI allowed the transfer of data seamlessly without any human intervention.
In 1982 to 1990 it was the beginning that B2B online shopping would be commercially lucrative but B2C would not be successful until the later widespread use of PC’s and the World Wide Web, also known as, the Internet. In 1982, France launched the precursor to the Internet called, Minitel.
The online service used a Videotex terminal machine that was accessed through telephone lines. The Minitel was free to telephone subscribers and connected millions of users to a computing network.
By 1999, over 9 million Minitel terminals had been distributed and were connecting approximately 25 million users in this interconnected network of machines. The Minitel system peaked in 1991 and slowly met its demise after the success of the Internet 3 years later. Eventually, in 2011, France Telecom announced its shutdown of the Minitel service system. Sadly, it had not become what it had hoped to be, the Internet.
In 1990 Tim Berners Lee, along with his friend Robert Cailliau, published a proposal to build a “Hypertext project” called, “World Wide Web.” The inspiration for this project was modeled after the Dynatex SGML reader licensed by CERN.
That same year, Lee, using a “Next Computer” created the first web server and wrote the first web browser. Shortly thereafter, he went on to debut the web on Aug. 6, 1991 as a publicly available service on the Internet. When Berner Lee, decided he would take on the task of marrying hypertext to the Internet, in doing that, the process led to him developing URL, HTML and HTTP.
When the National Science Foundation lifted its restrictions on commercial use of the NET in 1991, the Internet and online shopping saw remarkable growth. In September 1995, the NSF began charging a fee for registering domain names. 120,000 registered domain names were present at that time and within 3 years that number grew to beyond 2 million. By this time, NSF’s role in the Internet came to an end and a lot of the oversight shifted to the commercial sector.
E-Commerce in the era of globalization:
Globalization has brought in many changes in the business scenario with the whole world inching towards one big market place. Communication between the buyers and sellers has become critical as each can opt to explore a greater number of alternatives than ever before.
E-commerce through Internet, e-mails, websites, and other facilities, enables a businessman to be linked with every corner of the world, and thus opens up greater opportunities in the world market.
Another important factor is the time required for completing a business transaction. As markets are becoming competitive and information is more readily available, a quick, reliable and replicable transaction implies availing of prevailing opportunities. On the contrary, delays in processing a transaction might become synonymous to wasting an opportunity.
Therefore, a fast and alternative mechanism of communication, contract, and payment is an integral part of a globally competitive business organization. How important or relevant is ecommerce to the economy of Bangladesh – a developing economy – in general and to the export market in particular?
The Information Technology (IT) revolution has been too phenomenal to predict its future growth and its use in an economy like Bangladesh’s. In the light of the recent spate of globalization and the initiation of the World Trade Organization (WTO), assessing the immediate and short or medium term relevance of e-commerce to Bangladesh becomes imperative.
Objective of the study:
E-commerce has been shaking and shaping the business environment and breaking out new ways of doing business. It facilitates the very process of international transaction; this involves securing and finalizing a contract, delivery of the product, and finally payment for performance of the contract. The movement of goods and services, as well as the payment mechanisms within a country and more so outside a country, are governed by regulatory and legal issues. Hence, the regulatory environment is at the core of e-commerce development.
Thus it has become imperative to analyze the environmental elements, which will actively govern the implementation of e-commerce in Bangladesh. This paper aims to highlight the status, statutes, potential and constraints of e-commerce development in Bangladesh. Both the statutory laws as well as the challenges in implementing them will be attempted. Thus the objectives of the study are following
- Analyze the present environmental forces to judge whether e-commerce could successfully be implemented in Bangladesh.
- Potential customer.
- Suggest any improvement as required.
Dimension & Existing Situation of E-Commerce in Bangladesh:
Dimension of E-Commerce:
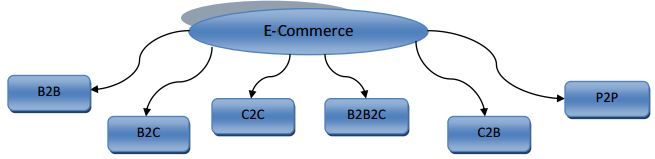
- Existing Situation in Bangladesh:
Internet services are presently available in Bangladesh. Its usage for e-commerce by the Bangladeshi producers to export as well as to access inputs will be dependent on their willingness and ability to use this medium as well as that of the buyers of final products and the sellers of intermediate goods and services.
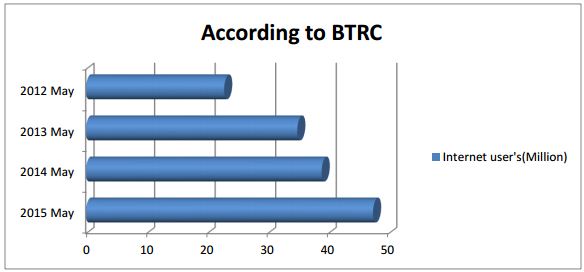
E-Commerce is just evolving in recent days, but the ball has been set rolling for an Internet revolution. E-commerce is no longer a luxury but a reality. Now, it is estimated that more than 180 ISP’s have been working in this country and according to BTRC 2015 may 47.421 million Internet users in the country. So, there is a vast chance for the expansion of ecommerce in Bangladesh. The usage of computer in Bangladesh is very low according to total population. Beside the speed of the Internet is very slow as the necessary advancement of telecommunication infrastructure is not in place. Bangladesh is recently connected to the rest of the world over a fibre-optic backbone. Before that ISPs in Bangladesh are providing Internet services via VSATs from Singapore. In Bangladesh, some companies/vendors have already started their business through E-Commerce, and they achieved some success.
- Existing Situation all over the world:
The worldwide expansion of the internet has considerably contributed to the transformation of trade and store transactions. E-commerce, or electronic commerce, largely means buying and/or selling products through the internet and is commonly associated with online shopping.
Ecommerce also makes use of regular technological maintenance to ensure the smooth functioning of online store sites, monetary transactions, as well as everything to do with providing and delivering products. E-commerce statistics confirm the explosive pace at which this industry has developed as worldwide amounted to more than 1.2 trillion US dollars in 2013. There are several different types of e-commerce, the most prevalent being B2B (business tobusiness), B2C (business-to-consumer) and C2C (consumer-to-consumer) e-commerce. Furthermore, mobile commerce in the shape of buying and selling goods and content via mobile devices such as Smartphone’s is also on the rise.
Current e-commerce statistics state that 40 percent of worldwide internet users have bought products or goods online via desktop, mobile, tablet or other online devices. This amounts to more than 1 billion online buyers and is projected to continuously grow.
According to popular e-commerce market data, US-founded Amazon is one of the leading ecommerce platforms worldwide. Asian competitors such as Rakuten or Alibaba are also constantly expanding their share within the B2C e-commerce market. Online auction website eBay is the most popular example for C2C e-commerce whilst also providing a platform for merchants to sell their goods.
Mobile commerce growth is another exciting trend to watch in terms of e-commerce statistics, considering the popularity and widespread use of smart phones and growing usage of tablets. In 2013, revenue amounted to more than 38 billion US dollars. This type of e-commerce includes mobile media and content, retail services, travel purchases and various other services.
Digital payments are also closely connected to e-commerce. Alternative payment methods such as digital wallets or online payment providers have seen increased adoption rates and rapid growth in the past few years. EBay-owned PayPal is one of the current market leaders with more than 14 billion US dollars in mobile payment volume alone. Digital payments are not only convenient for the mobile shopping experience but also for the increasingly available paid digital content like streaming music, online video subscriptions and apps. For example, global mobile app revenues are projected to surpass 30 billion US dollars in the coming year.
Supportive Framework:
Search Engine Optimization:
Search engine optimization is often about making small modifications to parts of your website. When viewed individually, these changes might seem like incremental improvements, but when combined with other optimizations, they could have a noticeable impact on your site’s user experience and performance in organic search results. You’re likely already familiar with many of the topics in this guide, because they’re essential ingredients for any web page, but you may not be making the most out of them.
- Create unique, accurate page titles:
A title tag tells both users and search engines what the topic of a particular page is. The title tag should be placed within the head tag of the HTML document. Ideally, you should create a unique title for each page on your site.
- Using “Meta Tag”:
A page’s description Meta tag gives Google and other search engines a summary of what the page is about. Whereas a page’s title may be a few words or a phrase, a page’s description Meta tag might be a sentence or two or a short paragraph. Google Webmaster Tools provides a handy content analysis section that’ll tell you about any description Meta tags that are either too short, long, or duplicated too many times Description Meta tags is important because Google might use them as snippets for your pages. Note that we say “might” because Google may choose to use a relevant section of your page’s visible text if it does a good job of matching up with a user’s query. Alternatively, Google might use your site’s description in the Open Directory Project if your site is listed there. Adding description Meta tags to each of your pages is always a good practice in case Google cannot find a good selection of text to use in the snippet.
- URL Structure Improvement:
Creating descriptive categories and filenames for the documents on your website can not only help you keep your site better organized, but it could also lead to better crawling of your documents by search engines. Also, it can create easier, “friendlier” URLs for those that want to link to your content. Visitors may be intimidated by extremely long and cryptic URLs that contain few recognizable words. URLs like can be confusing and unfriendly. Users would have a hard time reciting the URL from memory or creating a link to it. Also, users may believe that a portion of the URL is unnecessary, especially if the URL shows many unrecognizable parameters. They might leave off a part, breaking the link. Lastly, remember that the URL to a document is displayed as part of a search result in Google, below the document’s title and snippet.
- Easier Navigation:
The navigation of a website is important in helping visitors quickly find the content they want. It can also help search engines understand what content the webmaster thinks is important. Although Google’s search results are provided at a page level, Google also likes to have a sense of what role a page plays in the bigger picture of the site. All sites have a home or “root” page, which is usually the most frequented page on the site and the starting place of navigation for many visitors. Unless your site has only a handful of pages, you should think about how visitors will go from a general page to a page containing more specific content
- Quality Content & Services:
Creating compelling and useful content will likely influence your website more than any of the other factors discussed here. Users know good content when they see it and will likely want to direct other users to it. This could be through blog posts, social media services, email, forums, or other means. Organic or word-of-mouth buzz is what helps build your site’s reputation with both users and Google, and it rarely comes without quality content.
- Use Heading Tags Appropriately:
Heading tags are used to present structure on the page to users. There are six sizes of heading tags, beginning with “h1”, the most important, and ending with “h6”, the least important.
- Mobile Users:
One of the most common problems for webmasters who run both mobile and desktop versions of a site is that the mobile version of the site appears for users on a desktop computer, or that the desktop version of the site appears when someone accesses it on a mobile device. In dealing with this scenario a website owner have two options.
Redirect mobile users to correct versions or switch content based on user agent.
Electronic Storefront:
Ecommerce has allowed firms to establish a market presence, or to enhance an existing market position, by providing a cheaper and more efficient distribution chain for their products or services. One example of a firm that has successfully used ecommerce is Target.
This mass retailer not only has physical stores, but also has an online store.
An electronic storefront is an e-commerce solution for merchants who want to host a website that advertises their products or services and for which consumer transactions are generated online. Various software applications are available to merchants, which range from electronic shopping carts to secure payment gateways. Merchants that lack e-commerce technical skills find that storefront vendors are especially helpful when starting out or maintaining their online stores.
Components of electronic Storefront:
- Electronic catalog
- Search engine
- Electronic cart
- E-Auction facilities
- Payment gateway
Revenue Model:
- Advertising revenue model
Revenues are generated from advertisers in exchange for advertisements. This is an indirect revenue model.
Typically, fees are generated from advertisers in exchange for advertisements, which is ultimately the classic principal among the revenue models besides sales. Even if representatives of major media companies complain about earning less money with online advertising than with advertising in print or TV, the figures indicate steadily rising revenues.
The advertising revenue model is based on contacts making it one of the indirect sources of revenue. The conventional version is display-marketing – for example wallpaper, super banner, rectangle, and skyscraper. This is paid according to traffic (invoice per CPC/cost-per-click or CPX/cost-per-action). The main online advertising variations are besides display-marketing, affiliate-marketing (advertising on many websites, CPX) and search-engine-marketing (CPC). Special models are e-mail-marketing and social-media marketing. Red box is an example of advertising revenue model.
- Subscription revenue model
User charges a periodic fee to subscribe to a service or product. For example www.bikroy.com . In this website sell their product. In order to gain more customers user have to subscribe with a nominal fee. When a particular customer will look for that particular product that users product will show up first with a tagline “Top Ads”.
- Transaction fee revenue model
In this model a company receives commission based on the volume for enabling or executing transactions. A company receives commissions based on volume for enabling or executing transactions. The revenue is generated through transaction fees by the customer paying a fee for a transaction to the operator of a platform. The company is a market place operator providing the customer with a platform to place his transactions.
During this process the customer may be presented as a buyer as well as a seller. To actively participate in this e-market, customers must register, so both parties of a transaction taking place are identified. From a business perspective, the offer is determined by others as customers offer their goods online and are acting as sellers. The amount of the transaction fee can be both – fixed and percentage calculated. For example it could be “BKash”. In our country most of the e-tailor uses Bkash for transaction. If an e-tailor asks Bkash for a commission then it’s a transaction revenue model.
- Sales revenue model
A company derives revenue by selling information, goods or services. E-trailer, live shopping, shopping clubs uses this revenue model. www.kaymu.com sales goods and services in order to generate revenue.
- Affiliate revenue model
A company steers business to an affiliate and receives a referral fee or percentage of the revenue from any resulting sales. E-trailer, e-malls are appropriate for this revenue model.
The affiliate program is an online distribution solution which is based on the principle of commission. Merchants advertise and sell their products and services through links to partner-websites. It is a pay-for-performance model: Commissions are only paid for actual revenue or measurable success. An affiliate-link includes a code, which identifies the affiliate. That’s how clicks, leads or sales are tracked. The affiliate therefore acts as the interface between merchants and customers. This model leads to a win-win situation: the merchants sell their products or services and the affiliates get their commissions.
Variations include banner exchange, pay-per-click and revenue sharing programs. The affiliate model is well-suited for the web and therefore very popular. For example www.amazon.com
- Other
Different revenue models are appropriate for different types of product and business.
Therefore the revenue models must be adjusted based on the needs of the customers and the business plan. There is also other revenue model as well and they are Sponsoring, content syndication, and data mining. http://www.bbs.gov.bd/ uses data mining revenue model. They research the market and create statistics based on that analysis and lastly they sell the information to a third party.
Cyber Law:
Bangladesh plans for strict cyber-crime laws Bangladesh is planning stringent measures to fight cyber-crime amid the rapid expansion of the information and communications technology and telecommunications networks in the South Asian country. Bangladesh’s ICT industry has been expanding exponentially and is making its presence strongly felt both in the public and private sectors. MM Neazuddin, Joint Secretary to the Science and ICT Ministry said that the government, which has pledged a “Digital Bangladesh” by the year 2021, had approved in principle to amend previous legislation calling for jail terms and heavy financial penalties to tackle new forms of crime. The proposed law has suggested provisions for a maximum 10 years in jail and taka 10 million (US$150, 000) in fines for hacking into computer networks and putting false and libelous information or indecent material online. For the speedy and effective prosecution of the offences, the government will consult with the Supreme Court to set up one or more Cyber Tribunals. The Penal code of Bangladesh contains very few provisions regarding cybersquatting. But in case of cybercrime like Hacking, Internet time thefts, Email bombing- there is nothing contained in our penal code. So it can be said that it is not possible for our government to control cyber-crime by using some provision of the penal code. To controlled cyber-crime it is necessary to enact special law which only deals with cyber related matters. The Government of Bangladesh passed Information Technology Act on 2006. This is the most recent statute enacted by the government of Bangladesh with a view to consolidate Computer related matters and also prosecute computer and computer network related Offence. This statute contains several provisions regarding damage to computer and computer system. Cybercrime dictates that prohibits attacks or unauthorized access to computers and computer systems. According to Section 66 of the ICT Act provides Punishment for tampering with computer source documents. Section 66 says whoever intentionally destroys or alters or intentionally or knowingly causes any other person to conceal, destroy or alter any computer source code used for a computer, computer program, computer system or computer network, shall be punishable with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to three years, or with fine which may extend to Taka two lakhs, or with both. Section 67 Hacking with computer system. Whoever, with the intent to cause or knowing that he is likely to cause wrongful loss or damages to the public or any other person, does any act and thereby destroys, deletes or alters any information residing in a computer resource or diminishes its value or utility or affects it injuriously by any means, commits the offence of “hacking”.
Section 68 of the ICT Act provides punishments for the hackers. Section 68 says that whoever commits hacking shall be punished with imprisonment for a term which may extend to three years or with fine which may extend to taka two lakhs or with both. But the problem of this act is this act deals with so many things. The act is made to cover all the information technology related matters. But it is not possible to cover all the things by implementing just only one act. In order to control cyber-crime we need to have one specific cyber law in our country.
E-Marketing in Bangladesh
Green And Red
Green & Red Technologies (G&R) was formed in late 2009 with a view to injecting some much needed life into the internet space in Bangladesh. As one of Bangladesh’s dedicated online media groups, G&R set out to build web-based technology and solutions that would enable a sustainable online ecosystem.
G&R started out initially by launching a consumer facing website, “GoromCha” in January 2010. The aim for “GoromCha” was to connect internet users with information about their local areas. The site is currently going through a major overhaul and will look to re-launch in 2014. In June 2011 G&R launched the G&R Ad Network, the first and leading online display advertising network in Bangladesh. Internet advertising provides marketers with an ideal solution to reach their target audience in a cost-effective manner. Most importantly, it also provides the necessary metrics to be able to track ROI. Typically, reaching a Bangladeshi audience online has been a painstaking and unrewarding task. Not only have publishers been unable to provide accurate, timely reporting, the price of running campaigns for advertisers has been high, resulting in little or no visible ROI.
The G&R Ad Network has changed all of that. This platform is G&R’s flagship product and the team is determined to help local publishers better monetize their websites and for advertisers to enhance their reach online.
G&R’s mission is to make the internet more meaningful in Bangladesh – for consumers, website owners and advertisers. We aim to achieve this by constantly striving to be innovative, embracing the unconventional and applying a highly data-driven approach.
E-Marketing supportive Framework:
i) AD Code: ad code is the HTML that is placed on any page of a publisher website that allows ads to be shown on that page in a specific ad layout format.
ii) AD Auction: ad auction happens when you have one ad space and mutiple ad campaigns competing to be served in that ad space. The auction has a couple rules that define the winner – CTR and CPM/CPC.
iii) Banner AD: A banner ad is a form of online advertising. It entails embedding an advertisement onto a webpage. Banner ads come in different shapes and sizes, but all are meant to increase brand awareness or drive traffic to a specific website.
iv) Bounce Rate: Bounce Rate is the percentage of visitors to a particular website who navigate away from the site after viewing only one page.
Bounce rate is important to monitor because it helps you know how engaging your website is for visitors. If you Bounce Rate is high – over 50% – you know that your site (or specific pages) need to be edited and optimized.
v) Click through Conversation: Click Through Conversion happens when a customer clicks on an ad and then makes a conversion on the website that the ad links to.
vi) Display Network: A Display Network is a network of sites on which ads can be served.
vii) Fill Rate: Fill Rate refers to the rate at which we were successfully able to serve ads on a given website. This is also sometimes called Sell Through Rate.
viii) Frequency Capping: This describes the process of using cookies to track the impression count of ads served and stops any given ad being shown to a single visitor more than a set number of times.
- Frequency: Frequency refers to the number of times a visitor to a website/network is shown a single AD.
- Unique User: Unique users refer to the number of people who visit a site for the first time.
- VIEW-THROUGH-CONVERSION: A View-Through-Conversion happens when a customer views an ad, but does not click it at that moment. Later, they visit your site and complete a conversion.
Social Media Marketing:
Social media marketing (SMM) is a form of Internet marketing that utilizes social networking websites as a marketing tool. The goal of SMM is to produce content that users will share with their social network to help a company increase brand exposure and broaden customer reach.
To promote your business or products or services ‘Social Media Marketing’ method is the smartest way in this age of technology. There are so many sophisticated audiences in front of this social media and the number is very large.
Dell, Intel, FedEx, Comcast, and CISCO even a huge number of the popular companies are building their social media marketing strategy and they are getting a good result. But in our Bangladesh its right that rich-media (Internet, Computer) is not available to use for all. After that there is a large and active communities are involving with Social Media.995,560 of total number of people are involved with Internet and approx. 83% of them are using social media.
So it’s not a small deal. Actually in this way one sentence can change your though. That is “People will bring and send you others, Easy to going most of the audience”.
In Bangladesh this social media strategy is not being practiced. But we should. We think we should think globally. Most of our country’s largest companies are not using social media. But yes of course social media is a very strong tool to reach to the audience within short time and short investment.
E-mail Marketing:
E-mail marketing refers the promotion of products or services via email. Email is a very versatile medium. Formats range from simple text to HTML & rich media. Content can be one-size-fitsall or highly customized. Frequency can consist of fixed, frequent intervals or sporadic intervals, with transmissions occurring only when something newsworthy comes along. Sophistication (and cost) can be very low or very high.
Along with the power of email comes the abuse of email, commonly known as spam. Is spam email considered marketing? Technically, the answer is probably yes, but it is certainly not responsible email marketing. While some users fail to distinguish between permission marketing and email spam, spam is actually a major threat to legitimate email marketers, as a glut of messages could make the entire email medium less effective. In Bangladesh “Zaman IT” provides e-mail marketing service.
- Quick response & quick delivery.
- Lowest cost and highest benefit.
- Directly reach to the targeted people.
- Website address and email address can be linked directly.
- Advertising space is not a issue. You can use unlimited space for advertisement.
- You can use both picture and text. Beside this, you can use feedback form in email
- You can increase your sells by email marketing. Beside this your company gets a brand position.
- Email will delivered by using your company email. So you will get any kind of reply in your email from clients.
Major Constraints to E-Commerce
Many of these constraints are endemic across the business sector and demands major reforms through strong political commitment and ability to implement policy changes. A list of specific constraints to e-commerce that policy makers can address in the short and medium term is summarized below.
- Absence of a strong independent regulatory body for the telecommunication sector.
- Absence of encryption law that precludes acceptance of digital signature.
- Strong dependence of Letter of Credit to conduct international transactions.
- Non-issuance of international credit cards for cross border transactions.
- Interest rate ceiling on export loans.
Conclusion:
Despite being a poor country, selected segments of the Bangladeshi business community has embraced technology with reasonable success. The Facsimile in the 1980’s and mobile telephones in the 1990’s popularized modern technology in the mass market. Personal computers and the Internet are also emerging as day-to-day business tools. These positive indicators are favoring the prospects of e-commerce in Bangladesh.
The focus of this paper was on the current state of the regulatory environment in the financial and technological sectors of Bangladesh. Necessary reforms in order to introduce e-commerce have also been suggested. Lack of awareness among the policymakers has been identified as the major deterrent to introducing e-commerce. Conventional understanding of payment mechanisms raises false alarms against the flight of capital if e-commerce is implemented. Synergy between telecommunications and information technology has the proven capability of monitoring and administering the real-time transactions. Therefore, liberalizing the telecom and IT sectors as well as reforming the country’s financial and commercial procedures is the preconditions of successfully implementing ecommerce in Bangladesh. In the case of marketing, simply having a website in the vast sea of the Internet is not sufficient. Uniformity is an important factor in the commencing of contracts through the Internet. Therefore, to take advantage of the newer opportunities that IT development presents, the Bangladeshi companies have to attain internationally accepted certification on quality control, competitive price and timely delivery.
This paper presents possible e-commerce application in the RMG sector. Availing of the IT technology by the RMG as well as other export-oriented industries is likely to become a necessity (because of international demands and expectations) rather than a choice. Banks, customs and other supporting institutions, along with the entrepreneurs exporting goods and services, will have to accommodate the external demands in order to maintain competitiveness and open new global opportunities. Creating awareness among the Bangladeshi exporters regarding e-commerce is essential. They have to be knowledgeable to appreciate and to utilize the benefits of IT. The exporters are not required to acquire operating knowledge on IT. Their understanding on the cost-benefit aspects followed by adopting e-commerce would be an achievement. Business associations can play a major part at this juncture by highlighting the benefits of IT to its members, and encouraging them to use customized software for their day-today operations.
The overview of the legal and regulatory statutes suggests that Bangladesh has made significant progress in facing the challenge of globalization and concurrently, embracing e-commerce in due course. Technological and infrastructural constraints to e-commerce can be overcome if existing laws and regulations are implemented. A better understanding of the potential benefits of ecommerce by the policy makers and bureaucrats is essential for speedy implementation and further reforms.