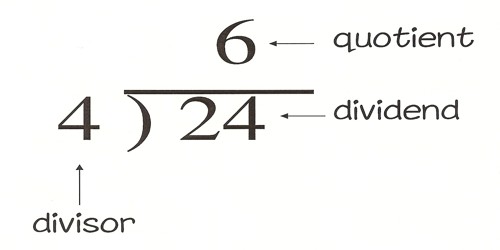Division Algorithm
The dividend is the number we are dividing into. The divisor is the number we are dividing by and the quotient is the answer. A division algorithm is an algorithm which, given two integers N and D, computes their quotient and/or remainder, the result of division.
We know that: Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
Thus, if the polynomial f(x) is divided by the polynomial g(x), and the quotient is q(x) and the remainder is r(x) then
f(x) = g(x) . q(x) + r(x).
Clearly, if the polynomial f(x) is divided by (x – γ), and the quotient q(x) while the remainder is r the
f(x) = (x – γ) . q(x) + r.
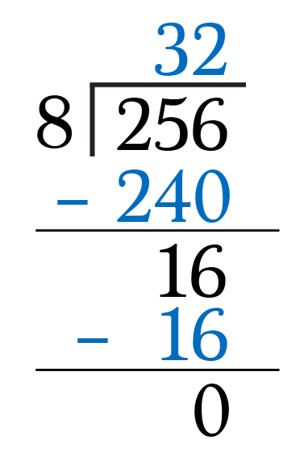
Division algorithms fall into two main categories: slow division and fast division. Slow division algorithms produce one digit of the final quotient per iteration. Examples of slow division include restoring, non-performing restoring, non-restoring, and SRT division.
The Division Algorithm for Integers
The division algorithm for integers states that given any two integers a and b, with b > 0, we can find integers q and r such that 0 < r < b and a = bq + r.
The numbers q and r should be thought of as the quotient and remainder that result when b is divided into a. Of course the remainder r is non-negative and is always less that the divisor, b.
Examples:
- If a = 9 and b = 2, then q = 4 and r = 1.
- If a = 12 and b = 17, then q = 0 and r = 12.
- If a = -17 and b = 3, then q = -6 and r = 1.
- If a = 18 and b = 6, then q = 3 and r = 0.
Division Algorithm for Polynomials
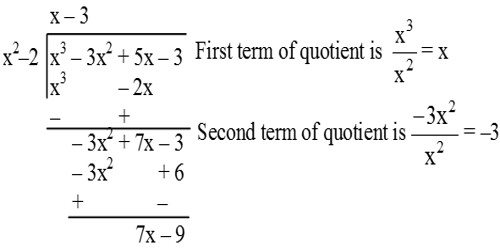
If p(x) and g(x) are any two polynomials with
g(x) ≠ 0, then we can find polynomials q(x) and r(x) such that
p(x) = q(x) × g(x) + r(x)
where r(x) = 0 or degree of r(x) < degree of g(x).
The result is called Division Algorithm for polynomials.
Dividend = Quotient × Divisor + Remainder
Information Source: