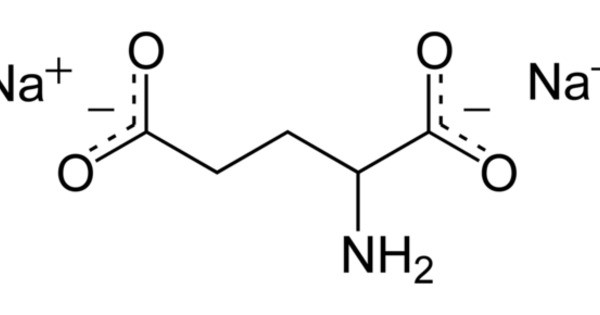
Disodium glutamate, abbreviated DSG, (Na2C5H7NO4) is a sodium salt of glutamic acid. It is used as a flavoring agent to impart umami flavor. It is more commonly known as monosodium glutamate (MSG) when referring to its food additive form, is a sodium salt of glutamic acid, an amino acid naturally found in many foods. It enhances flavor by stimulating umami taste receptors, giving food a savory taste.
Disodium glutamate appears as a white, crystalline powder and is highly soluble in water. It is widely used in processed foods, canned soups, snacks, and Asian cuisine. Though generally recognized as safe by food authorities like the FDA and WHO, some individuals report sensitivity symptoms, often called “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome,” including headaches or nausea. However, scientific evidence has not conclusively linked MSG to serious health issues.
Formation
Disodium glutamate can be produced by neutralizing glutamic acid with two molar equivalents of sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Properties
- Chemical formula: C5H7NNa2O4
- Molar mass: 191.09 g/mol
- Appearance: white crystalline powder
- Odor: practically odorless
- Boiling point: 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) (decomposes)
- Solubility in water: 73.9 g/100 mL (25 °C)
- Solubility: sparingly soluble in alcohol
- Acidity (pKa): 6.8
Natural Occurrence
- In Nature: While glutamic acid occurs abundantly in nature (e.g., in tomatoes, seaweed, cheese, and meats), disodium glutamate does not occur naturally in significant quantities. It is a synthetic compound made for specific uses in food or chemical processes.
- In Biological Systems: Disodium glutamate may transiently form in highly alkaline environments or in laboratory settings, but it’s not a common biological form of glutamate.
Synthesis
Produced by neutralizing glutamic acid with two equivalents of sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Example reaction:
C₅H₉NO₄+2NaOH→C₅H₇NO₄Na₂+2H
Uses
- Food Industry: Rarely used compared to MSG. MSG is the more stable and palatable salt for culinary use.
- Industrial or Research Applications: Sometimes used in biochemical research for studying glutamate transport or as a reagent in specific buffer solutions.
Safety and Regulation
- Similar safety profile to MSG.
- Not commonly listed as a food additive under that name — may appear in certain buffer formulations or niche industrial processes.