Different Activities in Risk Management Division of Bank Asia Limited
Last Four Years(2009-2012) Financial Performance of Credit Department
This report aims toward providing an overview on Credit Department, Risk Management & Performance Analysis of Bank ASIA Ltd. While preparing this report it has been tried to reveal the insights of the Credit Department, Risk Management & Performance Analysis of the bank a few recommendations and suggestions were also prescribed based on the observation and findings.
The Bank Asia Ltd. is a private commercial bank which is operated by the Banking Companies Act 1991. It was established in 1999 with a view to providing financial assistance including all kinds of banking facilities to accelerate the pace of development to small industry of Bangladesh. As a broad policy objective in respect of small industry financing the Bank undertakes the following tasks: extends financial assistance to small industries in private sector, financial assistance to micro-enterprises and collaborates with other institution engaged in financing and developing such enterprises.
The aim of this paper is to analyze Credit Department, Risk Management & Performance Analysis of Bank Asia Ltd. to make it more competitive in the banking industry with a view to how to counter the ensuing challenges in the industry as a consequence of changing global business nature and technological development. For this purpose, business philosophy, mission, objectives, activities and current strategies of Bank Asia Limited are analyzed at the initial stage. Finally, identifying the shortcomings of strategies Bank Asia is currently applying an attempt has been made to recommend the strategic options for Bank Asia to become more competitive in the banking industry.
Introduction
Bank Asia has been launched by a group of successful entrepreneurs with recognized standing in the society. The management of the Bank consists of a team led by senior bankers with decades of experience in national and international markets. The senior management team is ably supported by a group of professionals many of whom have exposure in the international market.
It set milestone by acquiring the business operations of the Bank of Nova Scotia in Dhaka, first in the banking history of Bangladesh. It again repeated the performance by acquiring the Bangladesh operations of Muslim Commercial Bank Ltd. (MCB), a Pakistani bank.
In the year 2003 the Bank again came to the limelight with oversubscription of the Initial Public Offering of the shares of the Bank, which was a record (55 times) in our capital market’s history and its shares commands respectable premium. The asset and liability growth has been remarkable. Bank Asia has been actively participating in the local money market as well as foreign currency market without exposing the Bank to vulnerable positions. The Bank’s investment in Treasury Bills and other securities went up noticeably opening up opportunities for enhancing income in the context of a regime of gradual interest rate decline.
Bank Asia Limited started its service with a vision to serve people with modern and innovative banking products and services at affordable charge. Being parallel to the cutting edge technology the Bank is offering online banking with added delivery channels like ATM, Tele-banking, SMS and Net Banking. And as part of the bank’s commitment to provide all modern and value added banking service in keeping with the very best standard in a globalize world.
Vision
Bank Asia’s vision is to have a poverty free Bangladesh in course of a generation in the new millennium, reflecting the national dream. Our vision is to build a society where human dignity and human rights receive the highest consideration along with reduction of poverty.
Mission
- To assist in bringing high quality service to our customers and to participate in the growth and expansion of our national economy.
- To set high standards of integrity and bring total satisfaction to our clients, shareholders and employees.
- To become the most sought after Bank in the country, rendering technology driven innovative services by our dedicated team of professionals.
Core Values
- Place customer interest and satisfaction as first priority and provide customized banking products and services.
- Value addition to the stakeholders through attaining excellence in banking operation.
- Maintain high ethical standard and transparency in dealings.
- Be a compliant institution through adhering to all regulatory requirements.
- Contribute significantly for the betterment of society.
- Ensure higher degree of motivation and dignified working environment for our human capital and respect optimal work-life balance.
- Committed to protect the environment and go green.
Project Part
Introduction
Bank Asia is one of the recognized private commercial bank in Bangladesh within a short period of time after its operations began it has created an image in the banking sector in spite of existing numerous rivals. From the beginning till now Bank Asia is strongly committed to provide a better quality service to the customer and at a time the authority is providing an excellent facility to the employees. Here at Bank Asia I started my internship from the 8th
- General banking of May. This is the first time I am working in a professional environment, and I didn’t find it difficult to adjust. Through this internship program I have got to learn a lot in the banking sector, about the professional life, etc. The Bank contains three departments at a time.
- Credit department
- Foreign exchange
Credit Department
Bank’s basic work is to create a channel through depositing money from the surplus unit and provide funding to borrowers with productive investment opportunities. Thus the necessity of credit and loan department in bank occurs. Credit is the most important department of a bank. The money mobilized from ultimate surplus units are allocated through this department to the ultimate deficit unit (borrower). The success of this department keeps a great influence over the profit of a bank. Failure of this department may lead the bank to huge losses or even to bankruptcy.
The Bank implemented the system of credit risk assessment and lending procedures by stricter separation of responsibilities between risk assessment, lending decisions and monitoring functions to improve the quality and soundness of loan portfolio. The Bank recorded an 11.48% growth in advances with a total loans and advances portfolio of BDT 92,329 million at the end of December 2012 compared to BDT 82,820 million at the end of December 2011.
Responsibilities of Credit Risk Management Department
- Review and analysis of credit proposals, sent by the branches and ensuring that all the elements of the credit application, analysis, statement, reports are obtained and in order.
- Assessing the Credit Risk Grading (CRG) in order to determine whether to lend or not to lend.
- Preparation of credit proposal using the prescribed format for placing the same before the Credit Committee of the Board/Board of Directors for approval and communicate the decision to the concerned branches.
- To provide advice/assistance regarding all credit matters to Relationship Management.
- To ensure that credit officers/executives have adequate experience and/or training in order to carry out job duties effectively.
- Oversight of the Bank’s credit policies, procedures and control relating to all credit risks.
Credit Administration Department
- To ensure that all security documentation complies with the terms of approval and is enforceable.
- To monitor insurance coverage with a view to ensure appropriate coverage is in place over assets pledged as collateral, and is properly assigned to the bank.
- To control loan disbursement only after all terms and condition of the approval have been met, and all security documentation is in place.
- To monitor borrower’s compliance with covenants and agreed terms and conditions, and general monitoring of account conduct/performance.
- Past due principal or interest payments, past due trade bills, account excesses and breach of loan covenants and covenants breaches or exceptions are referred to CRM Department and the concerned branch for timely follow-up.
- Ensure accurate & timely submission of returns of Corporate Office and Bangladesh Bank.
Legal & Recovery Department
- Directly manage all Substandard, Doubtful & Bad and Loss accounts to maximize recovery.
- Determine Account Action Plan/Recovery Strategy.
- Pursue all options to maximize recovery.
- Ensure that adequate and timely loan provisions are made based on actual and expected losses.
- Maintain liaison with the Bank’s lawyers and follow up the suit for filed cases regularly for early settlement towards recovery of Bank’s dues.
- Reviews of Grade 6 or worse accounts on regular basis.
General Policy Guidelines
The following general policy guidelines govern the implementation of the business strategy of Bank Asia with respect to credit risk:
- Bank Asia makes loan only to eligible and reputable clients who are involved in legitimate business activities and whose income and wealth are derived from legitimate sources.
- Bank Asia encourages lending to society desirable, nationally, important and financially viable sectors and will not lend for unproductive purposes or socially undesired projects.
- At all times a policy of “know your customer” must be foremost in the credit application processing.
- Bank Asia extends credit in its discretion, only to qualified borrowers where the amount and intended purpose or use of proceeds are clear and legitimate and where the amount and use of funds is reasonable in the context of what is known about the particular client and the intended use or purpose.
- Bank Asia requires that borrowers have a source of repayment established at the inception of the credit, and that any exception must be specifically addressed in the approval of credit. There should be identified, whenever possible, a secondary source of repayment. As with any funds received, any and all repayment sources must be legitimate and consistent with what is known and documented about client. Borrowers must provide, and the credit approval package must contain, sufficient information on the borrower, business, & industry to approve the extension of credit. Satisfactory security and collateral is required as appropriate.
- Bank Asia discourages clients with relatively low or no funds of their own i.e. highly leveraged clients, as clients with a relatively high ratio of borrowed to own funds tend to face liquidity problems, with adverse repercussions on their ability to service their obligations.
General Procedure for Loans and Advances
Bank Asia limited follows the general procedure for giving loans and advances as the guideline given by Bangladesh Bank. The general lending procedure is given below:
First Information Sheet (FIS): First information sheet (FIS) is the prescribed from provided by the respective branch that contains basic information of the borrower. It contains following particulars.
- Name of the concern with its factory location, office address and telephone number.
- Name of the main sponsors with their educational qualification
- Business experience of the sponsors, details of past and present business, its achievement and failures, name of ill the concerns wherein the sponsors have involvement.
- Income tax registration no. With the amount of tax paid for the last three years.
- Details of unencumbered assets (movable & immovable) personally owned by the sponsors.
- Details of liabilities with other banks and financial institutions including securities held there against.
- Purpose of loan sought from Bank Asia Limited.
- Estimated cost of the project & means of finance.
Application for Credit Line: After receiving the first information sheet from the borrower Bank official verifies all the information carefully. He also checks the account maintains by the borrower with the Bank. If the official become satisfied then he gives application to the bank prescribe format supplied by the bank called Credit for request limit.
Credit Sanction & Appraisal Process
Borrowers Credit Worthiness Analysis by Bank Asia Limited following 6 “C”s:
The question that must be dealt with before any other whether or not the customer can service the loan that is pay out the loan when due with a comfortable margin of error. This usually involves a detailed study of six aspects of the loan application: character, capacity, cash, collateral, conditions and control. All must be satisfied for the loan to be a good one from the lender’s (Bank Asia Limited) point of view.
- Character: The loan officer must be convinced that the customer has a well defined purpose for requesting credit and a serious intention to pay. Responsibility, truthfulness, clean past record, true purpose and honest intention to repay the loan make up what a loan officer calls character.
- Capacity: The customer requesting credit must have the authority to request such and the legal standing to sign a binding loan agreement.
- Cash: The borrower should have the ability to generate enough cash flow to repay the loan. This cash flow can be generated from sales or income from the sales or income, from the sale of liquidation of assets or funds raised through debt or equity securities.
- Collateral: The borrower must possess adequate net worth or enough quality assets to provide adequate support for the loan. The value of the collateral security must cover the loan exposure.
- Conditions: The recent trend of borrower’s line of work or industry must be taken into considerations by the lender.
- Control: The lender should be careful about whether changes in law regulation could adversely affect the borrower and whether loan request meets the Bank’s and regulatory authority’s standards for loan quality.
Collecting CIB Report from Bangladesh Bank: After receiving the application for credit line, Bank sends a letter to Bangladesh Bank for obtaining a report from there. This report is called CIB (Credit Information Bureau) report. Basically branch seeks this report from the head office for all kinds of loans. The purpose of this report is to being informed that whether the borrower has taken loan from any other bank; if ‘yes’, then whether the party has any overdue amount or not.
Making Credit Proposal (CP): Branch then has to find the right borrower by considering the following 6 C’s. These are character, capital, capacity, cash, collateral, condition (economic). If the branch thinks that the project is feasible then he will prepare a Proposal. Bank prepares the proposal in a specific from called credit proposal. Significance the proposal branch sends it to head office for approval.
Credit Assessment: A thorough credit and risk assessment should be conducted prior to the granting of loans, and at least annually thereafter for all facilities. The results of this assessment should be presented in a credit application that originates from the Relationship Manager, and is recommended by Branch Credit Committee (BCC). The RM should be the owner of the customer relationship, and must be held responsible to ensure the accuracy of the entire credit application submitted for approval. RMs must be familiar with the bank’s Lending Guidelines and should conduct due diligence on new borrowers, principals and guarantors. Credit Applications should summarize the results of the RMs risk assessment and include as a minimum, the following details:
- Amount and type of loan(s) proposed
- Purpose of loans
- Loan structure (Tenor, Covenant, Repayment Schedule, Interest)
- Security arrangements
In addition, the following risk areas are analyzed:
- Borrower analysis
- Industry analysis
- Supplier/ Buyer analysis
- Historical financial analysis
- Projected financial performance
- Account conduct
- Loan structure
- Security
Risk Grading: All Banks should adopt a credit risk grading system. The system should define the risk profile of borrower’s to ensure that account management, structure and pricing are commensurate with the risk involved. Risk grading is a key measurement of a Bank’s asset quality, and as such, it is essential that grading is a robust process. All facilities should be assigned a risk grade. Where deterioration in risk is noted, the Risk Grade assigned to a borrower and its facilities should be immediately changed. Borrower Risk Grades should be clearly stated on Credit Applications.
Project Appraisal: It is the pre-investment analysis done by the officer before approval of the project. Project appraisal in the banking sector is needed for the following reasons:
- To justify the soundness of an investment
- To ensure repayment of bank finance
- To achieve organizational goals
- To recommend if the project is not designed properly
Head Office Approval: The respective officer of Head Office appraises the project by preparing a summary named “Top Sheet” or “Executive Summary”. Then he sends it to the Head Office Credit Committee (HOCC) for the approval of the loan. The Head Office Credit Committee (HOCC) considers the proposal and takes decision whether to approve the loan or not. If the loan is approved by the HOCC, the HO sends the approval to the concerned branch with some conditions. These are like.
- All other terms and conditions, as per policy and practice of the bank for such advance to safeguard the banker’s interest shall also be applicable for this sanction also.
- Branch shall not exceed the sanctioned limit.
- Required charge documents with duly stamped should be obtained.
- Drawing shall be allowed only after completion of mortgage formalities and other security arrangement.
Sanction Letter: After getting the approval from the HO, the branch issues the sanction letter to the borrower. The borrower receives the letter and returns a copy of this letter duly signed by him as a token of having understood and acceptance of the terms and condition above.
Documentation of Loans and Advances: In spite of the fact that banker lends credit to a borrower after inquiring about the character, capacity and capital of the borrower, he must obtain proper documents executed from the borrower to protect him against willful defaults. Moreover, when money is lent against some security of some assets, the document must be executed in order to give the banker a legal and binding charge against those assets. Documents contain the precise terms of granting loans and they serve as important evidence in the law courts if the circumstances so desire. That is why all approval procedure and proper documentation shall be completed before the disbursement of the facilities.
Disbursement: After verifying all the documents the branch disburses the loan to the borrower. A loan repayment schedule is also prepared by the bank and given to the borrower.
Follow-up: After the disbursement of the loan bank officials time to time monitor the loan by physical observation of the activities of the party. It is done in the following manner.
- Constant supervision
- Working capital assessment
- Stock report analysis.
Loan classifications:
Classifications Scale
- Unclassified: Repayment is regular
- Substandard: Repayment is irregular or stopped but has reasonable prospect of improvement.
- Doubtful Debt: Unlikely to be repaid but special collection efforts may result in partial recovery.
- Bad/loss: Very little chance of recovery
Credit Monitoring: Monitoring is a process of taking case of loan cases starts from the selection of the borrower and remains live throughout the life of a loan.
To minimize credit losses, monitoring procedures and systems should be in places that provide an early indication of the deteriorating financial health of a borrower. At a minimum, systems should be in place to report the following exceptions to relevant executives in CRM and RM team:
- Past due principal or interest payments, past due trade bills, account excesses, and breach of loan covenants;
- Loan terms and conditions are monitored, financial statements are received on a regular basis, and any covenant breaches or exceptions are referred to CRM and the RM team for timely follow-up.
- Timely corrective action is taken to address findings of any internal, external or regulator inspection/audit.
All borrower relationships/loan facilities are reviewed and approved through the submission of a Credit Application at least annually. Two possible solutions to minimize the credit loss:
Early Alert Process
Despite a prudent credit approval process, loans may still become troubled. Therefore, it is essential that early identification and prompt reporting of deteriorating credit signs be done to ensure swift action to protect the Bank’s interest.
Credit Recovery
Commercial Banks sanction loan to different categories of borrowers for various purposes. Before sanctioning of loans and advances (short term loan, long term loan) bank appraises a loan proposal and analyze information relating to the borrower and purpose of the loan to determine viability of the loan proposal. If the proposal is found viable and safe for lending, loan is sanctioned and disbursed.
At the time of sanctioning loan, along with all other terms and conditions repayment period and installment is fixed. Recovery of loan starts just after the maturity of grace period. But more exhaustive appraisal of the loan proposal in the pre-sanction stage is not the guarantee to recover the loan money with interest unless a built in system of supervision & follow up is applied and proper treatment is given as and when problem arises.
Risk Management Division
Risk Management Division is one of the core & sensitive division of any bank. The core responsibilities of risk management division includes analysis of relevant aspects of the bank to identify possible risk, assessment of level of severity of identified risk, recommend and ensure implementation of control mechanism and reporting of risk status to board of directors, senior management & respective risk committees. The captioned division is also responsible ensured that capital is allocated adequately based on the actual/ presumed risk exposure. Risk management is important for every bank and also the process or techniques of mitigation of those risks are also necessary.
Basic Risks of Bank Asia Ltd
There are some crucial risks associated with Bank Asia. According to the “First pillar” of “Basel- 1” the “Core Risks” of the bank are –
- Credit Risk.
- Operational Risk.
- Market Risk.
There is also a practice of Basel-2 implication of “Bank Asia’ according to the guideline of “Bangladesh Bank” which is called “The Supervisory Review Process (SRP)”. According to the second pillar of Basel 2 the main risk of “Bank Asia” are-
- Systematic Risk.
- Concentration Risk.
- Strategic Risk.
- Reputational Risk.
- Pension Risk.
- Reputational Risk.
- Liquidity Risk.
- Legal Risk.
Basically I have worked here for particular risks associated with Bank Asia. I worked in Bank Asia for Credit Risk Management, Market Risk Management, & Operational Risk. & I worked for implementation of concentration risk. The main area of risks in which I have worked & learn many things regarding risk management is as follows:
Credit Risk
At the very beginning of joining this bank at first I have to work in “Credit Risk Management Division” There I have learned a lot of things regarding Credit Risk Management. How they give loan to the customer. Basically I was there for sector code allocation of CRM files. And there I have to look after more than 1000 files along with the help of another three interns from different universities. So I must have to know about the procedure of CRM’s regarding giving the loan and the process of avers the risks. The approval process of loan in credit risk management division shows in the credit department.
Market & Liquidity Risk
Definition of ‘Value at Risk: VaR A statistical techniques used to measure and quantify the level of financial risk within a firm or investment portfolio over a specific time frame. Value at risk is used by risk managers in order to measure and control the level of risk which the firm undertakes. The risk manager’s job is to ensure that risks are not taken beyond the level at which the firm can absorb the losses of a probable worst outcome.
Investopedia explains ‘Value at Risk – VaR’ Value at Risk is measured in three variables: the amount of potential loss, the probability of that amount of loss, and the time frame. For example, a financial firm may determine that it has a 5% one month value at risk of $100 million. This means that there is a 5% chance that the firm could lose more than $100 million in any given month.
The Calculation of VAR Requires a Number of Inputs:
- Market value of the position
- Daily volatility of the currencies
- Holding period
- Level of confidence
Market Value of Position
The market value of position, expressed in US Dollars, is the base Point from which expected losses are calculated. In other words, adding or Subtracting (depending on whether the position is long or short) the VAR on a position to the market value will give the worst probable market value of the position.
Daily Volatility
Foreign Exchange volatility is calculated from the daily movements in the foreign exchange rate over a specified historic time period. A key assumption in the calculation of historic volatility is that recent events play a more significant role in determining likely rate movements in the future than events, say that took place a year ago. As a result, recent rate movements are usually given higher weight age in the calculation of volatility. An Alternative method commonly used in the market is to limit the historic period used to calculate volatility, and not apply any weighting. A third method is to use implied volatility i.e. the actual volatility traded in the Market.
Holding Period
The holding period for VAR refers to the liquidity of the position i.e. how long it will take to liquidate the position in terms of number of trading days. The majority of positions (regardless of size) in freely floating currencies should be able to be liquidated within a twenty-four hour period.
Level of Confidence
The level of confidence selected determines the probability and Frequency that there will be a rate movement in excess of the predicted (i.e. VAR) amount.
Market volatility is quoted to one standard deviation, thereby inferring that once in every five trading days the calculated worst probable loss will be exceeded. At two standard deviations, this raised to one in every forty trading days. At three standard deviations this is increased to once in every two hundred days.
Calculation Foreign Exchange VAR
Gross VAR
Gross VAR is calculated as follows, using the inputs discussed above:
Gross VAR = Market value of the position * Daily Volatility * Level of confidence * Holding Period.
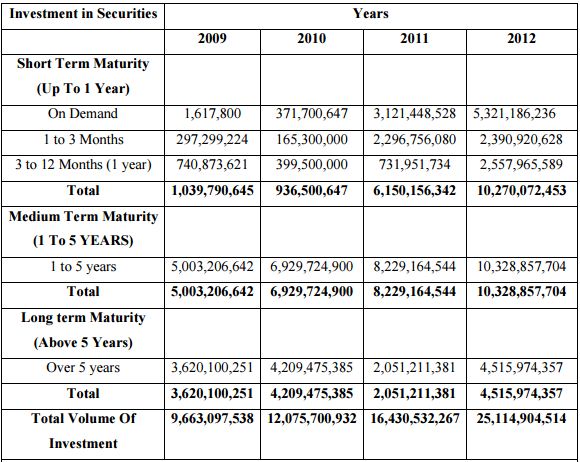
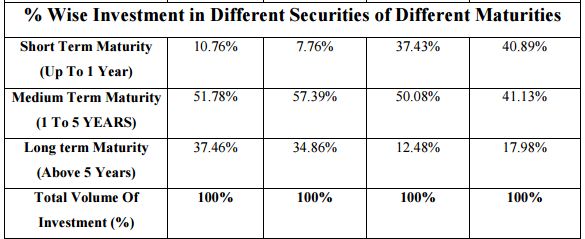
Investment Maturity Strategy & % Wise Investment in Different Securities of Different Maturities
Conclusion
Banking sector in Bangladesh is very much competitive. Along with local banks there are many foreign banks are also operating in Bangladesh. The banking sector seems to be operating satisfactorily with the orientation of an increasing number of banks into the economy. Apart for mobilizing untapped resources, the banks are also creating deposit in the economy. Depending on the value of money multiplier, the advance of one bank generally opens up the prospect of creating additional deposit basis in subsequent generations of bank with the intermediation of funds. I have seen that the major problem in the banking sector can be briefly summarized as directed loans & it is ended up with a large volume on classified loans due to extension of loans without proper security and without following proper banking norms, reflecting largely the reform measures and consequent improvement in the operation of the bank as a whole, classified loans came down to 32 percent recently. Moreover it is obvious that private sector banks are involved with the more resilient portion of the economy.
Bank Asia Ltd. is one of the leading banks in Bangladesh. Risk management division is one of the core divisions in Bank Asia. This division is responsible for identifying the possible risk and also assessment the level of severity of identified risk. This division is trying to averse the mentioned risks by keeping proper documents & also works on some different terms that the other banks are not doing these things recently & rapidly. Risk Management division in Bank Asia is trying to go to a benchmark level with compare with the other banks in Bangladesh & within three months It is obvious that it should reach its desired point or goal.