For a corporation, reserves and provisions are both essential and one does not decrease the value of the other. It is a smart idea, according to business experts, to save some portion of the profit as reserves for the unforeseen future; therefore, businesses build a contingency to meet those events. Stores are what a business would take care of from its benefits for future possibilities and fortifying of the business, while, arrangements are planned to fulfill a foreseen known to use.
The fundamental difference between the provision and the reserve is that net profit is measured only after all provisions are given effect, while reserves are produced only after profit is measured.
Reserves: Reserve is the term that refers to an amount or percentage of profit that a corporation holds or keeps aside to meet potential contingencies that may arise at the end of a financial year. It is used to improve the business as well. Reserves are usually created to fulfill unknown potential obligations that might occur for miscellaneous business reasons. For any of the purposes given, the amount appropriated in the name of the reserves may be used:
- For purchasing an asset in the future.
- To pay the dividends to shareholders consistently year by year.
- For meeting out unexpected contingencies.
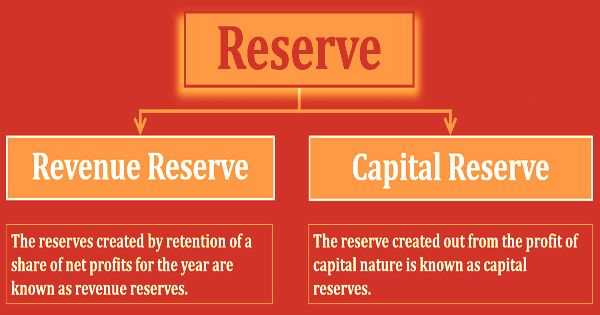
There are two types of reserves in an organization
- Capital Reserve
- Revenue Reserve
Specific reserves are made for specific purposes, as the name implies, and can only be used for that particular purpose. A significant distinction between reserves and provisions is that a provision is often specific; reserves may, however, be generic.
Provision: The provision means that a certain sum of money is kept aside to cover up an anticipated liability resulting from past events. For a corporation, provisions are relevant as they cover such business costs and payments made for them. The fundamental reason to make provisions is to meet perceived future commitments which may emerge because of a particular business reason. Provisions ought not to be viewed as investment funds, as these are made to meet costs for a foreseen risk in the future.
If a provision is made in excess of the amount required, then it must be written back to the profit and loss account after paying off the liability. It appears in the form of expenditures in the income statement. For e.g., questionable debt provision, debtor discount provision, depreciation provision, repair and renewal provision, audit fee provision, taxation provision, etc.
The major differences between Reserves and Provisions are as under:
Reserve:
- Reserves are made to reinforce a company’s financial condition and meet uncertain liabilities & losses.
- For some specific potential use, the reserve is to keep any cash from the profit.
- It provides resources and protections against expenditures from unexpected contingencies for operating the business.
- Reserve management is not important because it is generated according to financial prudence.
- It is possible to use reserves to allocate dividends to shareholders.
- The existence of benefit is required for reserve allocation.
- The liability side of a balance sheet shows reserves.
- Outside industry and known as the Reserve Fund, funds may be invested.
- Reserves can be used outside the organization for investments.
Provision:
- Provisions are created for the execution of a particular obligation or contingency, such as a provision for questionable debts.
- The clause means holding some cash for a known liability that is expected to occur after a certain time.
- This protects the company from costs resulting from established liabilities.
- As per law, the development of provision is required.
- As they are made for a particular responsibility, provisions cannot be used to administer dividends.
- Presence of benefit which is not required for distribution.
- Provisions are excluded from the asset in question when it is generated against an asset while shown on the balance sheet as a liability when it is generated against a liability.
- Unless real liability is less than the amount provided for, provision can never be distributed as a benefit.
- Provision cannot be used for purposes of savings.
The benefit is reduced by both provision and reserves, but the production of provision is a must to cope with the known future cost. The revenue reserve is generated from the income obtained from a business or organization’s core activities. Liabilities must be remembered when and when they occur, which is why arrangements for the same are made.
Information Sources: