This section details fundamental credit risk management policies that are recommended for adoption by all banks in Bangladesh by Bangladesh Bank and EBL’s compliance status with these guidelines. The guidelines outline general principles that are designed to govern the implementation of more detailed lending procedures within individual banks. EBL’s practice regarding general credit risk management has been explained in the following section with their congruence with the regulatory guidelines.
LENDING GUIDELINES:
The bank has its established Credit Policies (“Lending Guidelines”) that clearly outline the senior management’s view of business development priorities and the terms and conditions that should be adhered to in order for loans to be approved. The Lending Guidelines is updated at least annually to reflect changes in the economic outlook and the evolution of the bank’s loan portfolio, and is distributed to all lending/marketing officers. The Lending Guidelines is approved by the Managing Director/CEO & Board of Directors of the bank based on the endorsement of the bank’s Head of Credit Risk Management and the Head of Corporate/Commercial Banking.
Any departure or deviation from the Lending Guidelines is explicitly identified in credit applications and a justification for approval is provided. The Lending Guidelines provides the key foundations for Relationship Managers (RM) to formulate their recommendations for approval, and includes the following:
INDUSTRY AND BUSINESS SEGMENT FOCUS:
The Lending Guidelines clearly identify the business/industry sectors that should constitute the majority of the bank’s loan portfolio. This will provide necessary direction to the bank’s marketing staff.
TYPES OF LOAN FACILITIES:
The type of loans that are permitted is clearly indicated and defined, such as Working Capital, Trade Finance, Term Loan, etc. A full list of EBL credit products for SME and consumer clients has been attached in the appendix.
SINGLE BORROWER/GROUP LIMITS:
In case of single borrower exposure limit the bank strictly follows Bangladesh Bank guidelines. The regulation regarding the stated purpose communicated vide BRPD circular no 5 dated April 09, 2005 is provided below:
“As a result of increase in capital of almost all the banks, now it has been decided to reduce the single borrower exposure limit from 50% to 35%, thus:
The total outstanding financing facilities by a bank to any single person or enterprise or organization of a group shall not at any point of time exceed 35% of the bank’s total capital subject to the condition that the maximum outstanding against fund based financing facilities (funded facilities) do not exceed 15% of the total capital.
Non funded credit facilities e.g. letter of credit, guarantee etc. can be provided to a single large borrower. But under no circumstances, the total amount of the funded and non-funded credit facilities shall exceed 35% of a banks total capital.
However, in case of export sector single borrower exposure limit shall remain unchanged at 50% of the bank’s total capital. But funded facilities in case of export credit shall also not exceed 15% of the total capital.”
DISCOURAGED BUSINESS TYPES:
The BB guideline advices that banks should outline industries or lending activities that are discouraged. As a minimum, the following should be discouraged:
- Military Equipment/Weapons Finance
- Highly Leveraged Transactions
- Finance of Speculative Investments
- Logging, Mineral Extraction/Mining, or other activity that is ethically or environmentally sensitive
- Lending to companies listed on CIB black list or known defaulters
- Counterparties in countries subject to UN sanctions
- Share Lending
- Taking an Equity Stake in Borrowers
- Lending to Holding Companies
- Bridge Loans relying on equity/debt issuance as a source of repayment.
Eastern bank limited follows the guideline and also in addition they have a list of the discouraged business of their own which can not be printed for the sake of confidentiality.
LOAN FACILITY PARAMETERS:
Facility parameters (e.g., maximum size, maximum tenor, and covenant and security requirements) is clearly stated. As a minimum, the following parameters (mentioned in the guideline) is adopted:
- Bank does not grant facilities where the bank’s security position is inferior to that of any other financial institution.
- Assets pledged as security is always properly insured. In fact, EBL ensures 110% insurance on the hypothecated security for a particular facility. The bank also has its own list of insurance companies from which the client can take insurance.
- Valuations of property taken as security is performed prior to loans being granted. Also recognized 3rd party professional valuation firm is appointed to conduct the valuations.
CREDIT ASSESSMENT:
A thorough credit and risk assessment is conducted prior to the granting of loans, and at least annually thereafter for all facilities. The results of this assessment are presented in a Credit Application that originates from the relationship manager/account officer (“RM”), and is approved by Credit Risk Management (CRM). The RM is the owner of the customer relationship, and is held responsible to ensure the accuracy of the entire credit application submitted for approval. RMs are familiar with the bank’s Lending Guidelines and should conduct due diligence on new borrowers, principals, and guarantors.
It is essential that RMs know their customers and conduct due diligence on new borrowers, principals, and guarantors to ensure such parties are in fact who they represent themselves to be. The bank has its established Know Your Customer (KYC) and Money Laundering guidelines which is adhered to at all times.
Credit Applications summarize the results of the RMs risk assessment and include, as a minimum, the following details:
- Amount and type of loan(s) proposed.
- Purpose of loans.
- Loan Structure (Tenor, Covenants, Repayment Schedule, Interest)
- Security Arrangements
In addition, the following risk areas are also addressed:
Borrower Analysis:
The majority shareholders, management team and group or affiliate companies is assessed. Any issues regarding lack of management depth, complicated ownership structures or inter-group transactions are addressed, and risks mitigated.
Industry Analysis:
The key risk factors of the borrower’s industry are assessed by the RM. Any issues regarding the borrower’s position in the industry, overall industry concerns or competitive forces is addressed and the strengths and weaknesses of the borrower relative to its competition should be identified.
Supplier/Buyer Analysis:
Any customer or supplier concentration is reported in the credit application, as these could have a significant impact on the future viability of the borrower.
Historical Financial Analysis:
An analysis of a minimum of 3 years historical financial statements of the borrower is presented in bank’s specified format. The analysis should address the quality and sustainability of earnings, cash flow and the strength of the borrower’s balance sheet. Specifically, cash flow, leverage and profitability must be analyzed.
Adherence to Lending Guidelines:
Credit Applications should clearly state whether or not the proposed application is in compliance with the bank’s Lending Guidelines.
Mitigating Factors :
Mitigating factors for risks identified in the credit assessment is identified and reported in the application.
Loan Structure:
The RM makes sure that the amounts and tenors of proposed financing are justified based on the projected repayment ability and loan purpose. Excessive tenor or amount relative to business needs increases the risk of fund diversion and may adversely impact the borrower’s repayment ability.
Security:
A current valuation of collateral is obtained and the quality and priority of security being proposed is assessed. Loans are not granted based solely on security. Adequacy and the extent of the insurance coverage are also taken into consideration.
Name Lending:
In this case bank also follows the prudential guidelines which says “Credit proposals should not be unduly influenced by an over reliance on the sponsoring principal’s reputation, reported independent means, or their perceived willingness to inject funds into various business enterprises in case of need. These situations should be discouraged and treated with great caution. Rather, credit proposals and the granting of loans should be based on sound fundamentals, supported by a thorough financial and risk analysis”.
APPROVAL AUTHORITY:
The prudential guidelines regarding approval authority by BB is stated below:
“The authority to sanction/approve loans must be clearly delegated to senior credit executives by the Managing Director/CEO & Board based on the executive’s knowledge and experience. Approval authority should be delegated to individual executives and not to committees to ensure accountability in the approval process. The following guidelines should apply in the approval/sanctioning of loans:
- Credit approval authority must be delegated in writing from the MD/CEO & Board (as appropriate), acknowledged by recipients, and records of all delegation retained in CRM.
- Delegated approval authorities must be reviewed annually by MD/CEO/Board.
- The credit approval function should be separate from the marketing/relationship management (RM) function. The role of Credit Committee may be restricted to only review of proposals i.e. recommendations or review of bank’s loan portfolios.
- Approvals must be evidenced in writing, or by electronic signature. Approval records must be kept on file with the Credit Applications. All credit risks must be authorized by executives within the authority limit delegated to them by the MD/CEO. The “pooling” or combining of authority limits should not be permitted.
- Credit approval should be centralized within the CRM function. Regional credit centers may be established, however, all large loans must be approved by the Head of Credit and Risk Management or Managing Director/CEO/Board or delegated Head Office credit executive.
- The aggregate exposure to any borrower or borrowing group must be used to determine the approval authority required.
- Any credit proposal that does not comply with Lending Guidelines, regardless of amount, should be referred to Head Office for Approval
- MD/Head of Credit Risk Management must approve and monitor any cross-border exposure risk.
- Any breaches of lending authority should be reported to MD/CEO, Head of Internal Control, and Head of CRM.
A monthly summary of all new facilities approved, renewed, enhanced, and a list of proposals declined stating reasons thereof should be reported by CRM to the CEO/MD”.
The bank tries to follow the above guidelines as perfectly as possible. The existing approval authority for approving credit proposals is summarized below:
| Type of Credit | Amount | Tenor | Approving Authority |
| Funded/ Non-funded | Up to TK 1.00 Crore | 12 month | Head of CRM |
| Funded/ Non-funded | Up to TK 1.50 Crore | 12 month | Head of CRM & Head of Corporate Banking (jointly) |
| Funded/ Non-funded | Up to TK 3.00 Crore | 12 month | DMD (singly) |
| Funded/ Non-funded | Up to TK 5.00 Crore | 60 month | DMD & MD (jointly) |
| Cash Against Security |
(Class A- EBL FDRs)Up to TK 25.00 Crore60 monthDMD & MD (any one)Cash Against Security
(Class B- FDRs/other bank)Up to TK 10.00 Crore60 monthDMD & MD (any one)Consumer BankingAll products (Exceptions)60 monthDMD & MD (any one)
SEGREGATION OF DUTIES:
EBL segregates the following lending functions:
- Credit Approval/Risk Management
- Relationship Management/Marketing
- Credit Administration
The purpose of the segregation is to improve the knowledge levels and expertise in each department, to impose controls over the disbursement of authorized loan facilities and obtain an objective and independent judgment of credit proposals.
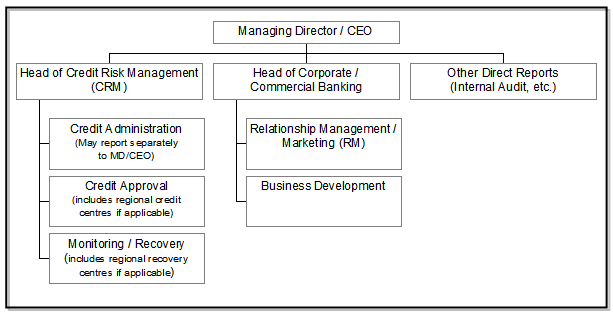
PREFERRED ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE & RESPONSIBILITIES:
The guideline proposes that appropriate organizational structure must be in place to support the adoption of the policies of the guidelines. The key feature is the segregation of the Marketing/Relationship Management function from Approval/Risk Management/Administration functions. It also proposes credit approval should be centralized within the CRM function. Regional credit centers may be established, however, all applications must be approved by the Head of Credit and Risk Management or Managing Director/CEO/Board or delegated Head Office credit executive.
The organizational structure of EBL (credit related) is compared below with that of the BB guideline. EBL ensures that all credit approvals are centralized within the CRM function. There are three regional corporate bases two in Dhaka and the other one in chittagong, however, all applications are submitted to CRM of Dhaka Head office and approved by the Board, MD/DMD or HOCRM as appropriate. For the SME sector, all proposals come to Dhaka SME center and then approved through CRM.The following chart represents the preferred management structure in the BB guideline:
Key Responsibilities:
Key responsibilities of concerned parties as mentioned in the prudential guidelines are discussed below:
Credit Risk Management (CRM):
- Oversight of the bank’s credit policies, procedures and controls relating to all credit risks arising from corporate/commercial/institutional banking, personal banking, & treasury operations.
- Oversight of the bank’s asset quality.
- Directly manage all Substandard, Doubtful & Bad and Loss accounts to maximize recovery and ensure that appropriate and timely loan loss provisions have been made.
- To approve (or decline), within delegated authority, Credit Applications recommended by RM. Where aggregate borrower exposure is in excess of approval limits, to provide recommendation to MD/CEO for approval.
- To provide advice/assistance regarding all credit matters to line management/RMs.
- To ensure that lending executives have adequate experience and/or training in order to carry out job duties effectively.
Credit Administration:
- To ensure that all security documentation complies with the terms of approval and is enforceable.
- To monitor insurance coverage to ensure appropriate coverage is in place over assets pledged as collateral, and is properly assigned to the bank.
- To control loan disbursements only after all terms and conditions of approval have been met, and all security documentation is in place.
- To maintain control over all security documentation.
- To monitor borrower’s compliance with covenants and agreed terms and conditions, and general monitoring of account conduct/performance.
Relationship Management/Marketing (RM):
- To act as the primary bank contact with borrowers.
- To maintain thorough knowledge of borrower’s business and industry through regular contact, factory/warehouse inspections, etc. RMs should proactively monitor the financial performance and account conduct of borrowers.
- To be responsible for the timely and accurate submission of Credit Applications for new proposals and annual reviews,
- To highlight any deterioration in borrower’s financial standing and amend the borrower’s Risk Grade in a timely manner. Changes in Risk Grades should be advised to and approved by CRM.
APPROVAL PROCESS:
The approval process segregates the work of Relationship Management/Marketing from the approving authority. The responsibility for preparing the Credit Application rests with the RM within the corporate/SME banking department. Credit Applications are recommended for approval by the RM team and forwarded to the approval team within CRM and approved by individual executives.
The recommending or approving executives take responsibility for and are held accountable for their recommendations or approval.
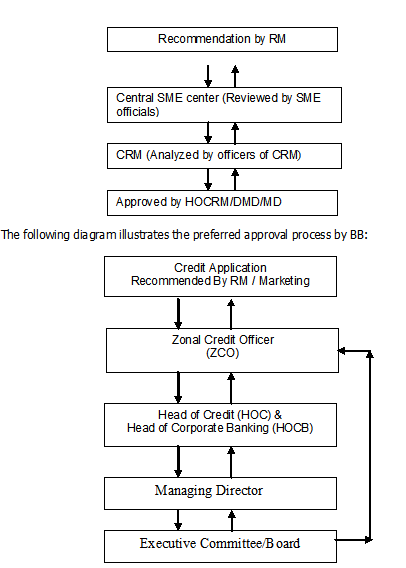
Approving SME proposals:
The RM first sends the credit application to the SME center in Head office Dhaka. The SME center then checks the documents and make sure they are well within the lending guidelines of the bank. They also provide additional condition for sanction as appropriate. After reviewing they send the proposal to the CRM department. The respective credit officers review the proposal and get the approval from the approving authority.
The routing process of credit proposals and its approvals can be summarized as follows:
CREDIT MONITORING:
To minimize credit losses, monitoring procedures and systems are in place that provides an early indication of the deteriorating financial health of a borrower. At a minimum, systems are in place to report the following exceptions to relevant executives in CRM and RM team:
- Past due principal or interest payments, past due trade bills, account excesses, and breach of loan covenants;
- Loan terms and conditions are monitored, financial statements are received on a regular basis, and any covenant breaches or exceptions are referred to CRM and the RM team for timely follow-up.
- Timely corrective action is taken to address findings of any internal, external or regulator inspection/audit.
- All borrower relationships/loan facilities are reviewed and approved through the submission of a Credit Application at least annually.
EBL has an excellent IT backbone, which produces the above information for central/head office as well as local review.
CONCLUSION:
Compliance with the guidelines of BB circulars or directions is a must for all the scheduled banks in the country. EBL is no exception is this case. All the circulars related to credit are properly filed in the department. It is made sure from the top management that each and every credit officer understands all the circulars and directions and exercise due diligence during operation regarding the stated issue. The following section discusses a similar topic, which necessarily requires bank’s strong compliance regarding it.