The practice of identifying and reducing business expenses in order to increase profits is known as cost control, and it begins with the budgeting process. It is the practice of identifying and managing costs. It is a critical factor in sustaining and increasing profitability. This begins with the budgeting exercise at the start of the year, in which costs and revenues for the coming year are estimated. These will be recorded throughout the year, and the results will be compared at the end. Thus, cost control is inextricably linked to aspects such as budgeting, comparing budgeted to actual results, and variance analysis.
Cost control is a finance professional practice that analyzes a company’s overall expenses and reduces project costs to increase profit. A company typically hires finance professionals to monitor their cost performance, plan a budget for each project, and change projects that can improve a company’s financial performance.
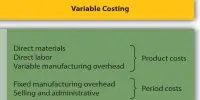
Cost Control is a practice of identifying costs and managing them. It is used by a company’s internal management team to identify all variable and fixed costs associated with the production process.
Cost control is an important outcome of these processes because incurred costs over the accounting period should be compared to expected results and variations identified in order to make future decisions. As a result, cost control is an important decision made by management. Cost control is primarily concerned with costs that are higher than expected. Such situations result in negative variances, which the cost accountant will bring to the attention of managers so that the managers can make the necessary decisions to implement corrective actions.
Cost control does not only refer to cost reduction; maintaining costs at current levels is also an important aspect of cost control. Cost control should give equal weight to both positive and negative variances. For example, if a specific cost has an unusually high favorable variance, this indicates that the targeted cost during budgeting is too high. In such cases, the budget should be revised even if no action is taken regarding the incurred cost.
Controlling costs is one method of planning for a target net income, which is calculated using the formula:
Sales – fixed costs – variable costs = target net income
Assume a retail clothing store wants to earn $10,000 in net profit from $100,000 in sales for the month. To achieve the goal, management examines both fixed and variable costs and makes efforts to reduce expenses. Inventory is a variable cost that can be reduced by locating alternative suppliers who may provide more competitive pricing.