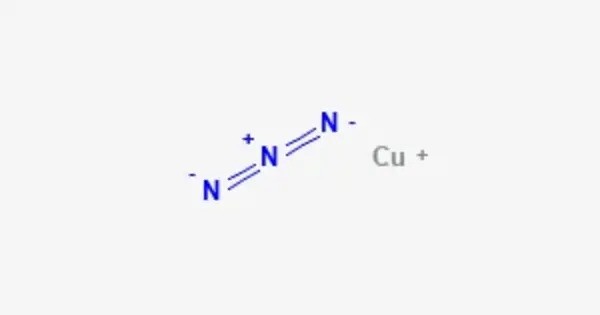
Copper(I) azide is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula CuN3. It is composed of a copper cation (Cu+) and an azide anion (N−3). It is sensitive to heat and shock and can be unstable, especially in larger amounts, potentially leading to detonation or explosion upon impact or excessive heating. Therefore, it is considered a highly sensitive and hazardous compound.
It is a coordination compound that has interesting chemical properties and applications. It has been studied for its potential use in explosives or as a detonator material because of its high reactivity. It also has applications in coordination chemistry and sometimes in pyrotechnics.
Properties
Copper(I) azide has been used in the preparation of high-energy materials using methods with low environmental cost. These preparations were completed using systems that were high in nitrogen and without any oxygen. Like most azides, it is explosive.
- Chemical formula: CuN3
- Molar mass: 105.57 g/mol
- Appearance: It is usually a light blue or blue-green solid.
- Stability: It is an unstable compound and can decompose violently, especially when subjected to heat or mechanical shock.
- Solubility: It is generally insoluble in water and most organic solvents.
- Chemical Reactivity: It is a strong oxidizing agent and can react with various materials. Upon decomposition, it releases nitrogen gas (N2N2) and copper metal.
Preparation
Copper(I) azide can be synthesized by reacting copper(I) salts, such as copper(I) chloride, with sodium azide in a suitable solvent like water or ethanol. The reaction is typically as follows:
CuCl + 3 NaN3 → CuN 3 + 3NaCl
Occurrences
Laboratory Preparation: Copper(I) azide is not a naturally occurring compound but is typically synthesized in laboratory settings or for specific industrial uses, particularly in pyrotechnics and explosives. It is not found in significant amounts in nature, as its instability limits its widespread presence.
Reactivity in Industry: Copper(I) azide has been used historically in the synthesis of other azide compounds, but its use is now restricted due to safety concerns arising from its explosive nature.
Applications
While Copper(I) azide is not widely used due to its instability, it has been investigated for use in explosives and as a precursor in certain chemical syntheses. Its decomposition can yield copper metal, which could potentially be used in catalytic reactions.
Safety Considerations
Because of its potential for violent decomposition, copper(I) azide should be handled with extreme caution. It should be stored away from heat, shock, and incompatible materials, and precautions like proper containment and protective equipment are essential when working with it.