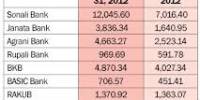
Co-operative banks are the banks whose main objective is to provide financial assistance to economically weaker sections of the society. Cooperative banking is retail and commercial banking organized on a cooperative basis. Such banks are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act. Cooperative banking institutions take deposits and lend money in most parts of the world. Simply, it is a bank that is owned by its members, who deposit money or who borrow money as loans. Examples of cooperative banks are The New India Cooperative Bank, Cosmos Co-op Bank, etc.
Cooperative Banks are financial entities established on a co-operative basis and belonging to their members. Cooperative banking, as discussed here, includes retail banking carried out by credit unions, mutual savings banks, building societies, and cooperatives, as well as commercial banking services provided by mutual organizations (such as cooperative federations) to cooperative businesses. It is the bank that holds deposits, makes loans, and provides other financial services to cooperatives and member-owned organizations. They are owned by members (usually their customers) rather than shareholders. As a result, they prioritize maximizing customer value over profits, and they typically focus on high street banking. These banks provide a wide range of regular banking and financial services. However, there are some points where they differ from other banks.
There are three types of cooperative banks-
- Primary Credit Societies – These institutions are formed at the village level or town level. The operations of such banks are limited to a very small area.
- District Central Cooperative Banks – These banks operate at the district level. They act as a link between primary credit societies and state cooperative banks
- State Cooperative Banks – State Cooperative Banks are the biggest forms of cooperative banks. They operate at the state level. Some State Cooperative banks operate in multi States.
The co-operative banking system came into being with the aim to promote saving and investment habits among people, especially in rural parts of the country. Co-operative banks are key actors in the European economy. They provide access to finance at the local level and are widespread even in remote areas of the continent. The cooperative banking system came into being with the aim to promote saving and investment habits among people, especially in rural parts of the country. Co-operative banks play a crucial role in rural financing, with funding of areas under agriculture, livestock, milk, personal finance, self-employment, setting up of small-scale units among the few focus points for both urban and rural cooperative banks.