Comparative Analysis of Teletalk Bangladesh Limited
The world is becoming closer day by day with the power of technology, internet & telecommunication. There was a time when people used to wait for weeks to communicate with others. The strength of telecommunication industry has removed this distance from each other all over the world. Now Bangladesh has 6 mobile phone operators. They are Grameenphone (GP), Banglalink, Robi, Airtel, Teletalk & Citycel. Among all the mobile phone operators in Bangladesh, Teletalk is the only domestic and state-owned operator which was incorporated on December 26, 2004 as a public limited company under the Companies Act, 1994 with an authorized capital of Tk.2000 crore. On the 31 march 2005, they have started their operation officially. The mission & vision of Teletalk is given below:
“To innovate and constantly find new ways to enhance our services to our customer‟s current needs and desire for the future. Our vision is to know our customers and meet their needs better than anyone else”
Teletalk Bangladesh limited was established with a view to achieving some objectives such as
- To provide mobile telephone service to the people from the public sector,
- To ensure fair competition between public and private sectors and thereby to safeguard public Interest,
- To meet a portion of unmitigated high demand of mobile telephone,
- To create a new source of revenue for the government. (About Teletalk)
The objective of the project can be divided into two categories. Those are:
Broad Objective
The broad objective is to know about the contribution of Teletalk Bangladesh Limited in Telecom Industry of Bangladesh.
Specific Objective
- To know the overall condition of telecom industry
- To know the position of Teletalk Bangladesh Limited in Telecom industry regarding market share and profit.
- To analyze the performance of Teletalk
- To identify the future prospect of Teletalk in Telecom Industry of Bangladesh after implementing 3G
Methodology
The procedure of collecting information from various resources is known as methodology. There are two sources from where I had collected my information.
Primary Sources
- Onsite Task
- Official (Teletalk) supervisor Interview
- Employee of other unit
- Departmental (Business Partner) Raw document.2.
Secondary Sources
- Official Website: www.teletalk.com.bd
- BTRC website: www.btrc.gov.bd
- Different Articles on telecom industry of Bangladesh
- Management profile of Teletalk
Current Situation:
From the starting of Teletalk, it is providing 2G mobile network service in the whole country. Initially, it had started its operation with 634 BTS in 64 districts. Up gradation work is going on as a chronological process. At the end of this quarter their total number if BTS will be 1725 which will cover 448 upazila‟s, 1.8 million subscribers handling capacity. Besides, Teletalk also build data network for 3 lakhs subscribers. On 14 October, 2012 Teletalk started 3G network service in Dhaka. Then they are gradually expanding it. Till now, Dhaka, Chittagong, Gazipur & Narayanganj is under 3G network coverage. According to Teletalk authority, 3G network expansion work is going on. Initially, they are planning to form 700 BTS for 3G network service. They are planning to spread 3G across the country by 2013. By using Teletalk 3G people can use
- Faster Internet (Up to 4 mbps speed)
- Video call facility & Mobile TV Service
Divisions
- Admin
Administration division works to control the business facility layout, safety & maintenance, controlling overall employee management, security staffs & personnel management etc. Besides, maintaining alternative sites for emergency evacuation is also a part of administrative job. They also do HR work.
- Planning and Implementation
Planning and Implementation is another important division. They bassically do planning for future activity of the company. Besides planning, they also do the drawback about how the plan will be implemented.
- Regulatory and Corporate Relation
This division is mainly responsible for creating and maintaining corporate relationship. In order to succeed in the present business market you need strong corporate linkage. This division is in charge of all handling legal issues by govt. & so on.
- Marketing and Sales
Marketing and sales division is responsible for acquiring monthly targeted sales given by top management. The division works to develop brand & market communication, sales of corporate & business products, maintenance of contact centre as well as participate in building up pricing strategy of new products. This division is also in charge of all the CSR activities approval, analysis of event management & sponsorship, maintaining relations with media.
- System Operations
System Operation is one of the most important department in Teletalk, System operation division basically does regular tower operation & maintenance activity. They also supervise core nework, radio network and transmission links. For smooth operation Teletalk divide their operation in two zones:
- Central Zone
- Chittagong Zone
- Customer Relation Management (CRM)
Customer Relation Management department basically works to maintain active relationship with the existing subscribers & communicate with new subscriber. CRM basically store and analyze the subscriber data which includes usage pattern, type, volume. After analyzing data, they basically help other department by providing subscriber profile.
- Finance and Accounts
Finance and Accounts is the heart of any business functions because they are responsible for budgeting. Finance and Accounting division of Teletalk Bangladesh Limited is accountable for financing into different proposals, business partnering, as well as new product development. Finance controls financial accounting, creating salary sheets for employees, maintaining compliances & so on.
- IT and Billing
IT department is basically maintained and install the official IT utensils. They manage LAN and WAN. They also ensure proper hardware, software and network upgrades installation, reinstallation, changes & relocations. They also do troubleshooting for different IT problem. Billing department works on billing issues of customers. They are basically responsible for the charging and billing from subscribers. (Alam, 2013)
Telecom Industry Overview
Telecom Market
Cell phone has become an indispensable part for the people of Bangladesh everyday-life and has made our life safer and faster as we can communicate with others at any time when we need. So we really need to escalate the telecom-revolution and its relentless development that together have made this country more competitive with the developed and developing world. This is the prime communication device that we now use to express ourselves, get our work done and share our pains and desires to others. With the support of this cell phone technology different cell phone operators both local and foreign have established a strong base in Bangladesh. This operator‟ sactivities have taken this telecom industry on stage of saturation.
Structure of Telecommunication
In accordance with the National Telecommunications Policy 1998 and International Long Distance Telecommunications Services (ILDTS) Policy 2007, all cellular operators needs to interconnect through Interconnection Exchange (ICX) and all international calls need to be controlled by the International Gateway (IGW) that needs to be connected to the cell phone and fixed operators through the ICXs.
In addition the Interconnection Exchange (ICX) will receive all calls from the cell phones and fixed operators whenever the call is made to other network and will pass it to the destination network if the call is local, and will pass to the IGWs if the call is international. ICX will also deliver calls received from IGWs where the call is destined (Telecommunications in Bangladesh, Wikipedia, 2012).
Technologies
There are two types of cellular technology now present in Bangladesh, Such as
GSM: GSM stands for “Global System for Mobile Communications.” This is manly a European based system. However this system is almost unused in the United States. GSM can be said as a modified and far more efficient version of TDMA. GSM keeps the idea of timeslots and frequency channels. However it corrects several major shortcomings. As the GSM timeslots are smaller than TDMA technology, they hold less data but allow for data rates starting at 300 bits per second. Thus, a call can use as many timeslots as necessary up to a limit of 13 kilobits per second. When a call is inactive or may be compressed more, fewer timeslots are used. To facilitate filling in gaps left by unused timeslots, calls do “frequency hopping” in GSM. This means that calls will jump between channels and timeslots to maximize the usage if the system.
A control channel is used to communicate the frequency hopping and other information between the cell tower and the phone. To compare with the other systems, it should be noted that GSM requires one Watt of output power from the phone. (GSM, Wikipedia, 2012)
CDMA: CDMA stands for “Code Division Multiple Access” and is both the most interesting and the hardest to implement multiplexing method. CDMA has been likened to a party: When everyone talks at once, no one can be understood, however, if everyone speaks a different language, then they can be understood. CDMA systems have no channels, but instead encode each call as a coded sequence across the entire frequency spectrum. Each conversation is modulated, in the digital domain, with a unique code (called a pseudo-noise code) that makes it distinguishable from the other calls in the frequency spectrum. Using a correlation calculation and the code the call was encoded with, the digital audio signal can be extracted from the other signals being broadcast by other phones on the network. From the perspective of one call, upon extracting the signal, everything else appears to be low-level noise. As long as there is sufficient separation between the codes (said to be mutually orthogonal), the noise level will be low enough to recover the digital signal. Each signal is not, in fact, spread across the whole spectrum (12.5 MHz for traditional cellular or 60 MHz in PCS cellular), but is spread across 1.25 MHz “pass-bands.” Since CDMA offers far greater capacity and variable data rates depending on the audio activity, many more users can be fit into a given frequency spectrum and higher audio quality can be provide. The current CDMA systems boast at least three times the capacity of TDMA and GSM systems. The fact that CDMA shares frequencies with neighboring cell towers allows for easier installation of extra capacity, since extra capacity can be achieved by simply adding extra cell sites and shrinking power levels of nearby sites. CDMA technology also allows lower cell phone power levels (200 miliwatts) since the modulation techniques expect to deal with noise and are well suited to weaker signals. The downside to CDMA is the complexity of deciphering and extracting the received signals, especially if there are multiple signal paths (reflections) between the phone and the cell tower (called multi path interference). As a result, CDMA phones are twice as expensive as TDMA phones and CDMA cell site equipment is 3-4 times the price of TDMA equivalents. (Code division multiple access, Wikipedia, 2012)
Grameenphone
Grameenphone is considered as the number one cellular operator in Bangladesh that having its operation GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) technology. It has started its operation in Bangladesh operations on March 26, 1997. It is the only cellular operator public limited company that partly owned by Telenor (55.8%), Grameen Telecom (34.2%) and Public Share (10%). It is considered as one the fastest growing mobile telephone network in Bangladesh.Grameenphone‟s stated goal is to provide cost-effective and quality cellular services in Bangladesh.Moreover there are 2 technology support providers of Grameenphone those are Huawei and Ericsson. The tower range of GPexists 5-7 km. The technology used by Grameenphone is 1G(First Generation) which is supportable to 2G (Second Generation). The present CEO of Grameenphone is Mr. Tore Johnsen.
Banglalink
Banglalink is another major cellular operator in Bangladesh that started its business in February 2005 with its slogan “make it difference”. Formerly, it was known as Sheba Telecom Pvt. Ltd. It had been providing GSM (global system of mobile communication) services in Bangladesh since 1998. However in 2004, Orascom Telecom bought 100% share of Sheba Telecomas well as gave its new name as banglalink.
Nokia-Siemens network & Hawaii provides technological support to banglalink. The tower range of banglalink is 5-9 km. normally.However sometimes it varies to about 13-15 km. The technology used by banglalink is 1G (First Generation) which is supportable to 2G (Second Generation). Furthermore Banglalink has1500 km. of Fiber Optic cable which ensures good network for subscribers.
Citycell
Citycell (Pacific Bangladesh Telecom Limited) is the first cellular operator in Bangladesh. It is the only CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) network operator in the country. Citycell is currently owned by Singtel with 45% stake and the rest 55% owned by Pacific Group and Far East Telecom.
In 1989 Bangladesh Telecom Limited (BTL) was awarded a license to operate cellular, paging, and other wireless communication networks. Then in 1990 Hutchison Bangladesh Telecom Limited (HBTL) was incorporated in Bangladesh as a joint venture between BTL and Hutchison Telecommunications (Bangladesh) Limited. HBTL began commercial operation in Dhaka using the AMPS mobile technology in 1993 and became the 1st cellular operator in South Asia. Later that year Pacific Motors bought 50% of BTL. By 1996 HBTL was renamed as Pacific Bangladesh Telecom Limited (PBTL) and launched the brand name “Citycell Digital” to market its cellular products. Mr. Mehboob Chowdhuryis the present CEO of Citycell Hawaii, Ericsson and Motorola provide technological support to Citycell. The tower range of Citycell exists in between 5-6 km. in case sometime it varies to about 9 km. The technology used by Citycell is CDMA1X (Code division multiple access). Citycell is consolidating its position in wireless data by launching their Zoom EV-DO (evaluation data optimize) for the broadband wireless internet service.
Airtel
Airtel Bangladesh Limited is another GSM-based cellular operator in Bangladesh. Airtel is the sixth mobile phone carrier to enter the Bangladesh market, and originally launched commercial operations under the brand name “Warid Telecom” on May 10, 2007. Warid Telecom International LLC, an Abu Dhabi based consortium, sold a majority 70% stake in the company to India’s Bharti Airtel Limited for US$300 million. Bharti Airtel Limited took management control of the company and its board, and rebranded the company’s services under its own airtel brand from December 20, 2010. The Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission approved the deal on Jan 4, 2010. The present CEO of Airtel Bangla is Mr. Chris Tobit.
Teletalk
Teletalk Bangladesh Limited is a public limited company, registered under the Registrar of the Joint stock companies of Bangladesh. Total shares owned by the Government of the People‟s Republic of Bangladesh. Teletalk Bangladesh limited was established keeping a specific role in mind. Teletalk has forged ahead and strengthened its path over the years and achieved some feats truly to be proud of, as the only Bangladeshi mobile operator and the only operator with 100% native technical and engineering human resource base, Teletalk thrives to become the true people‟s phone “AmaderPhone”.
Robi
Robi Axiata Limited is a joint venture company between Axiata Group Berthed, Malaysia (70%) and NTT DOCOMO INC, Japan (30%). It was formerly known as Telekom Malaysia International (Bangladesh) which commenced operations in Bangladesh in 1997 with the brand name AKTEL. On 28 March 2010, the service name was rebranded as „Robi‟ which mean Sun in Bengali. The present CEO of Robi Axiata Limited is Mr. Michael Kuehner.
Market Share Analysis
The Market Share analysis of 6 Mobile Phone Operators are given below:
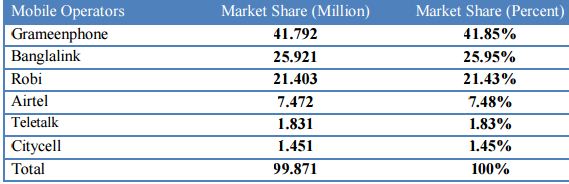
According to the previous figure Grameen phone is holding the highest amount of market share than comes Banglalink and Robi. Other three mobile operators are controlling 11 percent of the total market shares. So it is providing a clear indication that competitions are going in between Grameenphone, Banglalink and Robi. Others three telecom operators are clearly away from them and they have to make a huge jump if they want to be in the competitions.
Some Recent Updates by BTRC (March, 2013)
This is the last update by BTRC regarding the subscriber condition of different cellular operators in Bangladesh
- Grameenphone added 7 lac 89 thousand new subscribers in February 2013
- Banglalink added only 73 thousand new subscribers in February 2013
- Robi added only 1 lac 12 thousand new subscribers in February 2013
- Airtel Bangladesh added 1 lac 72 thousand subscribers in February 2013
- Teletalk added 1 lac 39 thousand subscribers in February 2013
- Citycell lost 8 thousand subscribers in February 2013
Total 1.28 million new subscribers added in February 2013 include all operators. (Mobile Phone Subscriiber, 2013)
Prospects
Expand Valued Added Services (VAS):
While the mobile VAS market has been growing, a number of initiatives still need to be undertaken to fully develop this market. The VAS contribution to revenue is upwards of 20% in emerging markets such as China, even without introduction of 3G, as compared to sub 10% in India. Teletalk got 3G, so it is a must to encourage the development of a robust VAS ecosystem in areas such as Agricultural VAS, Mobile Banking, M-Health and M/E-Commerce.
Convergence will become more important:
If service providers build service converged networks, then financial services, public services, and entertainment converged applications will be able to reach a far larger portion of the population. This is likely to have major implications for BD Telecoms companies and may lead them to invest in ISPs but also in IPTV, Video and Media and also game development as well as domestic web content.
Infrastructure Sharing:
One of the major new initiatives in 2010 has been infrastructure sharing agreements between GP & Banglalink and Robi & Banglalink. This trend will continue not only because it is partly enforced by the regulator but also as a matter of practical necessity. There are Public Private Partnerships (PPPs) opportunities for the operators to partner up with the Government of Bangladesh (GoB) in service delivery across the areas of e-education, e-health and e-governance.
Lower Broadband Costs: There is a strong case for GoB to substantially reduce broadband wholesale price further to also accelerate broadband access to a broader range of the public. This might be done in conjunction with the installation of a second submarine broadband cable. The terrestrial connection with neighboring India will also help to lower the broadband bandwidth price in the country.
Digital Bangladesh: Push to develop ITES and Outsourcing presents new business opportunities/diversification by the Telecoms companies. Such a strategy is already being adopted by Grameenphone who have established GP IT as a separate company and one that is already the largest IT Company in Bangladesh with around 300 employees.
Challenges
The Challenges facing the telecom industry of Bangladesh includes:
High Competition:
High competition in mobile or telecom sector in our country is one of the main problems. If we have a look in the primary stage of our telecom sector, we had only city cell and Grameenphone and they were operating their business in own way. They took the first mover advantages but when Banglalink, Robi, Teletalk, Airtel come to compete in the market then the market became more competitive and still there exist a high competition in this sector. So to face this competition/ challenge some of the operators are thinking to merge their business to survive in the market.
Poor Economic Background: As a least developed or developing country Bangladesh has a poor economic background where a major portion of our people are living under the poverty line. So it is difficult to operate such type of business in Bangladesh with making a remarkable profit. By considering this economic background, the telecom sector is to fixed the call rate, should reduce tax on SIM and sacrifice more to operate their business.
Instable Political Situation: Our previous history tells that Bangladesh is not a politically stable country. Different types of political violence, pressure of army, corruption and many more problems make our country instable and also has made this sector insecure. If we have a look last few year our democracy had face many ups and downs, as we don‟t have any foreign direct investment (FDI) in any of the sector.
High Rate of Corporate Tax: As the economic condition is not good of Bangladesh, the telecommunication sector is not able to make profit. Moreover they are to pay high corporate tax which is 40%-45%. It is another major problem or challenge to operate challenging day by day
SIM Tax: In Bangladesh the mobile operator is to pay Tk. 300 as tax in each SIM from fiscal year 2005-06. Firstly it was Tk. 1200 and later on by considering different facts it is fixed as Tk. 300. Though tax is to be paid by the subscribers directly but the company gives incentive to continue the sell the SIM at a lower price in the competitive market to hold their position. But now it become impossible for their all the company to carry on this burden. As the growth rate of the subscriber has been declined, the companies are in challenging position. (Sim Tax Reduce, 2013)
Import Tax: In case of technological perspective, Bangladesh is not good enough. So mobile phone operators is to transfer or import technologies, handsets and other equipment related to the telecommunication and for this they are to pay 35% import tax on it. It is also a great problem for this sector to make profit and survive in the market.
3G License uncertainty: The expected cost and terms on which 3G licenses will be issued remains unclear.
Marketing and Sales Division
Marketing and sales division is one of the most active departments in Teletalk. There activities are given below:
- One of the major responsibilities of marketing & sales department are acquiring monthly sales target with the help of sales and distribution team.
- Developing a strong brand image & build an uninterrupted market communication is another major responsibility of this department. So, all the types of marketing tools like advertisement, promotion are also done by this division.
- Marketing and Sales department normally create & maintain a strong relationship with the corporate client. Because, this department normally with the corporate subscribers.
- Marketing and Sales department is also responsible for the CSR activities. They also sponsor many events as a part of promotional strategy. Moreover, maintaining a good relationship with the media is also a job part of this division.
Comparative Analysis of Teletalk BD LTD
Market Characteristics
Mobile phone markets are one of the most turbulent market environments today due to the increased competition and rapid change of technology. The mobile market is also becoming increasingly important in developing countries, with benefits such as increased employment and wages. Bangladesh has a big market for mobile telecom business and the industry is expanding quickly. The estimated total population of Bangladesh was 154,991,191 on 27 May, 2013 and the total numbers of active mobile phone subscribers are 99.871 million at the end of March 2013, i.e. around 64.40% of total population use mobile phones. (Population of Bangladesh) People are increasingly using the mobile handset and modem to access internet and other data services taking advantage of all the new products and services offered by the operators. Around 90% of total internet users are now accessing internet through the mobile network and mobile internet would continue its dominance with the planned introduction of 3G in 2013. The current internet penetration has reached almost 10% and it was due to the contribution of the mobile operators.
The price of mobile phone services in Bangladesh is at present one of the lowest in the world. According to a Nokia Siemens Network study, published in 2009, Bangladesh actually has the third lowest total cost of ownership (TCO) per month with US$8.
Growth Potential and Trends
The mobile telecom sector is the fastest growing sector of the country and still there are around 55 million people who are yet to use cell phone. This implies that there are a lot unmet needs that could be a great potential for the industry. The literacy rate of the country is 67% which implies that major portion of the population have the academic depth to adopt new products and services, but they are highly price sensitive and prefer low prices for their poor economic condition. These statistics show that demographic trends are continuously diversifying, indicating why it is becoming ever so important to target specific customer groups, determine their needs, and then satisfy them. However, the overall trend of the industry shows that is downward sloping.
Performance of Teletalk over the Years
Subscribers
Teletalk Bangladesh Limited started their operation in 2004. Up to the year 2012, subscribers increased slowly. However, after adapting 3G technology, their subscribers increased dramatically. In fact, they are now the fastest growing operator in the market. The total number of subscribers has reached 1.831 million at the end of March 2013.
Growth Rate
The growth rate of teletalk is quite good. While the industry has been witnessing decreasing growth rates, Teletalk is actually experiencing an increasing growth rate recently. Specially, after getting 3G license the growth rate increase at an outstanding level.
Comparative Analysis of Performance with other operators
Origin
Citycell was the first mobile operator to enter the country. It was back in 1989 when Bangladesh Telecom Limited was awarded a license to operate cellular, paging and other wireless communication networks. However, it was not until February, 1996 that the company was renamed as Pacific Bangladesh Telecom Limited (PBTL) and the Citycell brand launched, just a year ahead of GP.
Grameenphone (GP) was formed through a joint venture between Telenor, a leading Norwegian mobile company, and Grameen Telecom, a not-for-profit organization established by Professor Dr. Yunus. More than 55% ownership belongs to Telenor while 34% ownership belongs to Grameen Telecom. The rest are publicly traded.
Telecom Malaysia International Bangladesh (TMIB) Ltd. was formed through a joint venture between Telecom Malaysia (70% equity interest) and A.K. Khan & Co. Ltd. back in 1996. They launched their mobile service, branded AKTEL, in 1997. However, on March 28, 2010 the company rebranded to Robi. Now the company is a joint venture flanked by Axiata Group Berhad, Malaysia & NTT DOCOMO Inc., Japan.
Banglalink entered the market in 2004. Naguib Sawiris, Chairman CEO of Orascom Telecom Holdings announced the acquisition of Sheba Telecom (Pvt.) Limited with a cost of US$60m in that year. Since its inception, it has been very aggressive to gain market share in the country. Teletalk caused quite a stir when it was finally formally introduced on December 28, 2004. The company gained 2.5 lac subscribers within the first few months. However, its growth faltered. But after adopting 3G in October 2012, the growth rate has increased at an excellent amount. Airtel Bangladesh Ltd. originally launched commercial operations under the brand name “Warid Telecom”. In December 2005, Warid Telecom International LLC paid US$ 50 million to obtain a GSM license from the BTRC. It sold a majority 70% stake in the company to India’s Bharti Airtel Limited for US$300 million. Bharti Airtel Limited took management control of the company and its board, and rebranded the company’s services under its own airtel brand from December 20, 2010.
SWOT Analysis of Operators
To understand the business environment of a particular firm, we need to analyze both the general environment and the firm„s industry and competitive environment. One of the most basic techniques for analyzing firm and industry conditions is SWOT analysis. It is a widely used technique through which managers create a quick overview of a company„s strategic situation.
Grameenphone
Strengths:
Providing quality services is one of the basic strength of Grameenphone. Grameenphone has the best network coverage, strong brand image, skilled workforce, strong financial position, excellent customer service, world class working environment.
Weaknesses
High tariff rate charge for different products and services is a major weakness for Grameenphone.
Besides, different recent news about the employee dissatisfaction within organization also creates a negative impression in the market.
Opportunity
As GP has the maximum network coverage in Bangladesh, so it has a huge opportunities in the internet market in Bangladesh. As rural area users have limited alternative options, so GP can earn huge market share from here.
Threats
The adoptability of upcoming technology (3G) with technological infrastructure is a challenge. Rapid changes and advancement in existing cellular technology, changes in customers‟ needs, proliferation of substitutes in the market etc. also pose threats to the company. IP telephony, by VoIP service providers, is the new threat in telecom industry. It has the potential to buoy a raft of new household brand.
Banglalink
Strengths
Lucrative product offerings are one of the basic strength of Banglalink. Easy to understand is one their basic criteria for any offer. They also have one of the largest (1,500 kilometer) optical fiber networks in Bangladesh.
Weaknesses
Low quality of network, lowest ARPU in the market are the major weakness of Banglalink. So, while it is true that Banglalink started the price war, it now needs to find a way to increase its revenue. Though their advertising expenditure is high but it is losing appeal.
Opportunities
The disposable income of people in Bangladesh is increasing every year. In addition, Bangladeshi market has high mobile phone acceptability. This may help them in increasing their ARPU. They can form new alliances with eminent companies of different countries to achieve higher competitiveness and bring more expertise inside the company. The company has the opportunity of external funding from various sources. The company’s management is seeking for merger or acquisition opportunity from the industry. Moreover, the company is planning to raise capital through issuing Initial Public Offering (IPO).
Threats
Banglalink grab its market by a price war. But, another price war would be a huge blow for Banglalink. They cannot sustain on such revenue. Inflation in the economy is also a threat for Banglalink. Another threat is the huge subscriber base of Grameenphone & 3G of Teletalk also.
Robi Axiata
Strengths
Good network coverage & strong branding is the major strength of Robi. The Chittagong division is a stronghold of Robi and it is a preferred brand there. They have the widest roaming coverage. Their HR is also very skilled. Their subscriber base also provides stable revenue.
Weaknesses
Limitation in customer service is one of the weaknesses of Robi Axiata. Product innovation skills are not that much effective. They have too many products and packages which causes confusion in the minds of the consumers.
Opportunities
Push to develop ITES and Outsourcing presents new business opportunities/diversification for Robi. We have already seen such a strategy being adopted by market leader GP who have established GP IT as a separate company and one that is already the largest IT Company in Bangladesh with around 300 employees.
Threats
3G license can be a major threat for them. If they cannot take the 3G license, then Robi will surely loose a huge number of subscribers.
Airtel Bangladesh
Strengths
Airtel has one of the most advanced networks in the country. Although they do not have the best coverage but the quality of the network is high. They are providing the lowest call rate now.
Weaknesses
Insufficient network coverage is one of their major weaknesses. Their product design and marketing are also weak. Their Value Added Services (VAS) is not also at par with the competition. The brand is also new relative to the competition. So they need time to build a loyal customer base.
Opportunities
Offering new & exclusive VAS can be a major opportunity for them.. They may also go for network sharing with the other operators to boost network quality in the short term.
Threats
High government tax and SIM tax is a threat for Airtel Bangladesh. SIM tax is particularly important because unlike Grameenphone, Banglalink and Robi Axiata they do not have a large install base. Wide coverage of competitors is also a serious threat. There is also a negative perception about the company in the minds of the people because it is an Indian brand.
Teletalk
Strength
Being a public company, it is the preferred brand of the people. It also has the 3G license ahead of the competition which gives them a huge advantage.
Weaknesses
As it is a company owned by the government, the administration is bureaucratic. Hence, it is slow to react to the market changes. The HR is not very skilled like the competition. The turnover rate of the employees is very high. The management is also not very efficient. Network coverage is also not adequate. Customer service is also not in standard.
Opportunities
After adopting 3G technology, their opportunity is really increase. Teletalk can offer more VAS which will bring new subscribers. They can design more attractive offer as they have the updated technology.
Threats:
The governing body is itself a threat for Teletalk. In efficient employees is another threat. The major threat will be the scenario of the market when 3G service will goes to other companies. As competitors company has better infrastructure & organizational capability, so Teletalk may lose their market after the 3G auction.
Citycell
Strengths
Citycell is the only CDMA service provider in Bangladesh. They have strong network coverage. There underlying technology also have some strengths that their competitors cannot provide. Moreover, they have one of the best data services in the country.
Weaknesses
The main weakness of Citycell is CDMA. Although CDMA is quite an advanced technology itself, it did not take off in Bangladesh. The lack of preferred handsets is also another issue that they need to solve in order to achieve high growth.
Opportunities
Opportunities of Citycell lie in the upcoming 3G technology. 3G is the future of telecom in Bangladesh and if they can get on the bandwagon it will help them to be a major force in the industry.
Threats
According to reports, Citycell is planning to provide GSM services. However, whether they will be able to provide the same services in GSM technology is not confirmed. If they fail to get a 3G license, they will remain one of the minor players in the market. Introduction of Wi-Max services in the country have caused uncertainty in their data business as well.
Performance Analysis by Porter’s Five Forces Model
According to the last few years, the competitive environment in the telecom industry has become intensely competitive, with not only constant special offers and new value added services, but also with new and bigger entrants, and their aggressive marketing. The following sections describe the competitive environment in the industry using Michael Porter‟s five forces model.
Threat of Rivalry
At the very beginning in the telecom industry, Grameenphone and AKTEL dominated the market. Both of the companies never did anything to reduce their charges for their consumers. But, at 2004 when Banglalink and Teletalk came to the market, market change drastically. Banglalink entered the market with a huge shake and kept the mindshare of the people over the years. Ever since Banglalink entered the market the industry has been on shaky grounds.
Suddenly all telecom companies stepped up their promotions. Banglalink started the first price war to penetrate the market and although this was good news for the subscribers, it was not the same thing for the operators. Revenue dropped fast and all the operators changed their strategy to volume based model of business.
After the rebranding, Robi has increased all of its branding & promotional activities. Besides, it also becomes aggressive in its campaigns. They have greatly increased their branding & advertising expenditures. As a result, it is now more visible and Robi becomes the well known company.
After launching Teletalk, competition becomes even more. Because, it had started to offer interconnection with T&T (BTCL) in a cheaper & broader way. So, people grab it. But, after a few days it loses its demand as it did not have any interconnection with the other private mobile operators. As a result, sales suffered and Teletalk never achieved the critical mass necessary to have an impact in the market.
After acquiring Warid, Airtel is constantly trying to capture market share. The visibility of the company is quite good. Combined with low call rate, it has the potential to be a big player. So, the rivalry among existing competitors is very high.
Performance Analysis by Porter’s Five
Forces Model
Threat of New Entrants
Mobile Telecom is capital and resource intensive business which poses a significant entry barrier for potential players in Bangladesh. All the existing company has a strong market & brad name. Government rules and regulations- like imposition of huge tax on SIM card, strong tariff control by the authority, can also create difficulties to entrants; in addition the price battle between the competitors brought the tariffs to its lowest in this region. Due to control over licenses, the major barrier to entry in Bangladesh mobile telecom market is to obtain a radio spectrum license from BTRC. However, companies are finding other ways to enter the industry, i.e. through merging with existing operators. For example, Bharti Airtel acquired 70% stake of Warid Telecom and rebranded as „Airtel‟ in order to enter the Bangladesh market. Hence it seems that the threats of new entrants in mobile industry are moderate to weak.
Threat of Substitute Products
Mobile telecommunications is a high-tech industry and the substitutes that would replace the products or services of today are strongly related to the factor of innovation. In case of Bangladesh mobile telecom industry, substitutes exist in the form of government fixed-land lines and some upcoming PSTN operators. Some additional substitutes include VoIP service providers (VSP), Skype, Google Talk, wireless Internet providers such as WiMax based companies etc.
However, there is no strong competitive substitute for mobile telecom industry as the existing alternatives are either nearly obsolete or in embryonic stage and thus poses very little threat to the industry.
Teletalk is only among the five operators in the country who provide services using 3G technology. Citycell is the only operator based on CDMA technology. Almost all of the companies provide basic data services. But, Teletalk offers 3G service which can be a basic differentiator in the market. But, Teletalk will not get this advantage for long time as other mobile operators will also get it very soon.
So, the threat from substitutes is weak in Bangladesh.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Now, there are 6 mobile operators running their business in Bangladesh whose are offering almost similar types of services. Besides, switching costs between operators are also low which provide buyers with extremely high bargaining power. But, the scenario is not same for the remote area where network alternative network is not available. But, in generally bargaining power of buyers in this industry is very high.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
All the mobile operators have international identity and have experience to work in the global platform. The companies have the opportunity to acquire necessary equipment from different international chains across the globe. The bargaining power of suppliers in the mobile industry varies depending on the brand name and strategic importance of the supplies as well as the size of the Company, such as Ericsson and Nokia Siemens in the mobile telecom machinery industry is that type of suppliers who enjoy strong power in the industry. On the other hand there are many potential suppliers and vendors in telecom industry e.g. Cisco, Siemens Enterprise
Communications, Alcatel-Lucent, Huawei and Motorola, Nortel, Oracle, Nokia, Samsung, Juniper, Converse, HP, Sun etc. In 2010, Huawei, the Chinese telecom equipment manufacturer, was one of the major suppliers of telecom equipment in Bangladesh and its major clients include Grameenphone, Banglalink, Robi, Citycell, Teletalk and BTCL; while VimpelCom (a.k.a ‘BeeLine’) provided voice and data services to Djuice of Grameenphone and Banglalink, and ACME Tele Power Ltd. (India) provided solar power support to Grameenphone. Recently, Huawei Technology played an important role in modernizing GP„s network infrastructure on the new 3G platform (Star Business, 2010). All of these available resources ensure competitive price and abundant supply support to the country’s telecom industry. Therefore, the bargaining power of suppliers in the industry is moderate to weak.
Findings
Overall findings of the report are given below:
- Grameenphone is the leading mobile phone operator with more than 40 million subscribers. They have the best network coverage but charging high for their services.
- Banglalink has better product quality and they are providing the lowest price but their network quality needs to be improved to get more subscribers.
- Robi is one of the major competitors in Bangladesh. Their network coverage is also better. But, product development & customer service team should work more effectively.
- Airtel is another growing mobile operator. Their main target market is the youth segment. Their product is good. But, they need to expand their network coverage & improve network quality.
- Teletalk is the only 3G service provider in Bangladesh right now. Their high speed internet, video call facility & mobile TV service has already created a buzz in the market. But, they need to expand their 3G network & design new product.
- Citycell is the only CDMA operator in Bangladesh. CDMA is the most updated technology than GSM. But, Citycell cannot take the advantage of it. They have a strong network base. But, they should offer more attractive offer. Moreover, they should offer new attractive handset.
Recommendation
After working the whole report, some recommendations has come to my mind. Those are given below:
First of all Teletalk should enrich their brand image. At the time of market visit during my internship, I noticed that a huge number of people considered Teletalk as a low profile brand. Their perception about Teletalk is that Teletalk service is not good. So they need to build a strong brand image.
Teletalk should expand their network coverage. Now Teletalk has 2G network coverage in 64 districts & 3G coverage in Dhaka, Narayanganj Town & Chittagong only. Their network is basically covered on town area. So, it is really hard for any subscriber to get network in the village area. In order to compete, their network coverage should be increased. Otherwise, they will lose the first mover advantage for 3G Service.
Right now, Teletalk has the highest internet speed among all the mobile operators. So, they should focus more on their data business.
After getting 3G, Teletalk is offering Mobile TV service which becomes so much popular among subscribers. So, they should offer more VAS as they have the latest technology.
Customer service of Teletalk is one of the major improvement areas. Their helpline number 121 normally does not work properly. Teletalk customer service department does not have adequate resource including manpower & instrument. So, subscriber is extremely dissatisfied about their customer service. Teletalk governing body should take it as a prior concern & should take necessary steps.
For the success of any organization, they need skilled workforce. To become skilled, employee needs routine training facility. Teletalk has one of the weakest HR in
Bangladesh. So, Teletalk should build a strong HR team. So that, their employee will be as skilled as motivated.
Conclusion
Doing internship with the county‟s first 3G service provider “Teletalk” is my immense pleasure. It is more satisfactory when I can write a conclusion after successfully complete my internship. In my whole report I tried my best to provide as much information as possible. I said as possible, because of the confidentiality issues of Teletalk I cannot take much information from office. Telecom industry in Bangladesh is highly competitive. In this competitive environment, Teletalk was a small player before October 2012. At October 2012, Teletalk launches country‟s first 3G services in Bangladesh. After that, the growth increase in an excellent rate. On October 2012, the total number of Teletalk subscriber was 1.3 million. At the end of March 13, the number of total subscribers becomes 1.8 million. On March 13, subscriber growth rate was 8.21. So, the growth of Teletalk is increasing day by day.
At the ending, it can be said that Teletalk started to become one of the preferred brand among the subscribers for some unique service offerings. If they can not only maintain their quality but also introduce new services, their future will be bright in future.