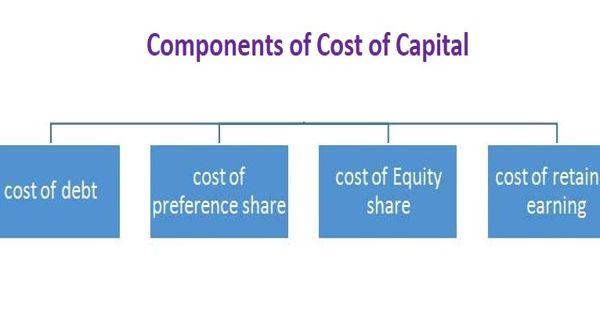
Common Components of Cost of Capital
Cost of capital is a composite cost of the individual sources of funds including equity shares, preference shares, debt, and retained earnings. The individual cost of each source of financing is called a component of the cost of capital. The overall cost of capital depends on the cost of each source and the proportion of each source used by the firm. The component of the cost of capital is also known as the specific cost of capital which includes the individual cost of debt, preference shares, ordinary shares, and retained earnings. Such components of the cost of capital have been presented below:

(A) Cost of Debt – Debt may be issued at par, at premium or discount. It may be perpetual or redeemable. A bond is a long-term debt instrument or security. Bonds are issued by the Government and the public sector companies. Bonds issued by the government do not have any risk of default, because it honors the obligation of its bonds.
- Cost of perpetual or irredeemable debt
- Cost of non-perpetual or redeemable debt
- Cost of debt issued on redeemable condition
- Cost of callable debt.
(B) Cost of Preference Share – The cost of preference share capital is the dividend expected by its holders. The computation of the cost of preference capital however poses some conceptual problems. In the case of borrowings, there is a legal obligation on the firm to pay interest at fixed rates while in the case of preference shares, there is no such legal obligation. The payment of preference dividend is not adjusted for taxes as they are paid after taxes and is not deductible.
- Cost of perpetual preference Share
- Cost of redeemable preference Share
(C) Cost of ordinary/equity shares or common stock – The computation of the cost of equity capital is a difficult task. Some people argue, as observed in the case of preference shares, that the equity capital does not involve any cost. The cost of equity share may be defined as the minimum rate of return that the company must earn on that portion of the total capital employed which is financed by equity capital so that the market price of the share of the company remains unchanged.
(D) Cost of retained earning – According to this approach, it is the earning per share which determines the market price of the shares. This is based on the assumption that the shareholders capitalize on a stream of future earnings in order to evaluate their shareholdings. A bond is a long-term debt instrument or security. Bonds are issued by the Government and the public sector companies. Bonds issued by the government do not have any risk of default, because it honors the obligation of its bonds.