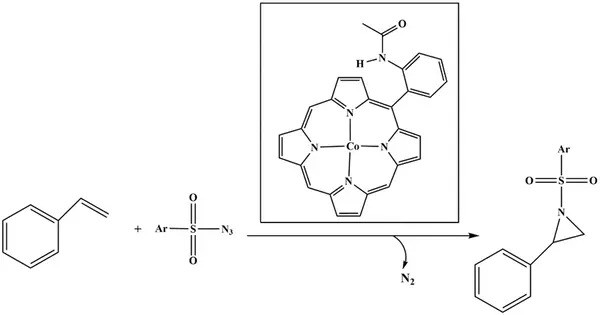
Cobalt(II) azide is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula Co(N3)2. It consists of cobalt in the +2 oxidation state and two azide ions (N3−). is an interesting and hazardous compound, typically synthesized for specific laboratory or industrial applications. Its explosive properties and instability make it useful for niche purposes, but also require caution when handling. It can be formed through the reaction between dicobalt octacarbonyl and iodine azide.
Co2(CO)8 + 4IN3 → 2Co(N3)2 + 8CO + 2I2
Properties
Aqueous solutions of cobalt(II) azide change in color when introduced to suitable organic solvents, from pink-violet to a blue shade. Like most azides, it is explosive.
- Chemical formula: Co(N3)2
- Molar mass: 142.97 g/mol
- Appearance: It is typically a light blue or pale blue crystalline solid.
- Molecular Weight: The molar mass is approximately 174.94 g/mol.
- Solubility: It is generally insoluble in water, but can dissolve in some organic solvents.
- Stability: It is considered to be a sensitive compound and can be unstable, especially when dry. It is considered hazardous due to its tendency to decompose explosively under certain conditions.
Chemical Properties
Azide compounds are generally quite reactive, and cobalt(II) azide is no exception. Azide salts tend to be sensitive to heat, shock, and friction, which can make them hazardous. This reactivity is attributed to the instability of the azide ion, which can release nitrogen gas upon decomposition.
Occurrence of Cobalt(II) Azide
Cobalt(II) azide does not naturally occur in the environment in significant quantities. It is usually synthesized in laboratories, often for experimental or industrial purposes, particularly in studies related to explosives, propellants, or as a precursor for other cobalt compounds.
- Synthesis: Cobalt(II) azide can be prepared by reacting cobalt(II) salts, such as cobalt(II) chloride, with sodium azide in aqueous solution. The reaction typically yields cobalt(II) azide as a precipitate:
CoCl2+2NaN3→Co(N3)2+2NaCl
- Laboratory Use: Cobalt(II) azide may be used in research on energetic materials due to its explosive potential, but it is not a commonly used compound outside of specialized applications.
Uses
Due to the high reactivity of azides, cobalt(II) azide is not commonly used in most practical applications, but like many azides, it can be involved in explosive research or as a precursor to other compounds in chemical synthesis.
Safety
Cobalt(II) azide should be handled with extreme caution. Azides are known to be highly sensitive to external stimuli (heat, friction), and cobalt compounds can also be toxic or harmful to health, so proper safety protocols must be followed when working with this compound.