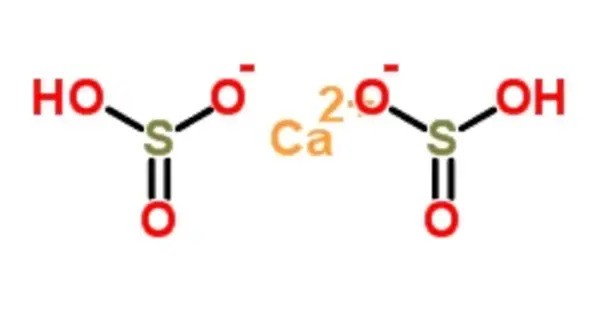
Calcium bisulfite (calcium bisulphite or calcium hydrogen sulfite) is an inorganic compound which is the salt of a calcium cation and a bisulfite anion. It is a chemical compound that typically appears as a white or colorless crystalline solid. It is commonly produced as a byproduct in processes such as the reduction of sulfur dioxide (SO₂) in industrial settings, particularly in the paper and pulp industry, where it is used in the bleaching process.
It may be prepared by treating lime with an excess of sulfur dioxide and water. As a food additive it is used as a preservative under the E number E227. Calcium bisulfite is an acid salt and behaves like an acid in aqueous solution. It is used in the sulfite process for producing paper from wood chips.
Synthesis
Calcium bisulfite can be prepared by treating lime (chemical formula Ca(OH)2) with an excess of sulfur dioxide and water. Upon synthesis of calcium bisulfite solution, it will have a green to yellow opaque appearance as an aqueous solution.
Calcium bisulfite is also known for its role in the preservation of food and beverages, as it can act as a preservative due to its ability to inhibit the growth of microorganisms. It is sometimes used in wine making, though it’s more common to see its salts, such as potassium bisulfite, used for this purpose.
Properties
Physical Appearance: It usually appears as a white to off-white solid or powder when dry. In solution, it can appear colorless or slightly cloudy.
Solubility: It is soluble in water, forming a solution of calcium bisulfite in aqueous form.
Acidity: It is acidic in nature due to the presence of the bisulfite ion (HSO₃⁻), which can release hydrogen ions in solution.
Stability: It is relatively unstable and decomposes over time, especially when exposed to air or if the solution is not properly maintained.
Chemical Reactivity: In its aqueous form, calcium bisulfite can act as a reducing agent due to the presence of the bisulfite ion.
It can react with oxidizing agents, and this reactivity is utilized in the bleaching of wood pulp.
Occurrence
Industrial Production: It is produced primarily for use in industries, especially in the pulp and paper industry, as part of the sulfite process. This process involves the use of sulfur dioxide (SO₂) to break down the lignin in wood, making it easier to separate cellulose fibers.
Bleaching Agent: It is commonly used as a bleaching agent in the manufacture of paper and textiles. In this process, it is used to bleach wood pulp and other fibrous materials.
Occurrence in Nature: It does not naturally occur in large quantities in the Earth’s crust or natural environments. However, sulfite ions and calcium ions are present in various natural systems, such as in certain mineral deposits or in reactions within the environment (e.g., in some sulfurous waters).
Role in Chemistry
Calcium bisulfite is important in various chemical processes, including being a reducing agent and an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, such as sulfur-based compounds.