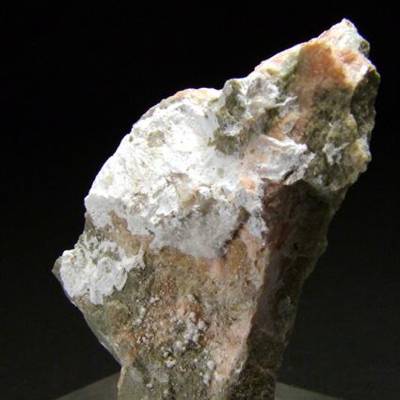
Brassite is a rare arsenate mineral with the chemical formula Mg(AsO3OH)·4(H2O). It is a rare arsenate mineral, first discovered in 1973 in Jachymov (Joachimsthal), Czech Republic. The mineral was named after Rejane Brasse, who first synthesized the compound.
It was named brassite, in 1973, to honor French chemist R`ejane Brasse, who first synthesized the compound. The type locality for brassite is Jáchymov of the Czech Republic.
General Information
- Category: Arsenate mineral
- Formula: Mg(AsO3OH)·4(H2O)
- Crystal system: Orthorhombic
- Crystal class: Dipyramidal (mmm).

Properties
Brassite is a white mineral, having a white streak and perfect cleavage. The density is 2.28 g/cm3.
- Color: White
- Crystal habit: Cryptocrystalline crusts
- Cleavage: {001} Perfect
- Fracture: Irregular/uneven, splintery
- Tenacity: Brittle
- Luster: Silky, dull, earthy
- Streak: White
- Diaphaneity: Translucent
- Specific gravity: 2.28
Occurrence
Brassite occurs as a rare reaction product of arsenic-rich solutions with Ca-Mg carbonates. It is closely associated with dolomite, realgar, arsenic, rauenthalite, haidingerite, weilite, picropharmacolite, and pharmacolite.
It occurs as an alteration of magnesium carbonate minerals by arsenic-bearing solutions. It occurs associated with pharmacolite, picropharmacolite, weilite, haidingerite, rauenthalite, native arsenic, realgar, and dolomite.
Information Source: