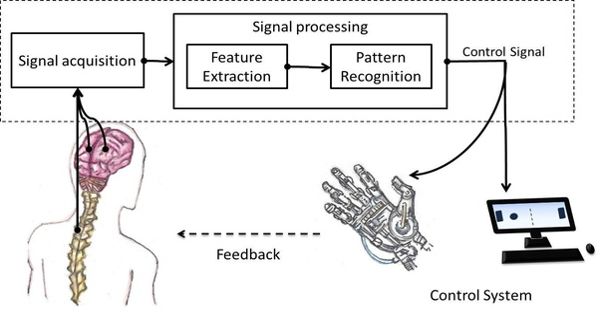
Bio-inspired robotic movement is a relatively young subcategory of bio-inspired design. It is about learning insights from nature and applying them to the design of real-world engineering systems. It refers to the design and development of robots that are inspired by the locomotion techniques and mechanisms observed in living animals. More specifically, this field is concerned with creating robots that are inspired by biological systems, including Biomimicry. Engineers and academics frequently look to nature for inspiration when developing robots that can handle varied terrains efficiently and successfully.
Biomimicry has resulted in the development of a new field of robotics known as soft robotics. The biological systems have been optimized for certain activities based on their environment. They are, however, multipurpose and are not intended for a single use. Engineers hope to construct robots that can move more adeptly in challenging situations such as uneven terrain, limited areas, or underwater by replicating natural principles and techniques.
Some of the key areas of bio-inspired robotic locomotion include:
- Biomimicry: Engineers investigate the movements and locomotion systems of animals, insects, and other species in order to better understand their behavior and apply it to the creation of robots. Robots that resemble the slithering of snakes, the crawling of insects, or the walking of diverse animals are examples.
- Soft Robotics: Soft robotics is concerned with the development of robots with flexible and changeable structures that can adapt to their surroundings, similar to the soft bodies of certain animals. This method allows robots to explore confined spaces and interact securely with humans and sensitive settings.
- Legged Locomotion: Researchers build robots with legged locomotion systems to traverse uneven terrain, climb barriers, and operate in demanding surroundings, inspired by numerous species with legs such as mammals, insects, and arachnids.
- Flying and Swimming Robots: Researchers also draw inspiration from birds, insects, and marine animals to develop robots capable of flying or swimming. These robots are designed to mimic the aerodynamics of birds or the swimming mechanisms of aquatic creatures to achieve efficient and agile movement in the air or underwater.
Bio-inspired robotics is the study of biological systems in order to find methods that can solve engineering problems. The designer should then attempt to simplify and improve that process for the specific task at hand. Bio-inspired roboticists are typically interested in biosensors (for example, the eye), bioactuators (for example, muscle), or biomaterials (for example, spider silk). The majority of robots feature some form of movement system.
Bio-inspired robotic locomotion has several uses, including search and rescue missions, environmental monitoring, hazardous environment investigation, and industrial automation. These robots can execute jobs that traditional machines find difficult or impossible to complete by harnessing the efficiency and adaptability of natural systems. Ongoing research in this area continues to develop robotic system capabilities, making them more versatile, adaptable, and resilient for a variety of real-world applications.