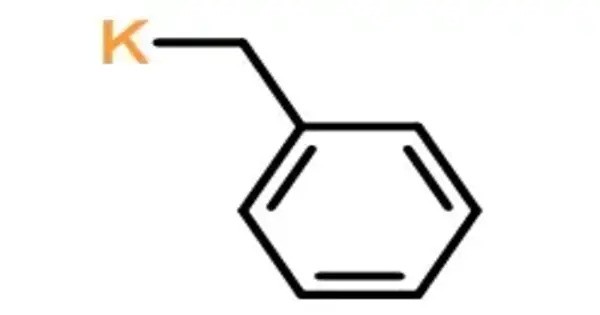
Benzylpotassium – an organopotassium compound
Benzylpotassium is an organopotassium compound with the formula C6H5CH2K, an orange powder. It is a type of organometallic compound, where a potassium atom is attached to a benzyl group. Like organo-alkali metal reagents in general, benzyl potassium is highly reactive, so much so that it reacts with most solvents. It is highly air sensitive.
Properties
Benzylpotassium is soluble in some organic solvents like ether, and it reacts with water, forming potassium hydroxide (KOH) and releasing hydrogen gas (H₂). It is highly reactive, especially with water, and must be handled carefully under anhydrous (water-free) conditions.
- Chemical formula: C7H7K
- Molar mass: 130.231 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Orange solid
Synthesis
One early synthesis proceeds by two-step transmetallation reaction by p-tolylpotassium:
(CH3C6H4)2Hg + 2 K → 2 CH3C6H4K + Hg
CH3C6H4K → KCH2C6H5
A modern synthesis involves the reaction of butyllithium, potassium tert-butoxide, and toluene. Although potassium hydride can also be used as a strong base for preparing potassium salts, benzyl potassium has the advantage of being molecular and hence more fast-acting.
Preparation
Benzylpotassium can be synthesized by reacting benzyl chloride (C₆H₅CH₂Cl) with potassium metal (K) in an anhydrous solvent such as ether:
𝐶6𝐻5𝐶𝐻2𝐶𝑙+𝐾→𝐶6𝐻5𝐶𝐻2𝐾+ 1/2𝐻2
This reaction typically occurs under anhydrous conditions to prevent hydrolysis by water.
Uses
- Nucleophilic Substitution: Benzylpotassium can act as a strong nucleophile in organic reactions, particularly in nucleophilic substitution reactions. It is commonly used to introduce the benzyl group into other molecules.
- Organic Synthesis: It is utilized in the preparation of a variety of organic compounds, including benzyl derivatives of other organic substrates.
- Strong Base: It can be used as a base in organic reactions where a strong base is required, such as in deprotonation reactions.
Safety Considerations
Benzylpotassium is highly reactive, especially with water, and must be handled with care. Its reaction with water produces potassium hydroxide (a strong base) and hydrogen gas, which can be dangerous in confined spaces.
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats should be worn when handling this substance.