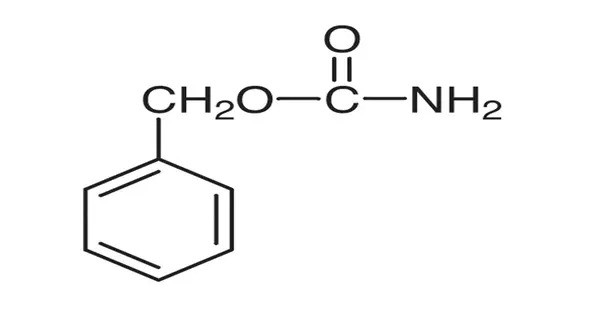
Benzyl carbamate is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2OC(O)NH2. The compound can be viewed as the ester of carbamic acid (O=C(OH)(NH2)) and benzyl alcohol, although it is produced from benzyl chloroformate with ammonia. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents and moderately soluble in water.
Benzyl carbamate is used as a protected form of ammonia in the synthesis of primary amines. After N-alkylation, C6H5CH2OC(O) group is removable with Lewis acids. It is derived from carbamic acid and benzyl alcohol, with the structure consisting of a benzyl group (C6H5CH2) attached to the carbamate group (–NH–COO).
Properties
- Chemical formula: C8H9NO2
- Molar mass: 151.165 g·mol−1
- Appearance: white solid
- Melting point: 88 °C (190 °F; 361 K)
- Solubility in water: moderate
Synthesis
Benzyl carbamate can be synthesized by the reaction of benzyl alcohol with carbamic acid or its derivatives (such as phosgene or carbamoyl chlorides), leading to the formation of the carbamate bond.
Applications
Benzyl carbamate has some industrial and chemical applications, though it’s more commonly used in research and synthesis. Some areas of interest include:
- Intermediate in organic synthesis: Used for making other compounds or as a precursor to more complex molecules.
- Insecticides: Certain carbamates, including derivatives of benzyl carbamate, are used in the formulation of insecticides.
- Pharmaceutical research: Carbamate groups are commonly used in medicinal chemistry, where they are often involved in designing enzyme inhibitors or other biologically active molecules.
Safety and Handling
Benzyl carbamate itself is not highly toxic, but, like many carbamates, it can be harmful if ingested or inhaled in large amounts. It should be handled in a well-ventilated area with appropriate protective equipment to avoid prolonged exposure.