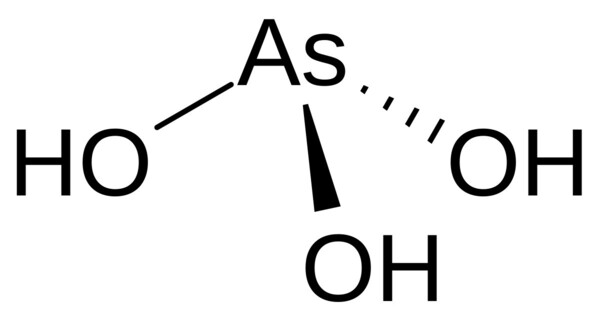
Arsenous acid (or arsenious acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula H3AsO3. It is a weak acid and is usually found in its salt forms, such as arsenites. In its pure form, it’s a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic substance. It is known to occur in aqueous solutions, but it has not been isolated as a pure material, although this fact does not detract from the significance of As(OH)3.
Arsenous acid is used in various chemical processes and can also be found in some pesticides and wood preservatives. It’s important to handle it with care due to its toxic nature.
Properties
As(OH)3 is a pyramidal molecule consisting of three hydroxyl groups bonded to arsenic. The 1H NMR spectrum of arsenous acid solutions consists of a single signal consistent with the molecule’s high symmetry. In contrast, the nominally related phosphorous acid H3PO3 adopts the structure HPO(OH)2. The structural analogue of arsenous acid (P(OH)3) is a very minor equilibrium component of such solutions.
- Chemical formula: H3AsO3
- Molar mass: 125.94 g/mol
- Appearance: Only exists in aqueous solutions
- Conjugate base: Arsenite
- Acidity: It is a weak acid, and its acidity is due to the presence of arsenic in the +3 oxidation state.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water.
- Reactivity: It can act as a reducing agent and can be oxidized to arsenic acid (H₃AsO₄) in the presence of oxidizing agents.
Synthesis
The preparation of As(OH)3 involves a slow hydrolysis of arsenic trioxide in water. Addition of base converts arsenous acid to the arsenite ions [AsO(OH)2]−, [AsO2(OH)]2−, and [AsO3]3−.
Occurrences
Arsenous acid does not occur naturally in its pure form but can be found in various arsenic-containing minerals and ores. It is primarily obtained by dissolving arsenic trioxide in water. Arsenic trioxide is often a by-product of smelting and refining processes.
Usage
Historically, it has been used in pesticides and wood preservatives, though its use is now restricted due to its toxic nature. It’s also used in some pharmaceutical applications and in analytical chemistry.
Safety
Arsenous acid is highly toxic, and exposure can lead to arsenic poisoning. Proper handling and disposal are crucial to avoid health risks.