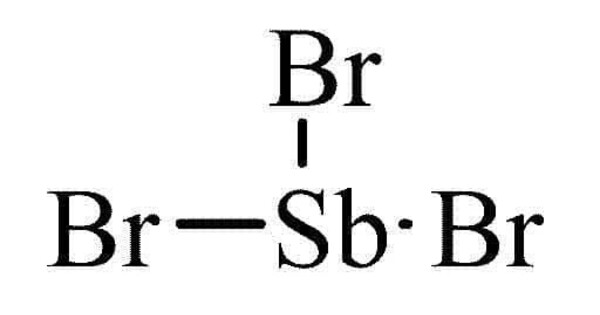Antimony tribromide (SbBr3) is a chemical compound containing antimony in its +3 oxidation state. It typically appears as a yellow or reddish-brown solid. It is soluble in organic solvents but not in water. It is often used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. It can serve as a halogenating agent in organic chemistry.
Antimony compounds can be toxic, so proper safety precautions should be taken when handling antimony tribromide, including using gloves and eye protection.
Production
Antimony tribromide may be made by the reaction of antimony with elemental bromine, or by the reaction of antimony trioxide with hydrobromic acid.
Alternatively, it can be prepared by the action of bromine on a mixture of antimony sulfide and antimony trioxide at 250 °C.
Properties
- Chemical formula: SbBr3
- Molar mass: 361.472 g/mol
- Appearance: colorless to yellow crystals hygroscopic
- Density: 4.35 g/cm3
- Melting point: 96.6 °C (205.9 °F; 369.8 K)
- Boiling point: 288 °C (550 °F; 561 K)
- Solubility in water: soluble,partial hydrolysis
- Solubility: soluble in dilute HCl, HBr, CS2, acetone, benzene, chloroform, ammonia, alcohol
Chemical properties
Antimony tribromide has two crystalline forms, both having orthorhombic symmetries. When a warm carbon disulfide solution of SbBr3 is rapidly cooled, it crystallizes into the needle-like α-SbBr3, which then slowly converts to the more stable β form.
Antimony tribromide hydrolyzes in water to form hydrobromic acid and antimony trioxide:
2 SbBr3 + 3 H2O → Sb2O3 + 6 HBr
Occurrences
- Natural Occurrence: Antimony is generally found in nature in sulfide ores like stibnite (Sb₂S₃). Antimony tribromide is not found in significant amounts in nature but can be synthesized from antimony and bromine.
- Synthesis: It can be prepared by reacting antimony with bromine or by the reaction of antimony trioxide with hydrobromic acid.
Uses
It can be added to polymers such as polyethylene as a fire retardant. It is also used in the production of other antimony compounds, in chemical analysis, as a mordant, and in dyeing.