Annuity
An annuity is a payment made to the insured annually. It is a financial product that pays out a fixed stream of payments to an individual, and these financial products are primarily used as an income stream for retirees. It is a contract between you and an insurance company in which you make a lump-sum payment or series of payments and, in return, receives regular disbursements, beginning either immediately or at some point in the future. When an insured under a life policy elects to receive the payment from the life insurance company at a specified rate throughout his life or for some fixed number of years, the sum of money (i.e. stated yearly sum) thus received annually instead of a lump amount is known as an annuity. The period of time when an annuity is being funded and before payouts begin is referred to as the accumulation phase. Examples of annuities are regular deposits to a savings account, monthly home mortgage payments, monthly insurance payments, and pension payments.
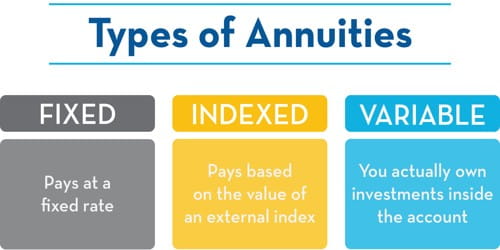
An annuity that provides for payments for the remainder of a person’s lifetime is a life annuity. Defined benefit pensions and Social Security are two examples of lifetime guaranteed annuities that pay retirees a steady cash flow until they pass. They are created and sold by financial institutions, which accept and invest funds from individuals. They can be structured into different kinds of instruments – fixed, variable, immediate, deferred income, that gives investors flexibility. Each type has its own level of risk and payout potential. Fixed annuities pay out a guaranteed amount.
The goal of an annuity is to provide a steady stream of income, typically during retirement. You can purchase an annuity to help grow or protect your retirement savings or to provide you with guaranteed income.