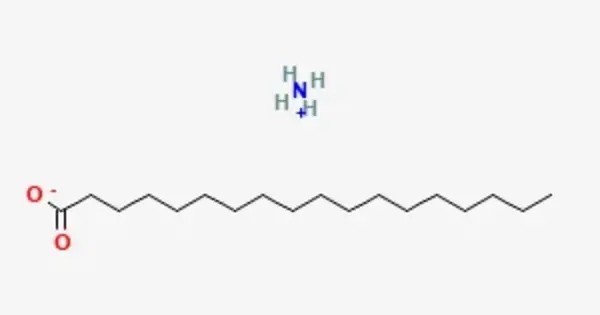
Ammonium stearate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)16COONH4. It is an organic ammonium salt of stearic acid, appearing as a white to yellow paste or powder with a faint ammonia odor. This is an organic ammonium salt of stearic acid. It is slightly soluble in water, soluble in methanol, ethanol, and hot toluene, but practically insoluble in acetone, benzene, xylene, and naphtha.
In cosmetics, it stabilizes emulsions, enhances viscosity, and reduces transparency in products like vanishing creams, makeup, and shampoos. It is also employed in waterproofing cements, textiles, adhesives, and polymers, acting as a lubricant and foam stabilizer.
Synthesis
The compound can be prepared by reacting stearic acid and excess 28-30% NH3 solution. Also by reacting stearic acid and ammonium carbonate or ammonium hydroxide.
Ammonium stearate has weak oxidizing or reducing properties and is not water-reactive, though it may release toxic ammonia and nitrogen oxides when heated or burned. Safety assessments, including by the Cosmetic Ingredient Review, confirm its low toxicity, with minimal skin or eye irritation at typical concentrations. It is generally recognized as safe for specific food-related uses by the FDA.
Property
The compound forms yellow-white powder. Soluble in methanol and ethanol; slightly soluble in water, benzene, xylene, naphtha; practically insoluble in acetone. When heated, the powder of ammonium stearate decomposes, releasing toxic fumes of NH3.
- Chemical formula: C18H39NO2
- Molar mass: 301.515 g·mol−1
- Appearance: Yellow-white powder
- Melting point: 70-75 °F
- Solubility in water: soluble
Reactivity and Stability
Not water-reactive, and its solutions are generally stable. Ammonium stearate emulsions have a shelf life of about six months, with good fluidity, stability, and resistance to thickening over time.patents.
Safety and Toxicity
- Considered a nuisance dust with no significant health hazards under normal use.
- Ingestion may cause irritation of the mouth and stomach; eye contact may cause irritation.
- Skin irritation studies show minimal to slight irritation at high concentrations. In a study, 1.5% ammonium stearate caused minimal to mild skin erythema in 7 out of 20 volunteers.
- The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel concluded that ammonium stearate is safe for use in cosmetics and personal care products.
- First aid: Flush eyes or skin with copious amounts of water; no treatment is typically required for inhalation or ingestion.cameochemicals.
Occurrences and Uses
Natural Occurrence: Ammonium stearate is not typically found in nature as it is a synthetic compound derived from stearic acid, a fatty acid present in animal and plant fats (e.g., cocoa butter, shea butter). Stearic acid, its parent compound, is a major component of various fats and oils, with chain lengths of C16–C20.drugs.
Industrial and Commercial Uses: Cosmetics and Personal Care: Widely used as a surfactant, emulsifier, dispersant, and cleansing agent in products like shampoos, soaps, vanishing creams, deodorants, and toothpaste. It reduces surface tension, stabilizes emulsions, and promotes foam formation.atamanchemicals.
Textile Industry: Used in acrylic latex compounds and as a processing aid in textiles, apparel, and leather manufacturing.
Polymers and Adhesives: Serves as a raw material in the production of polymers, adhesives, sealants, lubricants, and greases. Acts as an acid scavenger, release agent, and lubricant in plastics and rubber processing.atamanchemicals.
Printing: Aqueous dispersions are used in gravure printing to improve coating rheology and reduce foam tendency, particularly in food industry applications due to its vegetable-based origin.
Construction: Used in waterproofing cements, concrete, and stucco.
Food Industry: Functions as an anti-caking and anti-foaming agent in sugar production.
Other Applications: Found in solid deodorants, rubbers, latex paints, inks, and as a soap stabilizer and froth aid in latex systems.
Production
- Synthesized by reacting stearic acid with excess 28–30% ammonia solution, ammonium carbonate, or ammonium hydroxide.
- Emulsion production involves combining stearic acid, lauryl sodium sulfate, and water, followed by ammonia addition and emulsification at 10–25°C, yielding a stable, low-viscosity product.
Regulatory Status
Approved by the FDA as an indirect food additive and considered Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) when used in suitable grades. In the EU, ammonium stearate is permitted in cosmetics under the general provisions of the Cosmetics Directive, with stearic acid sourced from animal origins complying with EU animal by-products regulations.