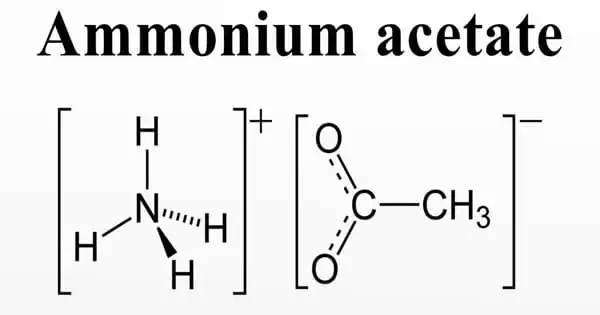
Ammonium acetate, often known as the spirit of Mindererus in aqueous solution, is a chemical compound having the formula NH4CH3CO2. It is an ammonium salt formed by reacting ammonia with acetic acid. It is a white, hygroscopic substance that can be produced by the interaction of ammonia and acetic acid. It is a commercially available product. It is also known as the spirit of Mindererus in an aqueous form, Azanium Acetate, or ammonium ethanoate. It is frequently utilized in chemical analysis, food preservation, and pharmaceuticals.
Properties
It is a white crystalline solid and has a slight acetous odour. It has a role as a food acidity regulator. It is an ammonium salt and an acetate salt. It is a white, hygroscopic solid and can be derived from the reaction of ammonia and acetic acid.
- Molecular weight: 77.083 g/mol
- Density: 1.17 g/cm3
- Melting point: 113 °C
- Viscosity: 21

Production
Ammonium acetate is produced by the neutralization of acetic acid with ammonium carbonate or by saturating glacial acetic acid with ammonia. Obtaining crystalline ammonium acetate is difficult on account of its hygroscopic nature.
Azanium Acetate is obtained in two methods viz
- By neutralizing acetic acid with ammonium carbonate [(NH4)2CO3] or
- By saturating glacial acetic acid (CH3COOH) with ammonia (NH3).
Ammonium acetate is an ammonium salt obtained by the reaction of ammonia with acetic acid. A deliquescent white crystalline solid, it has a relatively low melting point (114℃) for a salt.
Uses
It is the main precursor to acetamide:
NH4CH3CO2 → CH3C(O)NH2 + H2O
It is also used as a diuretic.
Buffer
Ammonium acetate, as the salt of a weak acid and a weak base, is frequently combined with acetic acid to form a buffer solution. At low pressures, ammonium acetate is highly flammable. As a result, it has been utilized to substitute cell buffers containing non-volatile salts in the preparation of samples for mass spectrometry. Because of this, it is also common as a buffer for mobile phases in HPLC with ELSD detection. Ammonium formate is another volatile salt that has been utilized for this purpose.
Other
- a biodegradable de-icing agent.
- a catalyst in the Knoevenagel condensation and as a source of ammonia in the Borch reaction in organic synthesis.
- a protein precipitating reagent in dialysis to remove contaminants via diffusion.
- a reagent in agricultural chemistry for the determination of soil CEC (cation exchange capacity) and determination of available potassium in soil wherein the ammonium ion acts as a replacement cation for potassium.
- part of calley’s method for lead artifact conservation
Food additive
Ammonium acetate is also used as a food additive as an acidity regulator; INS number 264. It is approved for usage in Australia and New Zealand.
Health hazards
Inhaling dust causes irritation in the mouth and nose. Swallowing this compound irritates stomach and mouth. When it comes in contact with eyes and skin can cause rashes.