Introduction
Amico Laboratories Limited, also known as Amico Laboratories is a major pharmaceutical company based in Bangladesh. It is part of the Mona Group of Companies.
Corporate history
Amico laboratories Limited has emerged one of the fastest growing Pharmaceutical companies in Bangladesh for manufacturing & marketing of human health care products.
Factories
The Factory is situated at the heart of the Industrial area in the capital city – Dhaka. The factory consists of Production department, R & D department, Accounts department and various other sub-departments. The factory is operating with over 350 employees. It is equipped with sophisticated and modern production and quality control equipments.
Amico Laboratories Limited. Type Ltd Industry Pharmaceutical, Founded 1976 Headquarters Tejgaon, Dhaka, Bangladesh Key people Al-Haj Mockbul Hossain Website http://www.amicolab.com/
Name of the Company: Amico Laboratories Limited
Establishment: Established in 1976
Change of Ownership and re-operation: 1994 July
Business type: Manufacturer, Marketer and Distributor of medicine & drugs
Ownership: Private Limited Company
Chairman: Al-Haj Mockbul Hossain
Group: A sister concern of Mona Group of Industries
Factory: 117, Tejgaon, Dhaka
Marketing Office: 22/10, Babor Road, Block:B, Shaymoli, Dhaka-1207
ISO Certicate No. : 94210, Issue No. – 1
Amico laboratories Limited has emerged one of the fastest growing Pharmaceutical companies in Bangladesh and dedicated towards manufacturing & marketing of human health care products. In this fast paced competitive business environment, Amico focuses on quality & efficacy of products. Amico Laboratories Limited strictly follows GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices). It has always been our endeavour to create an environment where in innovation of the highest order can blossom. To Keep our commitment on quality, we have worked hard to achieve ISO 9001:2000 for Quality Management System. This international recognition has enhanced out reputation with pride & dignity. The company, with its clear vision, marketing policies and long-term vision on customer satisfaction, has already created a favourable image in all over Bangladesh. With moderate product range, professional attitude and focused marketing policies, the company has availed a strong track record so far. Amico Laboratories Limited, indeed, is a newborn baby in the pharmaceutical industry and still has many more to offer to serve the nation with its health care products. Its increasing growth rate indicates a promising future.
| Product Type : | Tablets (coated-film coated / uncoated) Capsules Dry Powder for suspension Syrup Lotion Emulsion Cream Ointment |
Laboratory Equipment
According to the ICH guidelines the microbiology test of raw materials and finished product is an important parameter of the quality drug. According the SPLU2 has a special separate microbiology laboratory in order to carry out the microbiology tests order several sensitive products.
The microbiology test program includes the following:
- Test of raw material and packaging material.
- Test of finished product
- Environmental monitoring
- ETP water test.
Finished product Analysis for Tablet/Capsule:
- Appearance
- Identification
- Average weight of tablet
- Hardness
- Thickness
- Disintegration time
- Friability test
- Dissolution
- Content uniformity
- Chemicals assay
- Life of expiry
- Related substance
Packed analysis
- Pack analysis
- Appearance (pack)
- Appearance (product)
- Leakage test
- Unit pack description
- Life of expire

List of Laboratory equipment:
| SL NO | Name of Equipment | Model | Manufacturer/Supplier |
| 01 | Disintegration tester | ED-2SAPO | |
| 02 | Water Bath | H.H.S | |
| 03 | PH Meter | 3510 cyber Scan 500 | |
| 04 | Melting poit | 9100 | |
| 05 | UV-Spectrophotometer | UV-1700 Pharmaspec | Shimadzu,Japan |
| 06 | Karl Fischer | 870KF Titrino Plus | |
| 07 | Moisture Analyzer | MA 30 | Germany |
| 08 | Magnetic steer | HC501 | |
| 09 | Thermo lab humidity chamber | ||
| 10 | IR Spectrophotometer | FT/IR-460 Plus | JASCO-Japan |
| 11 | HPLC | SPD-10AVP | |
| 12 | Sonicator | ||
| 13 | Friability tester |
Disintegration tester:
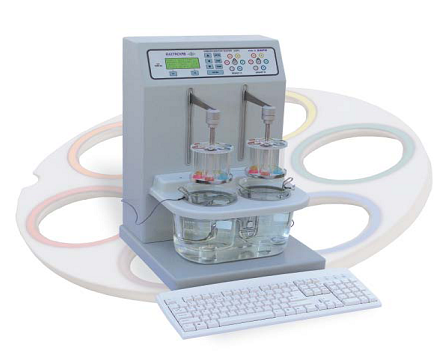
Disintegration time registration of each tablet
- USP / EP / IP compliant
- Unique camless drive
- Dual station with individual drive and timer
- Magnetic coupling to the moving arm allows quick, easy and safe basket handling
- Moulded water bath with fliptopcover
- Built-in stirrer for precise temperature control in the water bath
- Specially designed temperature probes for continuous monitoring of temperature in both the beakers.
- Illumination of tablets for better visibility of the disintegration process.
- PC keyboard interface provided for ease of entering product data.
Function of Disintegration Tester:
This equipment is used for disintegration testing of solid item, it has functions of double circle control systems, preset time of stop for each circle control system and beep hint, the latest temperature control technology is used for water temperature control.
UV spectrometer:
Function
It can also be used for other functions having to do with change in UV spectrum. We use it in our lab to track the folding and unfolding of proteins, since the two conformations have different absorbance maximums. We can tell the extent to which it folds/unfolds, and the time it takes to do so. Microbiologists use them to measure optical density (think of it as how cloudy a solution is) to track the growth of bacteria growing in liquid medium. The possibilities for good times are endless =)
PH meter:

Function of PH meter:
Glass electrodes are commonly used for pH measurements. There are also specialized ion sensitive glass electrodes used for determination of concentration of lithium, sodium, ammonium, and other ions. Glass electrodes have been utilized in a wide range of applications — from pure research, control of industrial processes, to analyze foods, cosmetics and comparison of indicators of the environment and environmental regulations: a microelectrode measurements of membrane electrical potential of a biological cell, analysis of soil acidity, etc.
Karl Fischer:
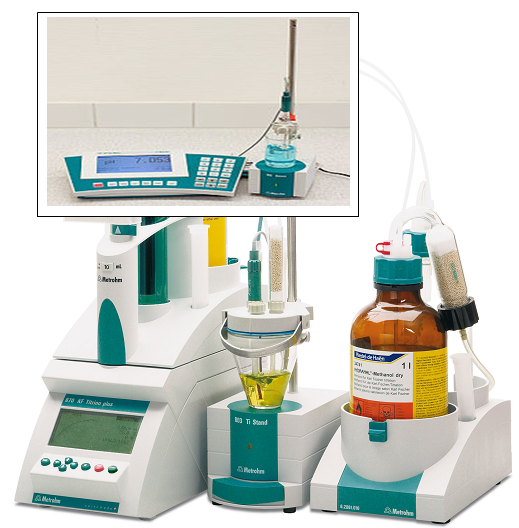

Routine determinations of water with the new 870 KF Titrino plus
The favorably priced 870 KF Titrino plus is Metrohm’s new Karl Fischer
titrator for volumetric water determinations. It can be used to determine
water contents from a few ppm up to 100% reliably and accurately in
solid, liquid and gaseous samples. With its new operating interface designed
for routine users, the 870 KF Titrino plus is so easy to operate that
it only requires a short familiarization period. Also its robustness makes it
the ideal titrator for routine determinations.
Moisture Analyzer:

Use of moisture meter:
Moisture meters are used to measure the percentage of water in a given substance. This information can be used to determine if the material is ready for use, unexpectedly wet or dry, or otherwise in need of further inspection.
Wood and paper products are very sensitive to their moisture content. Physical properties are strongly affected by moisture content. Dimensioning also changes with moisture content.
IR Spectrophotometer:

Uses and applications
Infrared spectroscopy is a simple and reliable technique widely used in both organic and inorganic chemistry, in research and industry. It is used in quality control, dynamic measurement, and monitoring applications such as the long-term unattended measurement of CO2 concentrations in greenhouses and growth chambers by infrared gas analyzers.
It is also used in forensic analysis in both criminal and civil cases, for example in identifying polymer degradation. It can be used in detecting how much alcohol is in the blood of a suspected drunk driver measured as 1/10,000 g/mL = 100 μg/mL.[citation needed]
A useful way of analysing solid samples without the need for cutting samples uses ATR or attenuated total reflectance spectroscopy. Using this approach, samples are pressed against the face of a single crystal. The infrared radiation passes through the crystal and only interacts with the sample at the interface between the two materials.
With increasing technology in computer filtering and manipulation of the results, samples in solution can now be measured accurately (water produces a broad absorbance across the range of interest, and thus renders the spectra unreadable without this computer treatment).
Some instruments will also automatically tell you what substance is being measured from a store of thousands of reference spectra held in storage.
Infrared spectroscopy is also useful in measuring the degree of polymerization in polymer manufacture. Changes in the character or quantity of a particular bond are assessed by measuring at a specific frequency over time. Modern research instruments can take infrared measurements across the range of interest as frequently as 32 times a second. This can be done whilst simultaneous measurements are made using other techniques. This makes the observations of chemical reactions and processes quicker and more accurate.
Infrared spectroscopy has also been successfully utilized in the field of semiconductor microelectronics:[3] for example, infrared spectroscopy can be applied to semiconductors like silicon, gallium arsenide, gallium nitride, zinc selenide, amorphous silicon, silicon nitride, etc.
The instruments are now small, and can be transported, even for use in field trials.
High-performance liquid chromatography:

High-performance liquid chromatography (sometimes referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography), HPLC, is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds and is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify and purify the individual components of the mixture.
Dissolution testing

In the pharmaceutical industry, drug dissolution testing is routinely used to provide critical in vitro drug release information for both quality control purposes, i.e., to assess batch-to-batch consistency of solid oral dosage forms such as tablets, and drug development, i.e., to predict in vivo drug release profiles.
In vitro drug dissolution data generated from dissolution testing experiments can be related to in vivo pharmacokinetic data by means of in vitro-in vivo correlations (IVIVC). A well established predictive IVIVC model can be very helpful for drug formulation design and post-approval manufacturing changes.
The main objective of developing and evaluating an IVIVC is to establish the dissolution test as a surrogate for human bioequivalence studies, as stated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Analytical data from drug dissolution testing are sufficient in many cases to establish safety and efficacy of a drug product without in vivo tests, following minor formulation and manufacturing changes (Qureshi and Shabnam, 2001). Thus, the dissolution testing which is conducted in dissolution apparatus must be able to provide accurate and reproducible results.
Several dissolution apparatuses exist. In United States Pharmacopeia (USP) General Chapter <711> Dissolution, there are four dissolution apparatuses standardized and specified. They are:
• USP Dissolution Apparatus 1 – Basket (37°C)
• USP Dissolution Apparatus 2 – Paddle (37°C)
• USP Dissolution Apparatus 3 – Reciprocating Cylinder (37°C)
• USP Dissolution Apparatus 4 – Flow-Through Cell (37°C)
USP Dissolution Apparatus 2 is the most widely used apparatus among these four.
The performances of dissolution apparatuses are highly dependent on hydrodynamics due to the nature of dissolution testing. The designs of the dissolution apparatuses and the ways of operating dissolution apparatuses have huge impacts on the hydrodynamics, thus the performances. Hydrodynamic studies in dissolution apparatuses were carried out by researchers over the past few years with both experimental methods and numerical modeling such as Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). The main target was USP Dissolution Apparatus 2.[1][4][5][6][7][8][9][10] The reason is that many researchers suspect that USP Dissolution Apparatus 2 provides inconsistent and sometimes fault data.[11][12][13][14][15][16][17] The hydrodynamic studies of USP Dissolution Apparatus 2 mentioned above clearly showed that it does have intrinsic hydrodynamic issues which could result in problems. In 2005, Professor Piero Armenante from New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) and Professor Fernando Muzzio from Rutgers University submitted a technical report to the FDA.[18] In this technical report, the intrinsic hydrodynamic issues with USP Dissolution Apparatus 2 based on the research findings of Armenante’s group and Muzzio’s group were discussed.
Amico laboratory limited is an attractive, protective, well organized and defined plant. Its location design, construction, adaptation and maintains is good for the operations to minimize risks of error and cross-contamination permit effective clearing and maintenance in order to avoid cross contamination, build-up of dirt and dust and in general any adverse on quality of the products.
We are enough to carry out the training without any difficulties from any side. We wish the management if Amico laboratories limited. Family to be so helpful to us our during four weeks training period. Here we indicate Amico laboratories limited. As a family because we found the whole working staff and officers just like a family member which encourage their working ability. In Amico laboratories we learn many factors which can not be learn by reading book.
Although there are some limitations Amico laboratories is only company that never compromise with quality. So we feel ourselves lucky to complete in-plant training in this company. We hope that it will improve day by day with their mission and vision.
At last we wish that this company would always prove worthy to attain its ultimate goals in promoting the country wide pharmaceutical area.
Suggestions:
- Apron and mask facilities can be increased.
- High efficient air lock door can be used in the production area.
- High efficient HVAC system can be installed to maintain the specific temperature & relative humidity.
- S.S vessel can be used in the liquid section ion case of plastic vessel.
- The instrument and man power if PD department can be increased.