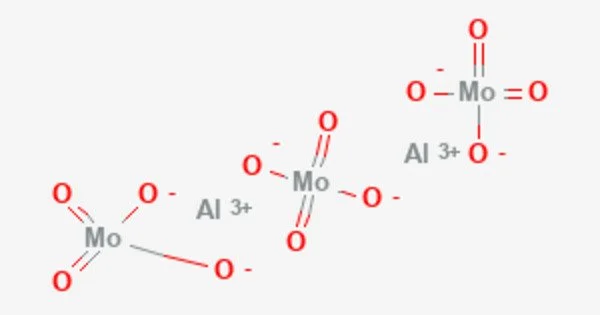
Aluminium molybdate is the chemical compound Al2(MoO4)3. It is a white solid that has various applications in different fields, particularly in materials science and industrial chemistry. It forms in certain hydrodesulfurization catalysts when alumina is doped with excess molybdenum.
When molybdates are used to inhibit corrosion in aluminum piping, the protective film formed is hydrated aluminum molybdate. Although small quantities of aluminum molybdate form during aluminothermic reduction of molybdia, mechanical activation inhibits their formation. Large-scale samples can be prepared via sol-gel synthesis, and have been proposed for molybdenum-99 storage in nuclear medicine.
Aluminum molybdate has a very low thermal expansion coefficient near room temperature.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Al2(MoO4)3
- Molar mass: 533.77 g mol−1
- Appearance: grey, metallic solid/powder, odorless
- Melting point: 705 °C (1,301 °F; 978 K)
- Solubility in water: slightly soluble in water
- Density: Varies depending on the crystalline form, but typically it is relatively dense compared to simple oxides.
Occurrences
Aluminium molybdate is not commonly found in nature as a distinct mineral. However, it can be synthesized through chemical reactions and may occur as a component of other complex molybdenum or aluminium-containing minerals in specialized geological environments. Some ways it can be synthesized include:
Synthetic Production: Aluminium molybdate is typically synthesized in laboratories or industrial settings through the reaction between aluminium salts (like aluminium nitrate) and molybdate salts (like ammonium molybdate or sodium molybdate) under controlled conditions.
Industrial Applications: It is often used in the production of molybdenum-based catalysts and as an additive in ceramic materials and refractory coatings due to its high melting point and stability under extreme conditions.
Molybdenum Deposits: While aluminium molybdate itself is not found naturally in large amounts, molybdenum ore deposits (such as molybdenite, MoS₂) may contain trace amounts of aluminium compounds. The synthesis of aluminium molybdate from such ores is possible in industrial processes that require high-purity molybdenum and aluminium.
Applications
- Catalysts: Aluminium molybdate is sometimes used in catalytic processes, particularly in the production of certain chemicals.
- Materials Science: It is sometimes incorporated into composite materials or ceramics for its unique properties, such as high thermal stability.
- Optical Coatings: Due to its refractive index, it might be used in certain optical applications.
- Electronics: As a part of more complex materials, aluminium molybdate may be explored in semiconductor or thin-film applications.