Aldermanite is a rare hydrated phosphate mineral with formula Mg5Al12(PO4)8(OH)22·32H2O. This is an orthorhombic colorless mineral containing aluminum, hydrogen, magnesium, oxygen, and phosphorus.
It’s named after Arthur Richard Alderman (1901–1980), Professor of Geology and Mineralogy, University of Adelaide. Its type locality is Moculta Phosphate Quarry (Klemm’s Quarry), Angaston, Barossa Valley, North Mount Lofty Ranges, Mount Lofty Ranges, South Australia, Australia.
General information
- Formula: Mg5Al12(PO4)8(OH)2232H2O
- Color: Colorless in transmitted light
- Lustre: Sub-Vitreous, Pearly
- Hardness: 2
- Specific Gravity: 2.1 (Calculated)
- Crystal System: Orthorhombic
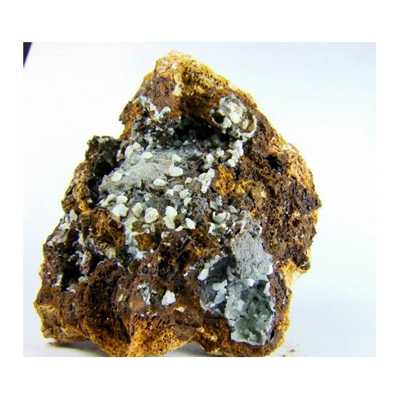

Physical Properties of Aldermanite
- Color: Colorless
- Diaphaneity: Transparent
- Habit: Fibrous – Crystals made up of fibers.
- Habit: Flakes – Flat, thin crystals or aggregates.
- Hardness: 2 – Gypsum
- Luster: Pearly
- Streak: White
Chemical Properties of Aldermanite gives us information about the mineral’s chemical composition. A mineral is basically composed of various elements in varying proportions. These elements define how the mineral will behave when exposed to different conditions. It is a generous covering of clear minyulite crystals with a couple of small tuffs of clear to white wavellite, and a couple of spots of white aldermanite visible underneath the minyulite. These chemical properties also depend on the way the mineral atoms are bound in the mineral’s crystal structure. The molecular weight of Aldermanite is 2,155.72 and Hawthorneite are 1,040.63. The Atomic Structure of Aldermanite properties of minerals gives us further information about a minerals atomic structure.
Occurrence: As a secondary mineral in cavities in a brecciated metamorphosed sedimentary phosphate deposit, formed by the alteration of fluellite (Moculta quarry, Australia).
Distribution: At the Moculta phosphate quarry, northeast of Angaston, South Australia.
Information Source: