Admontite is a hydrated magnesium borate mineral with formula MgB6O10·7H2O. It was named after Admont in Austria, the place where the mineral was initially discovered, near the original locality.
Occurrence – In a gypsum deposit. Associations: gypsum, anhydrite, hexahydrite, löweite, eugsterite, pyrite, quartz. It is named after Admont, Austria. Its Mohs scale rating is 2 to 3.
Admontite occurs in gypsum deposits. It is often associated with minerals such as gypsum, hexahydrite, loweite, anhydrite, pyrite, eugsterite, and quartz.
General Information:
- Category: Nesoborates
- Formula (repeating unit): MgB6O107H2O or MgB6O7(OH)6·4H2O
- Crystal system: Monoclinic
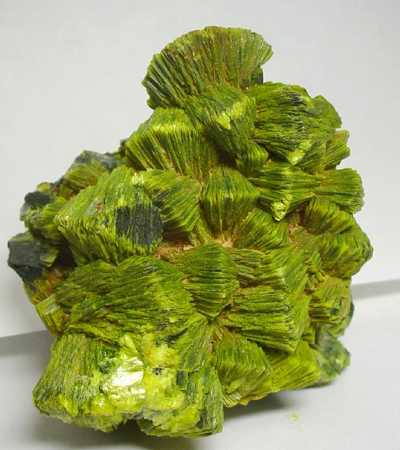

Identification
- Color: colorless
- Cleavage: Absent
- Fracture: Conchoidal – Fractures developed in brittle materials characterized by smoothly curving surfaces, (e.g. quartz)
- Mohs scale: hardness 2 – 3 – Gypsum-Calcite
- Streak: White
- Density: 1.82 – 1.87, Average = 1.84
- Optical properties: Biaxial (-)
It is colorless and transparent with no cleavage. This mineral has a white streak. The fracture on this mineral is conchoidal. It has non-fluorescent luminescence. The density of admontite is 1.82 to 1.87 g/cm3, with a hardness of 2 to 3 – between gypsum and calcite.
Physical Properties of Admontite
- Density: 1.82 – 1.87, Average = 1.84
- Diaphaneity: Transparent
- Fracture: Conchoidal – Fractures developed in brittle materials characterized by smoothly curving surfaces, (e.g. quartz).
- Habit: Euhedral Crystals – Occurs as well-formed crystals showing good external form.
- Hardness: 2-3 – Gypsum-Calcite
- Luminescence: Non-fluorescent.
Information Source: