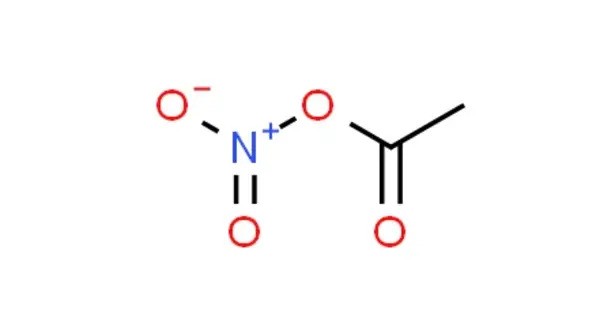
Acetyl nitrate is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)ONO2. It is a liquid at room temperature. It is a colorless to pale yellow liquid. It is classified as the mixed anhydride of nitric and acetic acids. It is a colorless explosive liquid that fumes in moist air. It has a pungent odor. It is miscible with organic solvents but not very soluble in water.
Properties
Acetyl nitrate is highly reactive and can be an explosive substance under certain conditions. It reacts vigorously with reducing agents and certain organic materials. It is generally unstable and can decompose when exposed to heat or shock.
- Chemical formula: C2H3NO4
- Molar mass: 105.049 g·mol−1
- Appearance: colorless liquid
- Density: 1.24 g/cm3 (15 °C)
- Boiling point: 22 °C at 70 Torr
Synthesis and reactions
It was first prepared in 1907 by Amé Pictet and E. Khotynsky from acetic anhydride and dinitrogen pentoxide, fuming nitric acid can also be used:
(CH3CO)2O + HNO3 → CH3C(O)ONO2 + CH3COOH
It hydrolyzes in moist air to acetic acid and nitric acid. Alternatively, nitric acid adds to ketene.
Applications
- Nitrate Esterification: Acetyl nitrate is used in the synthesis of other nitrate esters and as an intermediate in chemical reactions.
- Explosives: Due to its reactivity, it can be used in the preparation of explosive materials, though its use in this field is less common compared to other nitrate esters.
- Specialty Chemicals: It may be used in the production of certain specialty chemicals and as a reagent in various chemical processes.
Safety and Handling
Acetyl nitrate is hazardous and requires careful handling. It should be stored away from heat, sparks, and open flames. Proper protective equipment, including gloves and goggles, should be used to avoid exposure.